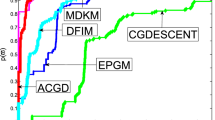
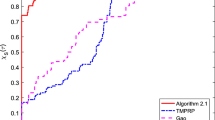
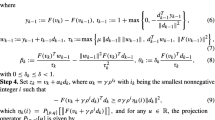Abstract
In this paper, a new Dai–Liao (DL)-type projection algorithm is presented for large-dimension nonlinear monotone problems with signal reconstruction and image recovery applications. The inspiration behind the work comes from two of the open problems propounded by Andrei (Bull Malays Math Sci Soc 34(2):319–330, 2011) involving the optimal value for the DL nonnegative parameter and the best conjugacy condition as well as the fine attributes expressed by four-term methods for unconstrained optimization. Based on the eigenvalue study of a symmetric DL-type iteration matrix, another optimal choice of the DL parameter is obtained, which is incorporated in a five-term direction scheme. Combining this with the projection method, a new DL algorithm which converges globally is developed. To implement the algorithm, a derivative-free line search mechanism is employed. Also, by conducting some numerical experiments with the new scheme and some recent DL-type methods, the efficiency of the former in solving nonlinear monotone problems as well as the \(\ell _1-norm\) regularized problems in compressed sensing is demonstrated.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abubakar, A.B., Kumam, P.: A descent Dai-Liao conjugate gradient method for nonlinear equations. Numer. Algor. 81(1), 197–210 (2018)
Abubakar, A.B., Kumam, P.: A descent Dai–Liao projection method for convex constrained nonlinear monotone equations with applications. Thai J. Math. 128–152 (2018)
Ahmed, K., Waziri, M.Y., Halilu, A.S.: On two symmetric Dai–Kou type schemes for constrained monotone equations with image recovery application. Euro J. Comput. Optim. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejco.2023.100057
Ahmed, K., Waziri, M.Y., Halilu, A.S., Murtala, S.: Sparse signal reconstruction via Hager–Zhang-type schemes for constrained system of nonlinear equations. Optimization (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/02331934.2023.2187255
Aminifard, Z., Babaie-Kafaki, S.: An optimal parameter choice for the Dai-Liao family of conjugate gradient methods by avoiding a direction of the maximum magnification by the search direction matrix. 4OR 17(3), 317–330 (2019)
Andrei, N.: Open problems in nonlinear conjugate gradient algorithms for unconstrained optimization. Bull. Malays. Math. Sci. Soc. 34(2), 319–330 (2011)
Arazm, M.R., Babaie-Kafaki, S., Ghanbari, R.: An extended Dai-Liao conjugate gradient method with global convergence for nonconvex functions. Glasnik Matematicki 52(72), 361–375 (2017)
Babaie-Kafaki, S., Ghanbari, R.: A class of descent four-term extension of the Dai–Liao conjugate gradient method based on the scaled memoryless BFGS update. J. Indust. Manag. Optim. 13(2), 649–658 (2017)
Babaie-Kafaki, S., Ghanbari, R., Mahdavi-Amiri, N.: Two new conjugate gradient methods based on modified secant equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 234, 1374–1386 (2010)
Babaie-Kafaki, S., Ghanbari, R.: A descent family of Dai–Liao conjugate gradient methods. Optim. Methods Softw. 29(3), 583–591 (2013)
Babaie-Kafaki, S., Ghanbari, R.: The Dai–Liao nonlinear conjugate gradient method with optimal parameter choices. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 234, 625–630 (2014)
Babaie-Kafaki, S., Ghanbari, R.: Two optimal Dai–Liao conjugate gradient methods. Optimization 64, 2277–2287 (2015)
Dai, Y.H., Yuan, Y.: A nonlinear conjugate gradient method with a strong global convergence property. SIAM J. Optim. 10, 177–182 (1999)
Dai, Y.H., Liao, L.Z.: New conjugacy conditions and related nonlinear conjugate gradient methods. Appl. Math. Optim. 43(1), 87–101 (2001)
Ding, Y., Xiao, Y., Li, J.: A class of conjugate gradient methods for convex constrained monotone equations. Optimization 66(12), 2309–2328 (2017)
