Abstract
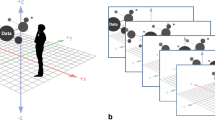
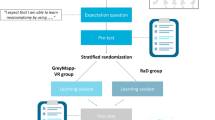
A major goal of education is to help students retain as much meaningful information as possible for long periods of time. The learning process by which students acquire new knowledge and behaviors is closely related to memory, which is the core of cognition. In a previous study, we developed virtual reality visualization model (VRVM) that can be applied to address difficulties with learning medical biochemistry. Validation and evaluation studies are necessary to assess the usefulness of VRVM. The purpose of the present study is to apply VRVM and evaluate its effectiveness in a real educational environment. We modeled and verified the concept of spatiotemporality of information obtained through VRVM, which augments memories in linkage with hippocampal-centered networks while helping students to transition to higher-order thinking. The effectiveness of VRVM of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, an onerous topic for medical students, was compared with that of traditional educational methods. The experimental group used VRVM to learn the TCA cycle, while the control group learned from PowerPoint (Microsoft Co., Redmond, WA, USA) presentations using 2-dimensional (2D) diagrams. Evaluations of short-term and long-term memory indicated that learning using VRVM was more effective than learning through traditional lecture-based methods, and that VRVM resulted in better recall compared to traditional methods. Our findings suggest that VRVM can be applied when teaching students about the complicated TCA cycle, and that it helps medical students to improve their recall of carbohydrate metabolism in the context of medical biochemistry studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addis, D. R., Pan, L., Vu, M. A., Laiser, N., & Schacter, D. L. (2009). Constructive episodic simulation of the future and the past: distinct subsystems of a core brain network mediate imagining and remembering. Neuropsychologia, 47(11), 2222–2238.
Atance, C. M., & O’Neill, D. K. (2001). Episodic future thinking. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 5(12), 533-539.
Botzung, A., Denkova, E., & Manning, L. (2008). Experiencing past and future personal events: functional neuroimaging evidence on the neural bases of mental time travel. Brain and Cognition, 66(2), 202–212.
Bradley, P. (2006). The history of simulation in medical education and possible future directions. Medical Education, 40(3), 254–262.
Brandt, L., Elen, J., Hellemans, J., Heerman, L., Couwenberg, I., Volckaert, L., et al. (2001). The impact of concept mapping and visualization on the learning of secondary school chemistry students. International Journal of Science Education, 23(12), 1303–1313.
Brown, T. I., Carr, V. A., LaRocque, K. F., Favila, S. E., Gordon, A. M., Bowles, B., et al. (2016). Prospective representation of navigational goals in the human hippocampus. Science (New York, N.Y.), 352(6291), 1323–1326.
Bullens, J., Igloi, K., Berthoz, A., Postma, A., & Rondi-Reig, L. (2010). Developmental time course of the acquisition of sequential egocentric and allocentric navigation strategies. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 107(3), 337–350.
Bunsey, M., & Eichenbaum, H. (1996). Conservation of hippocampal memory function in rats and humans. Nature, 379(6562), 255–257.
Buzsaki, G., & Moser, E. I. (2013). Memory, navigation and theta rhythm in the hippocampal-entorhinal system. Nature Neuroscience, 16(2), 130–138.
Byagowi, A., & Moussavi, Z. (2012). Design of a virtual reality navigational (VRN) experiment for assessment of egocentric spatial cognition. Conference proceedings : annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, 2012, 4812–4815.
Carnegie Mellon Institute. (2002). Capability maturity model® integration (CMMI SM), version 1.1. Pittsburgh: Carnegie Mellon University.
Constantinescu, A. O., O'Reilly, J. X., & Behrens, T. E. J. (2016). Organizing conceptual knowledge in humans with a gridlike code. Science (New York, N.Y.), 352(6292), 1464–1468.
Custers, E. J. (2010). Long-term retention of basic science knowledge: a review study. Advances in Health Sciences Education, 15(1), 109–128.
D'Argembeau, A., & Van der Linden, M. (2004). Phenomenal characteristics associated with projecting oneself back into the past and forward into the future: influence of valence and temporal distance. Consciousness and Cognition, 13(4), 844–858.
D'Argembeau, A., & Van der Linden, M. (2006). Individual differences in the phenomenology of mental time travel: the effect of vivid visual imagery and emotion regulation strategies. Consciousness and Cognition, 15(2), 342–350.
Dede, A. J., Frascino, J. C., Wixted, J. T., & Squire, L. R. (2016). Learning and remembering real-world events after medial temporal lobe damage. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(47), 13480–13485.
Eichenbaum, H. (2015). The hippocampus as a cognitive map of social space. Neuron, 87(1), 9–11.
Eichenbaum, H. (2017). The role of the hippocampus in navigation is memory. Journal of Neurophysiology, 117(4), 1785–1796.
