Abstract
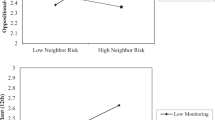
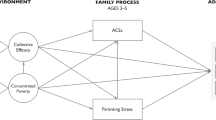
Associations among neighborhood disadvantage, maternal acculturation, parenting and conduct problems were investigated in a sample of 444 Chinese American adolescents. Adolescents (54% female, 46% male) ranged from 12 to 15 years of age (mean age = 13.0 years). Multilevel modeling was employed to test the hypothesis that the association between maternal acculturation and adolescents’ conduct problems could be explained by differences in mothers’ reliance on monitoring and harsh discipline. In addition, guided by segmented assimilation theory, measures of neighborhood disadvantage were expected not only to be related to differences in parenting, but also to moderate the effects of maternal acculturation on parenting. Results indicated that increased maternal acculturation was related to higher levels of maternal monitoring and lower levels of harsh discipline, which, in turn, were related to lower levels of adolescents’ conduct problems. Hierarchical linear modeling results revealed that neighborhood disadvantage was related to lower levels of maternal monitoring. However, neighborhood disadvantage did not moderate the link between maternal acculturation and parenting practices.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist 14–18 and 1991 profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont Department of Psychiatry.
Allison, P. D. (2001). Missing data. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, Inc.
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 1173–1182.
Baumrind, D. (1997). Necessary distinctions. Psychological Inquiry, 8(3), 176–182.
Bornstein, M. H., & Cote, L. R. (2004). Mothers’ parenting cognitions in cultures of origin, acculturating cultures, and cultures of destination. Child Development, 75(1), 221–235.
Bornstein, M. H., Haynes, O. M., Azuma, H., Galperín, C., Maital, S., Ogino, M., Painter, Kathleen, Pascual, L., Pêcheux, M. -G., Rahn, Charles, Toda, S., Venuti, P., Vyt, A., & Wright, B. (1998). A cross-national study of self-evaluations and attributions in parenting: Argentina, Belgium, France, Israel, Italy, Japan, and the United States. Developmental Psychology, 34(4), 662–676.
Brody, G. H., Ge, X., Conger, R. D., Gibbons, F. X., McBride Murry, V., Gerrard, M., & Simons, R. L. (2001). The influence of neighborhood disadvantage, collective socialization, and parenting on African American children’s affiliation with deviant peers. Child Development, 72(4), 1231–1246.
Brody, G. H., Ge, X., Kim, S. Y., Murry, V. M., Simons, R. L., Gibbons, F. X., Gerrard, M., & Conger, R. D. (2003) Neighborhood disadvantage moderates associations of parenting and older sibling problem attitudes and behavior with conduct disorders in African American children. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 71, 211–222.
Chao, R. K. (1994). Beyond parental control and authoritarian parenting style: Understanding Chinese parenting through the cultural notion of training. Child Development, 65, 1111–1119.
Chao, R., & Tseng, V. (2002). Parenting of Asians. In M. H. Bornstein (Ed.), Handbook of parenting (pp. 59–93). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
Conger, R. D., Patterson, G. R., & Ge, X. (1995). It takes two to replicate: A mediational model for the impact of parents’ stress on adolescent adjustment. Child Development, 66, 80–97.
Crouter, A. C., Davis, K. D., Updegraff, K., Delgado, M., & Fortner, M. (2006). Mexican American fathers’ occupational conditions: Links to family members’ psychological adjustment. Journal of Marriage and Family, 68, 843–858.
Dinh, K. T., Roosa, M. W., Tein, J.-Y., & Lopez, V. A. (2002). The relationship between acculturation and problem behavior proneness in a Hispanic youth sample: A longitudinal mediation model. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 30(3), 295–309.
Dishion T. J., & McMahon, R. J. (1998). Parental monitoring and the prevention of child and adolescent problem behavior: A conceptual and empirical formulation. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 1(1), 61–75.
Dumka, L. E., Roosa, M. W., & Jackson, K. M. (1997). Risk, conflict, mothers’ parenting, and children’s adjustment in low-income, Mexican immigrant, and Mexican American families. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 59, 309–323.
Eamon, M. K., & Mulder, C. (2005). Predicting antisocial behavior among Latino young adolescents: An ecological systems analysis. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 75(1), 117–127.
Earls, F., McGuire, J., & Shay, S. (1994). Evaluating a community intervention to reduce the risk of child abuse: Methodological strategies in conducting neighborhood surveys. Child Abuse & Neglect, 18, 473–485.
Farver, J. M., & Lee-Shin, Y. (2000). Acculturation and Korean-American children’s social and play behavior. Social Development, 9, 316–336.
Fridrich, A. H., & Flannery, D. J. (1995). The effects of ethnicity and acculturation on early adolescent delinquency. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 4, 69–87.