Dirkse, S.P., Ferris, M.C.: A collection of nonlinear mixed complementarity problems. Optim. Methods Softw. 5, 319–345 (1995)
Dolan, E.D., More, J.J.: Benchmarking optimization software with performance profiles. Math. Program. 91, 201–2013 (2002)
Figueiredo, M., Nowak, R., Wright, S.J.: Gradient Projection for Sparse Reconstruction, Application to Compressed Sensing and Other Inverse Problems, pp. 586–597. IEEE J-STSP IEEE Press, Piscataway, NJ (2007)
Fletcher, R., Reeves, C.: Function minimization by conjugate gradients. Comput. J. 7, 149–154 (1964)
Fletcher, R.: Practical Method of Optimization. Volume 1: Unconstrained Optimization, 2nd ed. Wiley, New York (1997)
Ford, J.A., Narushima, Y., Yabe, N.: Multi-step nonlinear conjugate gradient methods for unconstrained minimization. Comput. Optim. Appl. 40, 191–216 (2008)
Gaohang, Y., Shanzhou, N., Jianhua, M.: Multivariate spectral gradient projection method for nonlinear monotone equations with convec constraints. Jimo. 9(1), 117–129 (2013)
Hager, W.W., Zhang, H.: A survey of nonlinear conjugate gradient methods. Pac. J. Optim. 2, 35–58 (2006)
Halilu, A.S., Majumder, A., Waziri, M.Y., Ahmed, K., Awwal, A.M.: Motion control of the two joint planar robotic manipulators through accelerated Dai–Liao method for solving system of nonlinear equations. Eng. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1108/EC-06-2021-0317
Halilu, A.S., Majumder, A., Waziri, M.Y., Ahmed, K.: Signal recovery with convex constrained nonlinear monotone equations through conjugate gradient hybrid approach. Math. Comput. Simul. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2021.03.020
Halilu, A.S., Majumder, A., Waziri, M.Y., Awwal, A.M., Ahmed, K.: On solving double direction methods for convex constrained monotone nonlinear equations with image restoration. Comput. Appl. Math. 40, 1–27 (2021)
Hestenes, M.R., Stiefel, E.L.: Methods of conjugate gradients for solving linear systems. J. Res. Nat. Bur. Stand. 49, 409–436 (1952)
Ibrahim, A.H., Kumam, P., Abubakar, A.B., Abdullahi, M.S., Mohammad, H.: A Dai-Liao-type projection method for monotone nonlinear equations and signal processing. Demonstratio Mathematica 55, 978–1013 (2022)
Ivanov, B., Milanovic, G.V., Stanimirovic, P.S.: Accelerated Dai–Liao projection method for solving systems of monotone nonlinear equations with application to image deblurring. J. Glob. Optim. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-022-01213-4
Kiri, A.I., Waziri, M.Y., Ahmed, K.: A modified Liu–Storey scheme for nonlinear systems with an application to image recovery. Iran. J. Numer. Anal. Optim. (2022). https://doi.org/10.22067/ijnao.2022.75413.1107
Koorapetse, M., Kaelo, P., Lekoko, S., Diphofu, T.: A derivative-free RMIL conjugate gradient projection method for convex constrained nonlinear monotone equations with applications in compressive sensing. Appl. Numer. Math. 165, 431–441 (2021)
La cruz, W., Martinez, J.M., Raydan, M.: Spectral residual method without gradient information for solving large-scale nonlinear systems of equations: theory and experiments. Technical Report RT-04-08 (2004)
La Cruz, W.: A Spectral algorithm for large-scale systems of nonlinear monotone equations. Numer. Algor. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s1107s-017-0299-8
Liu, J.K., Li, S.J.: A projection method for convex constrained monotone nonlinear equations with applications. Comput. Math. Appl. 70(10), 2442–2453 (2015)
Liu, Y., Storey, C.: Efficient generalized conjugate gradient algorithms. Part 1: Theory. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 69, 129–137 (1991)
Li, G., Tang, C., Wei, Z.: New conjugacy condition and related new conjugate gradient methods for unconstrained optimization. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 202, 523–539 (2007)
