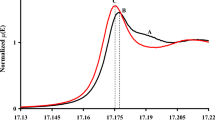
The complexation of As(V) in aqueous solutions in the presence of iron(III) was investigated spectrophotometrically with both variable and constant ionic strengths. The determined thermodynamic and stoichiometric formation constants of the FeHAsO4+ species are log10∘β = 9.21± 0.01 and log10Iβ (1.0mol⋅dm−3 NaClO4) = 7.78 ± 0.01, respectively. The numerical treatment of the obtained spectral data was performed with the SPECA program. The analysis required the consideration of the hydrolysis of Fe(III) and the protonation of As(V) in the pH range studied. No significant hydrolysis was observed because of the low pH values (pH < 2.5) involved. The stabilities of the solid Fe(III) arsenates was established by solubility experiments. All of the solubility experiments were performed in aqueous NaClO4 solutions at constant ionic strength (1.0mol⋅dm−3) and at 25∘C. The experimental data were consistent with FeAsO4⋅2H2O being the solid phase (log10 ∘ Kso = −24.30± 0.08). The corresponding thermodynamic constants were computed by means of the Modified Bromley's Methodology (MBM) that describes the variation of the activity coefficients of all of the ions involved in the complexation and precipitation equilibria with the medium and ionic strength. Finally, the solid phase obtained in this work was also characterized by FT-IR and FT-Raman spectroscopies, and the hydration of the solid iron arsenate was confirmed by X-ray diffraction data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. L. Pierce and C. B. Moore, Adsorption of Arsenite and Arsenate on Amorphous Iron Hydroxide, Water Res. 16, 1247–1253 (1982).
P. E. Mariner, F. J. Holzmer, R. E. Jackson, and H. W. Meinardus, Effects of High pH on Arsenic Mobility in a Shallow Sandy Aquifer and on Aquifer Permeability Along the Adjacent Shoreline, Commencement Bay Superfund Site, Tacoma, Washington, Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 1645–1651 (1996).
E. E. van der Hoek and R. N. J. Comans, Modelling Arsenic and Selenium Leaching from Acidic Fly Ash by Sorption on Iron(hydr)oxide in the Fly Ash Matrix, Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 517–523 (1996).
B. Daus, J. Mattusch, A. Paschke, H. Weiss, and R. Wennrich, Kinetics of the Arsenite Oxidation in Seepage Waters from a Tin Mill Tailings Pond, Talanta 51, 1087–1095 (2000).
L. G. Sillen and A. E. Martell, Stability Constants of Metal-Ion Complexes (Metcalfe & Cooper Limited, London, 1964).
J. D. Rimstidt and P. M. Dove, Solubility and Stability of Scorodite, FeAsO4⋅2H2O, Am. Miner. 72, 852–855 (1987).
C. R. Paige, W. J. Snodgrass, R. V. Nicholson, and J. M. Scharer, An Arsenate Effect on Ferrihydrite Dissolution Kinetics under Acidic Oxic Conditions, Water Res. 31, 2370–2382 (1997).
M. Leblanc, B. Achard, D. Othman, and J. M. Luck, Accumulation of Arsenic from Acidic Mine Waters by Ferruginous Bacterial Accretions (Stromatolites), Appl. Geochem. 11, 541–554 (1996).
G. Borge, R. Castaño, M. P. Carril, M. S. Corbillón, and J. M. Madariaga, Development of a Modified Bromley's Methodology (MBM) for the Estimation of Ionic Media Effects on Solution Equilibria. Part 1. Calculation of the Interaction Parameters in the Molar and Molal Scales at 25°C, Fluid Phase Equil. 121, 85–98 (1996).
G. Borge, N. Etxebarria, L. A. Fernandez, M. A. Olazábal, and J. M. Madariaga, Development of a Modified Bromley's Methodology (MBM) for the Estimation of Ionic Media Effects on Solution Equilibria. Part 2. Correlation of the Molar and Molal Interaction Parameters with the Charge and Crystal Radii of the Ions, Fluid Phase Equil. 121, 99–109 (1996).
Y. Belaustegui, Elimination of Fe(III), Zn(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) in Solutions with High HCl Concentrations by Ionic Exchange (Ph.D Thesis, UPV/EHU, Leioa, Spain, 1995).
J. C. Raposo, J. Sanz, O. Zuloaga, M. A. Olazábal, and J. M. Madariaga, The Thermodynamic Model of Inorganic Arsenic Species in Aqueous Solutions. Potentiometric Study of the Hydrolytic Equilibrium of Arsenic Acid, Talanta 57, 849–857 (2002).
G. H. Khoe and R. G. Robins, The Complexation of Iron(III) with Sulfate, Phosphate or Arsenate Ion Sodium Nitrate Medium at 25∘C, J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans: Inorg. Chem. 8, 2015–2021 (1998).
E. Bishop, Indicators (Pergamon Press, Oxford, Great Britain, 1972).
G. H. Jeffery, J. Basset, J. Mendham, and R. C. Denney, Vogel's Textbook of Quantitative Chemical Analysis (6th de Longman, London, Great Britain, 2000).
G. Gran, Determination of the Final Point in the Potentiometric Titrations II, Analyst 77, 661–671 (1952).
F. J. C. Rossotti and H. Rossotti, The Determination of Stability Constants (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1961, 127).
J. C. Raposo, J. Sanz, O. Zuloaga, M. A. Olazabal, and J. M. Madariaga, The Thermodynamic Model of Inorganic Arsenic Species in Aqueous Solutions. Potentiometric Study of the Hydrolytic Equilibrium of Arsenious Acid, J. Solution Chem. 32, 253–264 (2003).
N. Ingri and L. G. Sillén, High Speed Computers as Supplement to Graphical Methods II. Some Computer Programs for Studies of Complex Formation Equilibria, Acta Chem. Scand. 16, 173–191 (1962).
Excel 2000, Microsoft Corporation, Redmond. WA, 2001.
R. Cazallas, M. J. Citores, N. Etxebarria, L. A. Fernández, and J. M. Madariaga, SPECA a Program for the Calculation of Thermodynamic Equilibrium Constants from Spectrophotometric Data, Talanta 41, 1637–1644 (1994).
J. Ferre and F. X. Rius, Equivalence Between Selectivity and Variance Inflation Factors in Multicomponent Analysis, Quím. Anal. 15, 259–262 (1996).
C. F. Baes and R. E. Mesmer, The Hydrolysis of Cations (John Wiley & Sons, New York, USA, 1976).
K. Nakamoto, Infrared Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds (2nd Ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York, USA, 1963).
N. Miller and J. Wilkins, Infrared Spectra and Characteristic Frequencies of Inorganic Ions, Anal. Chem. 24, 1253–1294 (1952).
J. C. Raposo, O. Zuloaga, M. A. Olazábal, and J. M. Madariaga, Study of the Precipitation Equilibria of Arsenate Anion with Calcium and Magnesium in Sodium Perchlorate at 25∘C, Appl. Geochem. 19, 855–862 (2004).
I. Puigdomenech, MEDUSA, Make Equilibrium Diagrams using Sophisticated Algorithms (Department of Inorganic Chemistry, Royal Institute of Technology, S-100 44, Stockholm, Sweden, 1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raposo, J.C., Olazábal, M.A. & Madariaga, J.M. Complexation and Precipitation of Arsenate and Iron Species in Sodium Perchlorate Solutions at 25∘C. J Solution Chem 35, 79–94 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-006-8940-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-006-8940-5