Abstract
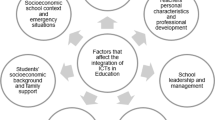
The purpose of this study was to explore the factors affecting ICT adoption process and the implications for faculty training and technology leadership. Respondents represented a wide range of academic and professional positions. They identified themselves as Assistant, Associate, and Professor as well as Instructional Designer, Director of Technology, Information Manager, eLearning Manager, Assistant Department Chair, Associate Vice President of Academic Affairs and Consultant. The respondents identified Organizational Support, Leadership, Training and Development, and Resources as the predominate themes affecting Information and Communication Technology (ICT) adoption process in higher education. Evidence from this study offers insights on how higher education administrators and technology leaders could help their faculty and staff to implement appropriate ICT tools and practices to improve student learning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Council on Education (1999) To touch the future: transforming the way teachers are taught: an action Agenda for College and University presidents. Retrieved January 24, 2008 from http://www.acenet.edu/resources/presnetiteacher-ed-rpt.pdf
Anderson T, Varnhagen S, Campbell K (1998) Faculty adoption of teaching and learning technologies: contrasting earlier adopters and mainstream faculty. Can J High Educ 28(23):71–78
Becker HJ (1994) Analysis and trends of school use of new information technologies. Department of Education, University of California, Irvine
Braak JV (2001) Individual characteristics influencing teachers’ class use of computers. J Educ Comput Res 25(2):141–157. doi:10.2190/81YV-CGMU-5HPM-04EG
Chiero R1 (1997) Teachers’ perspectives on factors that affect computer use. J Res Comput Educ 30(2):133–145
Choudrie J, Dwivedi YK (2005) Investigating the research approaches for examining technology adoption issues. J Res Pract 1(1):1–12
Cuban L (2001) Oversold and underused: computers in the classroom. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Cushman M, Klecun E (2006) How (Can) non-users engage with technology: bringing in the digitally excluded? In: Trauth E, Howcroft D, Butler T, Fitzgerald B, Gross JD (eds) Social inclusion: societal and organizational implications for information systems. Springer, Boston, pp 347–364
Dagada R (2005) The impact of the technology acceptance model (TAM) in determining the success or failure of computer-integrated education. In: Kommers P, Richards G (eds) Proceedings of world conference on educational multimedia, hypermedia and telecommunications 2005. AACE, Chesapeake, pp 1125–1129
Dooley LM, Metcalf T, Martinez A (1999) The adoption of computer technology and telecommunications by teachers. Int Forum Educ Technol Soc 2(4)
Fabry DL, Higgs 1R (1997) Barriers to the effective use of technology in education: current status. J Educ Comput Res 17(4):385–395
Frank KA, Zhao Y, Borman K (2004) Social capital and the diffusion of innovations within organizations: application to the implementation of computer technology in schools. Sociol Education 77:148–171
Grabe M, Grabe C (2008) Integrating technology for meaningful learning, 5th edn. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston
Hagenson L, Castle D (2003) The integration of technology into teaching by University College of education faculty. In: Crawford C, Willis DA, Carlsen R, Gibson I, McFerrin K, Price J, Weber R (eds) Proceedings of society for information technology and teacher education international conference. Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education, Chesapeake, pp 947–952
Hall GE, Hord SM (1987) Change in schools: facilitating the process. State University of New York Press, Albany
Jacobsen M, Clifford P, Friesen S (2002). Preparing teachers for technology integration: creating a culture of inquiry in the context of use. Contemp Issues Technol Teach Educ 2(3). Retrieved March 12, 2008, from http://www.citejournal.org/vol2/iss3/currentpractice/article2.cfm
Keengwe J, Anyanwu L (2007) Computer technology-infused learning enhancement. J Sci Educ Technol 16(5):387–393
Lincoln YS, Guba EG (1985) Naturalistic inquiry. Sage, Beverly Hills
Mayer RE (1996) Learners as information processors: legacies and limitations of educational psychology’s second metaphor. Educ Psychologist 31(3/4):151–161
McKenzie J (2001) How teacher learn technology best. From Now On: The Educational Technology Journal, 10(6). Retrieved January 02, 2008, from http://www.fno.org/mar01/howlearn.html
Medlin BD (2001) The factors that may influence a faculty member’s decision to adopt electronic technologies in instruction. (Doctoral dissertation, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, 2001). ProQuest Digital Dissertations. (UMI No. AAT 3095210)
Mooij T, Smeet E (2001) Modeling and supporting ict implementation in secondary schools. Comput Educ 36(3):265–281
National Education Association (2000) Annual NEA today readership survey. Retrieved February 10, 2008, from http://www.nea.org
Oppenheimer T (2003) The flickering mind: the false promise of technology in the classroom and how learning can be saved. Random House, New York
Parisot AH (1997) Distance education as a catalyst for changing teaching in the community college: implications for institutional policy. New Dir Community Coll 99:5–13
Pope M, Hare D, Howard E (2002) Technology integration: closing the gap between what preservice teachers are taught to do and what they can do. J Technol Teach Educ 10(2):191–203
Rogers EM (2003) Diffusion of innovations, 5th edn. Free Press, New York
Saadé RG, Nebebe F, Tan W (2007) Viability of the “technology acceptance model” in multimedia learning environments: a comparative study. Interdiscip J Knowl Learn Objects 3:175–184
Schrum L, Skeele R, Grant M (2002) One college of education’s effort to infuse technology: a systemic approach to revisioning teaching and learning. J Res Technol Educ 35(2):256–271
Sherry L (1998) An integrated technology adoption and diffusion model. Int J Educ Telecommun 4(2):113–145
Sherry L, Billig S, Tavalin F, Gibson D (2000) New insights on technology adoption in schools. T.H.E. Journal 27(7):43–46
Sherry L, Gibson D (2002) The path to teacher leadership. Contemp Issues Technol Teach Educ 2(2):178–203. Available: http://www.aace.org/dl/index.cfm/fuseaction/View/paperID/10585
Solomon L, Wiederhorn L (2000) Progress of technology in the schools: 1999 report on 27 states. Milken exchange on education and technology. Milken Family Foundation, Santa Monica
Spotts TH (1999) Discriminating factors in faculty use of instructional technology in higher education. Educ Technol Soc 2(4):92–99
Stuart WD (2000) Influence of sources of communication, user characteristics and innovation characteristics on adoption of a communication technology (Doctoral dissertation, The University of Kansas, 2000). ProQuest Digital Dissertations (UMI No. AAT 9998115)
Waxman H, Lin M, Michko GM (2003) A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of recent research on the effects of teaching and learning with technology on student outcomes. Retrieved July 24, 2007, from http://www.ncrel.org/tech/effects2/
Zhao Y, Cziko GA (2001) Teacher adoption of technology: a perceptual-control-theory perspective. Technol Teach Educ 9(1):5–30
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keengwe, J., Kidd, T. & Kyei-Blankson, L. Faculty and Technology: Implications for Faculty Training and Technology Leadership. J Sci Educ Technol 18, 23–28 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-008-9126-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-008-9126-2