Meintjes, K., Morgan, A.P.: A methodology for solving chemical equilibrium systems. Appl. Math. Comput. 22, 333–361 (1987)
Narushima, Y., Yabe, H.: A survey of sufficient descent conjugate gradient methods for unconstrained optimization. SUT J. Math. 50(2), 167–203 (2014)
Pang, J.S.: Inexact Newton methods for the nonlinear complementarity problem. Math. Program 36, 54–71 (1986)
Perry, A.: A modified conjugate gradient algorithm. Oper. Res. Tech. Notes 26(6), 1073–1078 (1978)
Polak, E., Ribi\(\acute{e}\)re, G.: Note Sur la convergence de directions conjugèes. Rev. Francaise Informat. Recherche Operationelle, 3e Ann\(\grave{e}\)e. 16, 35–43 (1969)
Polyak, B.T.: The conjugate gradient method in extreme problems. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 9, 94–112 (1969)
Raymond, H.C., Ho, C., Nikolova, M.: Salt-and-pepper noise re moval by median type noise detectors and detail-preserving regularization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 14(10), 1479–1485 (2005)
Solodov, M.V., Svaiter, B.F.: A globally convergent inexact Newton method for systems of monotone equations. In: Fukushima, M., Qi, L. (eds.) Reformulation: Nonsmooth, Piecewise Smooth, Semismooth and Smoothing Methods, pp. 355–369. Kluwer Academic Publishers, New York (1998)
Sun, W., Yuan, Y.X.: Optimization Theory and Methods: Nonlinear Programming. Springer, New York (2006)
Waziri, M.Y., Ahmed, K., Halilu, A.S., Sabi’u, J.: Two new Hager-Zhang iterative schemes with improved parameter choices for monotone nonlinear systems and their applications in compressed sensing. Rairo Oper. Res. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1051/ro/2021190
Waziri, M.Y., Ahmed, K., Sabi’u, J.: A Dai–Liao conjugate gradient method via modified secant equation for system of nonlinear equations. Arab. J. Math. 9, 443–457 (2020)
Waziri, M.Y., Ahmed, K., Sabi’u, J., Halilu, A.S.: Enhanced Dai–Liao conjugate gradient methods for systems of monotone nonlinear equations. SeMA J. 78, 15–51 (2020)
Xiao, Y., Wang, Q., Hu, Q.: Non-smooth equations based method for \(\ell _1-norm\) problems with applications to compressed sensing. Nonlinear Anal. Theory Methods Appl. 74(11), 3570–3577 (2011)
Xiao, Y., Zhu, H.: A conjugate gradient method to solve convex constrained monotone equations with applications in compressive sensing. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 405(1), 310–319 (2013)
Yabe, H., Takano, M.: Global convergence properties of nonlinear conjugate gradient methods with modified secant condition. Comput. Optim. Appl. 28, 203–225 (2004)
Yin, J., Jian, J., Jiang, X., Liu, M., Wang, L.: A hybrid three-term conjugate gradient projection method for constrained nonlinear monotone equations with applications. Numer. Algor. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-020-01043-z
Yu, N.: Gradient methods for minimizing composite functions. Math. Program. 140(2), 125–161 (2013)
Zhang, K., Liu, H., Liu, Z.: A new Dai–Liao conjugate gradient method with optimal parameter choice. Numer. Funct. Anal. Optim. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/01630563.2018.1535506
Zhang, L., Zhou, W., Li, D.: Some descent three-term conjugate gradient methods and their global convergence. Optim. Methods Softw. 22, 697–711 (2007)
Zhou, W., Zhang, L.: A nonlinear conjugate gradient method based on the MBFGS secant condition. Optim. Methods Softw. 21, 707–714 (2006)
Zhou, W.J., Li, D.H.: Limited memory BFGS methods for nonlinear monotone equations. J. Comput. Math. 25, 89–96 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the comments and suggestions offered by the anonymous referees.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Alexander Vladimirovich Gasnikov.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
The appendix contains six examples of the operator F, their dimensions, and six initial guesses.
