Abstract
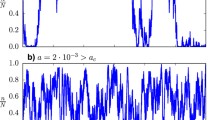
We study a generalization of the voter model on complex networks, focusing on the scaling of mean exit time. Previous work has defined the voter model in terms of an initially chosen node and a randomly chosen neighbor, which makes it difficult to disentangle the effects of the stochastic process itself relative to the network structure. We introduce a process with two steps, one that selects a pair of interacting nodes and one that determines the direction of interaction as a function of the degrees of the two nodes and a parameter α which sets the likelihood of the higher degree node giving its state to the other node. Traditional voter model behaviors can be recovered within the model, as well as the invasion process. We find that on a complete bipartite network, the voter model is the fastest process. On a random network with power law degree distribution, we observe two regimes. For modest values of α, exit time is dominated by diffusive drift of the system state, but as the high-degree nodes become more influential, the exit time becomes dominated by frustration effects dependent on the exact topology of the network.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liggett, T.M.: Interacting Particle Systems. Springer, New York (2005)
Vazquez, F., Eguiluz, V.M.: New J. Phys. 10, 063011 (2008)
Suchecki, K., Eguiluz, V.M., San Miguel, M.: Phys. Rev. E 72, 036132 (2005)
Sood, V., Redner, S.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 178701 (2005)
Suchecki, K., Eguiluz, V.M., San Miguel, M.: Europhys. Lett. 69, 228 (2005)
Castellano, C., Loreto, V., Barrat, A., Cecconi, F.: Phys. Rev. E 71, 066107 (2005)
Baxter, G.J., Blythe, R.A., Croft, W., McKane, A.J.: Phys. Rev. E 73, 046118 (2006)
Hubbell, S.P.: The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton (2001)
Castellano, C., Fortunato, S., Loreto, V.: Rev. Modern Phys. 81(2), 591 (2009)
Pastor-Satorras, R., Vespignani, A.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 3200 (2001)
Baxter, G.J., Blythe, R.A., McKane, A.J.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 101(25), 258701 (2008)
Castellano, C.: AIP Conf. Proc. 779, 114 (2005). ArXiv:cond-mat/0504522v1
Krapivsky, P.L.: Phys. Rev. A 45(2), 1067 (1992)
Redner, S.: A Guide to First-Passage Processes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Newman, M.E.J.: SIAM Rev. 45, 167 (2003)
Watts, D., Strogatz, S.: Nature 393, 440 (1998)
Krapivsky, P.L., Redner, S.: J. Phys. A 35, 9517 (2002)
Molloy, M., Reed, B.: Random Struct. Algorithms 6, 161 (1995)
Blondel, V.D., Guillaume, J.L., Hendrickx, J., de Kerchove, C., Lambiotte, R.: Phys. Rev. E 77, 036114 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schneider-Mizell, C.M., Sander, L.M. A Generalized Voter Model on Complex Networks. J Stat Phys 136, 59–71 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-009-9757-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-009-9757-6