Abstract
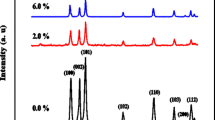
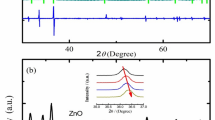
Lithium-doped ZnO (Zn1-xLixO) nanoparticles were fabricated using the hydrothermal process. XRD patterns showed that the Li+ ions substituted into different lattice sites depending on the level of the doping of Li+ into this semiconductor. The Williamson-Hall plots of the same XRD showed that the strains and sizes of the nanoparticles do not changed monotonically. Using the Tau plot to analyze the effects of the Li+ substitution on the optical (UV-Vis absorption) by the nanoparticles, the changes in the observed values of the energy gaps of the different doped semiconductor were seen not to decrease continuously. A VSM (vibrating sample magnetometer) was used to measure the hysteresis loops of our Zn1-xLixO NPs (originally, the nonmagnetic semiconductor XnO doped with the nonmagnetic Li+ ions). Our VSM measurements shows that the saturation magnetization (emu/g) and coercive force of these nanoparticles increased or decreased, respectively, as the level of Li+ doping increased. Photoluminescence emission at ≈ 510 nm showed that the Li+ doping led to the creation of more zinc vacancies, which in turn generates more virtual magnetic moments. Our results support the vacancy-induced d0 electron model of ferromagnetism in nonmagnetic ion-doped ZnO nanoparticles.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Venkatesan, M., Fitzgerald, C.B., Coey, J.M.D.: Unexpected magnetism in a dielectric oxide. Nat. 430, 630 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/430630a
Hong, N.H., Sakai, J., Poirot, N., Brize, V.: Room-temperature ferromagnetism observed in undoped semiconducting and insulating oxide thin films. Phys. Rev. B. 73(13), 132404 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.73.132404
Sundaresan, A., Bhargavi, R., Rangarajan, N., Siddesh, U., Rao, C.N.R.: Ferromagnetism as a universal feature of nanoparticles of the otherwise nonmagnetic oxides. Phys. Rev. B. 74(16), 161306(R) (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.74.161306
Gao, D., Zhang, Z., Fu, J., Xu, Y., Qi, J., Xue, D.: Room temperature ferromagnetism of pure ZnO nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 105(11), 113928 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3143103
Liu, W., Li, W., Hu, Z., Tang, Z., Tang, X.: Effect of oxygen defects on ferromagnetic of undoped ZnO. J. Appl. Phys. 110(1), 013901 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3601107
Zuo, X., Yoon, S.D., Yang, A., Duan, W.H., Vittoria, C., Harris, V.G.: Ferromagnetism in pure wurtzite zinc oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 105(7), 07C508 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3062822
Wang, Q., Sun, Q., Chen, G., Kawazoe, Y., Jena, P.: Vacancy-induced magnetism in ZnO thin films and nanowires. Phys. Rev. B. 77(20), 205411 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.77.205411
Limpijumnong, S., Zhang, S.B., Wei, S.H., Park, C.H.: Doping by large-size-mismatched impurities: the microscopic origin of arsenic- or antimony-doped-type zinc oxide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92(15), 155504 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.155504
Yi, J.B., Lim, C.C., Xing, G.Z., Fan, H.M., Van, L.H., Huang, S.L., Yang, K.S., Huang, X.L., Qin, X.B., Wang, B.Y., Wu, T., Wang, L., Zhang, H.T., Gao, X.Y., Lui, T., Wee, A.T.S., Feng, Y.O., Ding, J.: Ferromagnetism in dilute magnetic semiconductors through defect engineering: Li-doped ZnO. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104(13), 137201 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.137201
Wang, Q.J., Wang, J.B., Zhong, X.L., Tan, Q.H., Hu, Z., Zhou, Y.C.: Magnetism mechanism in ZnO and ZnO doped with nonmagnetic elements X (X = Li, Mg, and Al): a first-principles study. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100(13), 132407 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3698096
Lu, Y.B., Dai, Y., Guo, M., Yu, L., Huang, B.: Investigation of magnetic properties induced by group-V element in doped ZnO. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15(14), 5208 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CP44047H
Lee, J.S., Cha, S.N., Kim, J.M., Nam, H.W., Lee, S.H., Ko, W.B., Wang, K.L., Park, J.G., Hong, J.P.: p-type conduction characteristics of lithium-doped ZnO nanowires. Adv. Mater. 23(36), 4183–4187 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201101376
Park, C.H., Zhang, S.B., Wei, S.H.: Origin of p-type doping difficulty in ZnO: the impurity perspective. Phys. Rev. B. 66(7), 073202 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.66.073202
Wang, D., Zhou, J., Liu, G.: Effect of Li-doped concentration on the structure, optical and electrical properties of p-type ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel method. J. Alloys Comp. 481, 802–805 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.03.111
Awan, S.U., Hasanain, S.K., Bertino, M.F., Jaffari, G.H.: Ferromagnetism in Li doped ZnO nanoparticles: the role of interstitial Li. J. Appl. Phys. 112(10), 103924 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4767364
Gao, H.X., Xia, J.B.: Effect of Li-doping on the magnetic properties of ZnO with Zn vacancies. J. Appl. Phys. 111(9), 093902 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4707888
Awan, S.U., Hasanain, S.K., Anjum, D.H., Awan, M.S., Shah, S.A.: Room temperature p-type conductivity and coexistence of ferroelectric order in ferromagnetic Li doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 116(16), 164109 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4900413
Ghosh, S., Khan, G.G., Das, B., Mandal, K.: Vacancy-induced intrinsic d0 ferromagnetism and photoluminescence in potassium doped ZnO nanowires. J. Appl. Phys. 109(12), 123927 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3601340
Ghosh, S., Khan, G.G., Mandal, K., Thapa, S., Nambissan, P.M.G.: Positron annihilation studies of vacancy-type defects and room temperature ferromagnetism in chemically synthesized Li-doped ZnO nanocrystals. J. Alloys Comp. 590, 396–405 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.12.149
Silambarasan, M., Saravanan, S., Ohtani, N., Soga, T.: Structural and optical studies of pure and Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by simple solution combustion method. Japn. J. Appl. Phys. 53(5S1), 05FB16 (2014). https://doi.org/10.7567/jjap.53.05fb16
Rakkesh, R.A., Balakumar, S.: Structural, electrical transport and optical studies of Li ion doped ZnO nanostructures. Proc. Appl. Ceramics. 8(1), 7–13 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2298/PAC1401007R
Funding
We are grateful for the financial support from Science Achievement Scholarship of Thailand and Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University, for the grant. Finally, we also thank to King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi for the financial support provided by through the KMUTT 55th Anniversary Commemorative Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanyawong, S., Tang, IM., Herng, T.S. et al. Enhancement of Virtual Magnetic Moment Formation in ZnO NPs by Li+ Ion Doping. J Supercond Nov Magn 33, 2851–2859 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05547-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05547-6