The following are six examples of the operator F used in the experiment:
Example 1
Nonsmooth function obtained from [33].
\(F_i(x)=2x_i-\sin {|x_i|}\), \(\quad i=1,2, \dots ,n\),
where \({\mathcal {C}} ={\mathbb {R}}_+^n\).
Example 2
This is obtained from [57].
\(F_1(x)= 2x_1+\sin {x_1}-1\),
\(F_i(x)= -2x_{i-1}+2x_i+2\sin {x_i}-1\),
\(F_n(x)=2x_n+\sin {x_n}-1\),\(\quad i=2,\dots ,n-1\),
where \({\mathcal {C}} ={\mathbb {R}}_+^n\).
Example 3
Penalty function 1 obtained from [15].
\(F_i(x)=2\pi (x_i-1)+4(\sum _{j=1}^{n}x_j-0.25)x_i, \quad i=1,2,\dots ,n\),
where \(\pi =10^{-5}, \quad {\mathcal {C}} ={\mathbb {R}}_+^n\).
Example 4
Nonsmooth function [50].
\(F_i(x)=x_i-\sin {|x_i-1|}\), \(\quad i=1,2, \dots ,n\),
where \({\mathcal {C}} =\left\{ x\in {\mathbb {R}}^n:\displaystyle \sum _{i=1}^{n}x_i\le n, \quad x_i\ge -1, \quad i=1,2,\dots ,n\right\} .\)
Example 5
This example is obtained from [2].
\(F_1(x)=2.5x_1+x_2-1\),
\(F_i(x)=x_{i-1}+2.5x_{i}+x_{i+1}-1\),
\(F_n(x)=x_{n-1} + 2.5x_n-1, i=2,3,...,n-1\), where \(\mathcal {C} =\mathbb {R}_+^n\)
Example 6
Nonsmooth function obtained from [22].
\(F_i(x)=2x_i-\sin {|x_i-1|}\), \(\quad i=1,2, \dots ,n\),
where \({\mathcal {C}} =\left\{ x\in {\mathbb {R}}^n:\displaystyle \sum _{i=1}^{n}x_i\le n, \quad x_i\ge -1, \quad i=1,2,\dots ,n\right\} \).
A total of 18 experiments were conducted for each of the six examples of the operator F with dimensions \(10^4\), \(5\times 10^4\), \(10^5\), and the following initial guesses:
\(x_0^{1}\)\( =\left( \frac{1}{n},\frac{2}{n},...,1\right) ^T\), \(x_0^{2}\) \(=\left( \frac{3}{2},\frac{1}{2},...,-\frac{[(-1)^n-2]}{2}\right) ^T\), \(x_0^{3}\) \(=\left( \frac{1}{3},\frac{1}{3^2},...,\frac{1}{3^n}\right) ^T\),
\(x_0^{4}\) \(=\left( \frac{n-1}{n},\frac{n-2}{n},...,0\right) ^T\), \(x_0^{5}\) \(=\left( 3,1,...,-2\frac{[(-1)^n-2]}{2}\right) ^T\), \(x_0^{6}\)\(=\left( 1-\frac{1}{n},1-\frac{2}{n},...,0\right) ^T\).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, K., Waziri, M.Y., Murtala, S. et al. On a Scaled Symmetric Dai–Liao-Type Scheme for Constrained System of Nonlinear Equations with Applications. J Optim Theory Appl 200, 669–702 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-023-02281-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-023-02281-6