Fuligni, A. J., Tseng, V., & Lam, M. (1999). Attitudes toward family obligations among American adolescents with Asian, Latin American, and European backgrounds. Child Development, 70, 1030–1044.
Ge, X., Best, K. M., Conger, R. D., & Simons, R. L. (1996a). Parenting behaviors and the occurrence and co-occurrence of adolescent depressive symptoms and conduct problems. Developmental Psychology, 32, 717–731.
Ge, X., Conger, R. D., Cadoret, R. J., Neiderhiser, J. M., Yates, W., Troughton, E., & Stewart, M. A. (1996b). The developmental interface between nature and nurture: A mutual influence model of child antisocial behavior and parent behaviors. Developmental Psychology, 32(4), 574–589.
Gershoff, E. T. (2002). Corporal punishment by parents and associated child behaviors and experiences: A meta-analytic and theoretical review. Psychological Bulletin, 128(4), 539–579.
Gonzales, N. A., Deardorff, J., Formoso, D., Barr, A., & Barrera, M. Jr. (2006). Family mediators of the relation between acculturation and adolescent mental health. Family Relations, 55, 318–330.
Gutman, L. M., McLoyd, V. C., & Tokoyawa, T. (2005). Financial strain, neighborhood stress, parenting behaviors, and adolescent adjustment in urban African American families. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 15(4), 425–449.
Hill, N. E., Bush, K. R., & Roosa, M. W. (2003). Parenting and family socialization strategies and children’s mental health: Low-income, Mexican-American and Euro-American mothers and children. Child Development, 74(1), 189–204.
Jensen, P., Roper, M., Fisher, P., & Piacentini, J. (1995). Test-retest reliability of the Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children (DISC 2.1): Parent, child, and combined algorithms. Archives of General Psychiatry, 52, 61–71.
Kim, E., Cain, K., & McCubbin, M. (2006). Maternal and paternal parenting, acculturation, and young adolescent’s psychological adjustment in Korean American families. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Nursing, 19(3), 112–129.
Kim, S. Y., & Ge, X. (2000). Parenting practices and adolescent depressive symptoms in Chinese American families. Journal of Family Psychology, Special Issue: Cultural Variation in Families, 14(3), 420–435.
Klebanov, P. K., Brooks-Gun, J., & Duncan, G. J. (1994). Does neighborhood and family poverty affect mothers’ parenting, mental health, and social support? Journal of Marriage and the Family, 56, 441–455.
Knight, G. P., Virdin, L. M., & Roosa, M. (1994). Socialization and family correlates of mental health outcomes among Hispanic and Anglo American children: Consideration of cross-ethnic scalar equivalence. Child Development, 65(1), 212–224.
Kotchick, B. A., Dorsey, S., & Heller, L. (2005). Predictors of parenting among African American single mothers: Personal and contextual factors. Journal of Marriage and Family, 67(2), 448–460.
Kreft, I., & DeLeeuw, J. (1998). Introducing multilevel modeling. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Krull, J. L., & MacKinnon, D. P. (2001). Multilevel modeling of individual and group level medicated effects. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 36(2), 249–277.
Lansford, J. E., Chang, L., Dodge, K. A., Malone, P. S., Oburu, P., Palmerus, K., Bacchini, D., Pastorelli, C., Bombi, A. S., Zelli, A., Tapanya, S., Chaudhary, N., Deater-Deckard, K., Manke, B., & Quinn, N. (2005). Physical discipline and children’s adjustment: Cultural normativeness as a moderator. Child Development, 76(6), 1234–1246.
Lau, S., & Cheung, P. C. (1987). Relations between Chinese adolescents’ perception of parental control and organization and their perception of parental warmth. Developmental Psychology, 23, 726–729.
Leventhal, T., & Brooks-Gunn, J. (2000). The neighborhoods they live in: The effects of neighborhood residence on child and adolescent outcomes. Psychological Bulletin, 126, 309–337.
LeVine, R. A. (1988). Human parental care: Universal goals, cultural strategies, individual behavior. In R. A. LeVine, P. M. Miller, & M. M. West (Eds.), Parental behavior in diverse societies (pp. 5–12). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Lin, C. Y. C., & Fu, V. R. (1990). A comparison of child-rearing practices among Chinese, Immigrant Chinese, and Caucasian-American Parents. Child Development, 61, 429–433.
Loeber, R., & Dishion, T. (1983). Early predictors of male delinquency: A review. Psychological Bulletin, 94, 68–99.
Ngo, P. Y. L., & Malz, T. A. (1998). Cross-cultural and crossgenerational differences in Asian Americans’ cultural, familial systems and their impact on academic striving. In H. I. McCubbin & E. A. Thompson (Eds.), Resiliency in family series: Vol. 2. Resiliency in Native American and immigrant families (pp. 265–274). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Patterson, G. R., & Stouthamer-Loeber, M. (1984). The correlation of family management practices and delinquency. Child Development, 55, 1299–1307.
