Abstract
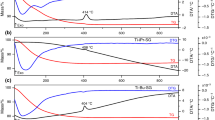
One of the important ways to improve photocatalytic efficiency is to prepare catalyst with enhanced surface area. In this work, titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles having enhanced surface area were synthesized under the interference of SiO2. The mixed oxide, SiO2-TiO2 (10% mol% Si), was prepared by a sol-gel procedure using titanium tetra-n-butoxide as Ti-precursor. The commercial SiO2 nanoparticles were added into the TiO2 sols after hydrolysis. After condensation and calcination heat treatment, the SiO2-TiO2 nanoparticles were obtained. To achieve the purpose of obtaining the high-surface-area TiO2, the SiO2 was removed subsequently by aqueous NaOH solution. The TiO2 products were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA), and by N2 adsorption-desorption isotherm. A fine mesoporous structure was formed for as-prepared TiO2 after calcination at 400∘C and the average pore diameter was about 7 nm. The porous TiO2 products possess mixing phases of anatase and rutile. Phase transformation from anatase to rutile occurred when the samples were calcined. The phase transition temperature is sensitive to the silicon content. The particle size of ∼43 nm remained constant upon calcinations from 500 to 700∘C. The specific surface area was increased up to 66% compared to regular TiO2 samples that were prepared by the similar sol-gel procedure. The porous TiO2 nanostructures exhibited enhanced photocatalytic performance to decompose methylene blue under UV irradiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.-V. Nguyen and O.-B. Yang, Catal. Today 87, 69 (2003).
C. Su, B.-Y. Hong, and C.-M. Tseng, Catal. Today 96, 119 (2004).
A. Scolan and C. Sanchez, Chem. Mater. 10, 3217 (1998).
M. Lal, V. Chhabra, P. Ayyub, and A. Maitra, J. Mater. Res. 13, 1249 (1998).
M. Wu, G. Lin, D. Chen, G. Wang, D. He, S. Feng, and R. Xu, Chem. Mater. 14, 1974 (2002).
C.-C. Wang and J.Y. Ying, Chem. Mater. 11, 3113 (1999).
R.S. Sonawane, S.G. Hegde, and M.K. Dongare, Mater. Chem. Phys. 77, 744 (2002).
W. Que, Y. Zhou, Y.L. Lam, Y.C. Chan, S.D. Cheng, Z. Sun, and C.H. Kam, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Tech. 18, 77 (2000).
M. Hirano, C. Nakahara, K. Ota, O. Tanaike, and M. Inagaki, J. Solid State Chem. 170, 39 (2000).
M. Hirano, C. Nakahara, K. Ota, and M. Inagaki, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85, 1333 (2002).
J. Han and E. Kumacheva, Langmuir 17, 7912 (2001).
Y.-H. Zhang and A. Reller, Mater. Lett. 57, 4108 (2003).
Y. Suyama and A. Kato, J. Ceram. Soc. Japan (Yogyo Kyokai-Shi) 86, 119 (1978).
X. Fu, L.A. Clark, Q. Yang, and M.A. Anderson, Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 647 (1996).
U. Diebold and T.E. Madey, Surf. Sci. Spectra 4, 227 (1996).
H. Zhang, X. Luo, J. Xu, B. Xiang, and D. Yu, J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 14866 (2004).
K.Y. Jung and S.B. Park, Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 25, 249 (2000).
C. Su, C.M. Tseng, L.-F. Chen, B.-H. You, B.C. Hsu, and S.S. Chen, Thin Solid Films (in press).
S.J. Gregg and K.S.W. Sing, Adsorption, Surface Area and Porosity 2nd (Academic Press, 1982).
R.W. Matthews, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1 85, 1291 (1989).
T. Zhang, T. Oyama, A. Aoshima, H. Hidaka, J. Zhao, and N. Serpone, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 140, 163 (2001).
C. Anderson and A.J. Bard, J. Phys. Chem. B 101, 2611 (1997).
M. Hirano, K. Ota, M. Inagaki, and H. Iwata, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 112, 143 (2004).
K. Tanabe, T. Sumiyoshi, K. Shibata, T. Kiyoura, and J. Kitagawa, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 47, 1064 (1974).
C.U.I. Odenbrand, J.G.M. Brandin, and G. Busca, J. Catal. 135, 132 (1992).
Z. Liu and R.J. Davis, J. Phys. Chem. 98, 1253 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, C., Lin, KF., Lin, YH. et al. Preparation and characterization of high-surface-area titanium dioxide by sol-gel process. J Porous Mater 13, 251–258 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-006-8012-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-006-8012-7