Eichenbaum, H., & Bunsey, M. (1995). On the binding of associations in memory: clues from studies on the role of the hippocampal region in paired-associate learning. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 4(1), 19–23.
Eichenbaum, H., & Cohen, N. J. (2014). Can we reconcile the declarative memory and spatial navigation views on hippocampal function? Neuron, 83(4), 764–770.
Eichenbaum, H., Dudchenko, P., Wood, E., Shapiro, M., & Tanila, H. (1999). The hippocampus, memory, and place cells: is it spatial memory or a memory space? Neuron, 23(2), 209–226.
Fassbender, E., & Heiden, W. (2006). The virtual memory palace. The Journal of Computer Information Systems, 2(1), 457–464.
Fortin, N. J., Agster, K. L., & Eichenbaum, H. B. (2002). Critical role of the hippocampus in memory for sequences of events. Nature Neuroscience, 5(5), 458–462.
Ge, S., Yang, C. H., Hsu, K. S., Ming, G. L., & Song, H. (2007). A critical period for enhanced synaptic plasticity in newly generated neurons of the adult brain. Neuron, 54(4), 559–566.
Greenstein, Y. J., Pavlides, C., & Winson, J. (1988). Long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus is preferentially induced at theta rhythm periodicity. Brain Research, 438(1–2), 331–334.
Hartley, T., Lever, C., Burgess, N., & O'Keefe, J. (2014). Space in the brain: how the hippocampal formation supports spatial cognition. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 369(1635), 20120510.
Hassabis, D., Kumaran, D., Vann, S. D., & Maguire, E. A. (2007). Patients with hippocampal amnesia cannot imagine new experiences. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(5), 1726–1731.
Horner, A. J., Bisby, J. A., Zotow, E., Bush, D., & Burgess, N. (2016). Grid-like processing of imagined navigation. Current Biology, 26(6), 842–847.
Kitamura, T., Saitoh, Y., Takashima, N., Murayama, A., Niibori, Y., Ageta, H., et al. (2009). Adult neurogenesis modulates the hippocampus-dependent period of associative fear memory. Cell, 139(4), 814–827.
Koehl, M., & Abrous, D. N. (2011). A new chapter in the field of memory: adult hippocampal neurogenesis. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 33(6), 1101–1114.
Kramar, E. A., Lin, B., Lin, C. Y., Arai, A. C., Gall, C. M., & Lynch, G. (2004). A novel mechanism for the facilitation of theta-induced long-term potentiation by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. The Journal of Neuroscience, 24(22), 5151–5161.
Krathwohl, D. R. (2002). A revision of bloom’s taxonomy: an overview. Theory Into Practice, 41(4), 212–218.
Maguire, E. A. (2001). Neuroimaging studies of autobiographical event memory. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 356(1413), 1441–1451.
Maguire, E. A., & Mullally, S. L. (2013). The hippocampus: a manifesto for change. Journal of Experimental Psychology. General, 142(4), 1180–1189.
Maguire, E. A., Woollett, K., & Spiers, H. J. (2006). London taxi drivers and bus drivers: a structural MRI and neuropsychological analysis. Hippocampus, 16(12), 1091–1101.
Markus, E. J., Barnes, C. A., McNaughton, B. L., Gladden, V. L., & Skaggs, W. E. (1994). Spatial information content and reliability of hippocampal CA1 neurons: effects of visual input. Hippocampus, 4(4), 410–421.
Milivojevic, B., & Doeller, C. F. (2013). Mnemonic networks in the hippocampal formation: from spatial maps to temporal and conceptual codes. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 142(4), 1231–1241.
Milivojevic, B., Vicente-Grabovetsky, A., & Doeller, C. F. (2015). Insight reconfigures hippocampal-prefrontal memories. Current Biology, 25(7), 821–830.
Milner, B., Squire, L. R., & Kandel, E. R. (1998). Cognitive neuroscience and the study of memory. Neuron, 20(3), 445–468.
Moffat, S. D., Zonderman, A. B., & Resnick, S. M. (2001). Age differences in spatial memory in a virtual environment navigation task. Neurobiology of Aging, 22(5), 787–796.
Morisaki, R., Bon, C., & Levitt, J. O. (2016). The use of an imagery mnemonic to teach the Krebs cycle. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education, 44(3), 224–229.
Mullally, S. L., & Maguire, E. A. (2014). Memory, imagination, and predicting the future: a common brain mechanism? Neuroscientist, 20(3), 220–234.
Nadel, L., Ryan, L., Hayes, S. M., Gilboa, A., & Moscovitch, M. (2003). The role of the hippocampal complex in long-term episodic memory. International Congress Series, 1250, 215–234.
National Research Council. (2006). Learning to think spatially. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press.
O'Keefe, J., & Nadel, L. (1978). The hippocampus as a cognitive map. New York: Oxford University Press.