Peeples, F., & Loeber, R. (1994). Do individual factors and neighborhood context explain ethnic differences in juvenile delinquency? Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 10, 141–157.
Pinderhughes, E. E., Nix, R., Foster, E. M., & Jones, D. (2001). Parenting in context: Impact of neighborhood poverty, residential stability, public services, social networks, and danger on parental behaviors. Journal of Marriage & the Family, 63(4), 941–953.
Portes, A., & Rumbaut, R. G. (1990). Immigrant America: A portrait. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
Rothbaum, F., & Weisz, J. R. (1994). Parental care giving and child externalizing behavior in nonclinical samples: A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 116, 55–74.
Rubin, D. B. (1987). Multiple imputation for nonresponse in surveys. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons.
Ryder, A. G., Alden, L. E., & Paulhus, D. L. (2000) Is acculturation unidimensional or bidimensional? A head-to-head comparison in the prediction of personality, self-identity, and adjustment. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 79, 49–65.
Samaniego, R. Y., & Gonzales, N. A. (1999). Multiple mediators of the effects of acculturation status on delinquency for Mexican American adolescents. American Journal of Community Psychology, Special Issue: Adolescent risk behavior, 27, 189–210.
Sampson, R. J., Morenoff, J. D., & Earls, F. (1999). Beyond social capital: Spatial dynamics of collective efficacy for children. American Sociological Review, 64(5), 633–660.
Seidman, E., Yoshikawa, H., Roberts, A., Chesir-Teran, D., Allen, L., Friedman, J. L., & Aber, L. (1998). Structural and experiential neighborhood contexts, developmental stage, and antisocial behavior among urban adolescents in poverty. Development and Psychopathology, 10, 259–281.
Shumow, L., & Lomax, R. (2002). Parental efficacy: Predictor of parenting behavior and adolescent outcomes. Parenting: Science and Practice, 2, 127–150.
Silk, J. S., Sessa, F. M., Morris, A. S., Steinberg, L., & Avenevoli, S. (2004). Neighborhood cohesion as a buffer against hostile maternal parenting. Journal of Family Psychology, 18, 135–146.
Simons, R. L., Johnson, C., Conger, R. D., & Lorenz, F. O. (1997). Linking community context to quality of parenting: A study of rural families. Rural Sociology, 62, 207–230.
Snyder, J., & Patterson, G. R. (1987). Family interaction and delinquent behavior. In H. C. Quay (Ed.), Handbook of juvenile delinquency (pp. 216–243). Oxford, England: Wiley.
Sobel, M. E. (1982). Asymptotic confidence intervals for indirect effects in structural equation models. In S. Leinhardt (Ed.), Sociological methodology 1982 (pp. 290–312). Washington, DC: American Sociological Association.
Stattin, H., & Kerr, M. (2000). Parental monitoring: A reinterpretation. Child Development, 71(4), 1072–1085.
Weaver, S. R., & Kim, S. Y. (2008). A person-centered approach to studying the linkages among parent–child differences in cultural orientation, supportive parenting, and adolescent depressive symptoms in Chinese American families. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 37(1), 36–49.
Weiss, B., Dodge, K. A., Bates, J. E., & Petit, G. S. (1992). Some consequences of early harsh discipline: Child aggression and a maladaptive social information processing style. Child Development, 63(6), 1321–1335.
Wu, D. Y. H. (1996). Chinese childhood socialization. In: M. H. Bond (Ed.), The handbook of chinese psychology (pp. 143–154). Hong Kong: Oxford University Press.
Xu, Z., Wan, C. W., Mussen, P. H., & Shen, J. X. (1991). Family socialization and children’s behavior and personality development in China. Journal of Genetic Psychology, 152, 239–253.
Zhou, M. (1997). Segmented assimilation: Issues, controversies, and recent research on the new second generation. International Migration Review, 31, 975–1008.
Acknowledgments
Support for this research was provided through awards to Dr. Su Yeong Kim from the (1) American Psychological Foundation/Council of Graduate Departments of Psychology, Ruth G. and Joseph D. Matarazzo Grant; (2) California Association of Family and Consumer Sciences, Extended Education Fund; and (3) American Association of Family and Consumer Sciences, Massachusetts Avenue Building Assets Fund; and an award to Dr. Angela Chia-Chen Chen from the (4) American Nurses Foundation Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L.L., Lau, A.S., Chen, A.CC. et al. The Influence of Maternal Acculturation, Neighborhood Disadvantage, and Parenting on Chinese American Adolescents’ Conduct Problems: Testing the Segmented Assimilation Hypothesis. J Youth Adolescence 38, 691–702 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-008-9275-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-008-9275-x