Okuda, J., Fujii, T., Ohtake, H., Tsukiura, T., Tanji, K., Suzuki, K., et al. (2003). Thinking of the future and past: the roles of the frontal pole and the medial temporal lobes. Neuroimage, 19(4), 1369–1380.
Preston, A. R., & Eichenbaum, H. (2013). Interplay of hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in memory. Current Biology, 23(17), R764–R773.
Quirk, G. J., Muller, R. U., & Kubie, J. L. (1990). The firing of hippocampal place cells in the dark depends on the rat’s recent experience. The Journal of Neuroscience, 10(6), 2008–2017.
Quiroga, R. Q., Reddy, L., Kreiman, G., Koch, C., & Fried, I. (2005). Invariant visual representation by single neurons in the human brain. Nature, 435(7045), 1102–1107.
Schiller, D., Eichenbaum, H., Buffalo, E. A., Davachi, L., Foster, D. J., Leutgeb, S., et al. (2015). Memory and space: towards an understanding of the cognitive map. The Journal of Neuroscience, 35(41), 13904–13911.
Schmidt-Hieber, C., Jonas, P., & Bischofberger, J. (2004). Enhanced synaptic plasticity in newly generated granule cells of the adult hippocampus. Nature, 429(6988), 184–187.
Shapiro, M. L., Tanila, H., & Eichenbaum, H. (1997). Cues that hippocampal place cells encode: dynamic and hierarchical representation of local and distal stimuli. Hippocampus, 7(6), 624–642.
Skaggs, W. E., & McNaughton, B. L. (1998). Spatial firing properties of hippocampal CA1 populations in an environment containing two visually identical regions. The Journal of Neuroscience, 18(20), 8455–8466.
Snyder, J. S., Kee, N., & Wojtowicz, J. M. (2001). Effects of adult neurogenesis on synaptic plasticity in the rat dentate gyrus. Journal of Neurophysiology, 85(6), 2423–2431.
Spreng, R. N., Mar, R. A., & Kim, A. S. (2009). The common neural basis of autobiographical memory, prospection, navigation, theory of mind, and the default mode: a quantitative meta-analysis. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 21(3), 489–510.
Squire, L. R., Knowlton, B., & Musen, G. (1993). The structure and organization of memory. Annual Review of Psychology, 44, 453–495.
Tashiro, A., Makino, H., & Gage, F. H. (2007). Experience-specific functional modification of the dentate gyrus through adult neurogenesis: a critical period during an immature stage. The Journal of Neuroscience, 27(12), 3252–3259.
Tavares, R. M., Mendelsohn, A., Grossman, Y., Williams, C. H., Shapiro, M., Trope, Y., et al. (2015). A map for social navigation in the human brain. Neuron, 87(1), 231–243.
Tulving, E. (2002). Episodic memory: from mind to brain. Annual Review of Psychology, 53, 1–25.
Tulving, E., & Markowitsch, H. J. (1998). Episodic and declarative memory: role of the hippocampus. Hippocampus, 8(3), 198–204.
Vargha-Khadem, F., Gadian, D. G., Watkins, K. E., Connelly, A., Van Paesschen, W., & Mishkin, M. (1997). Differential effects of early hippocampal pathology on episodic and semantic memory. Science (New York, N.Y.), 277(5324), 376–380.
Wallenstein, G. V., Eichenbaum, H., & Hasselmo, M. E. (1998). The hippocampus as an associator of discontiguous events. Trends in Neurosciences, 21(8), 317–323.
Ware, C. (2012). Information Visualization: Perception for Design. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann.
Wood, E. R., Dudchenko, P. A., & Eichenbaum, H. (1999). The global record of memory in hippocampal neuronal activity. Nature, 397(6720), 613–616.
Woollett, K., & Maguire, E. A. (2011). Acquiring “the knowledge” of London’s layout drives structural brain changes. Current Biology, 21(24), 2109–2114.
Zalesak, M., & Heckers, S. (2009). The role of the hippocampus in transitive inference. Psychiatry Research, 172(1), 24–30.
Zeithamova, D., Dominick, A. L., & Preston, A. R. (2012). Hippocampal and ventral medial prefrontal activation during retrieval-mediated learning supports novel inference. Neuron, 75(1), 168–179.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Sunghyo Park for advice on writing this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Grant K1813381 from Future Medicine, Fourth Industrial Revolution, and Artificial Intelligence of Korea University College and School of Medicine, and the Environmental Health Action Program (Title: Development of Receptor-based Environment-induced Diseases Prevention and Management System Using Real-time Collected Environment and Health Information; Project No. 2018001350005) by Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S., Heo, R., Chung, Y. et al. Virtual Reality Visualization Model (VRVM) of the Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) Cycle of Carbohydrate Metabolism for Medical Biochemistry Education. J Sci Educ Technol 28, 602–612 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-019-09790-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-019-09790-y