Abstract
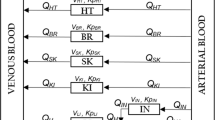
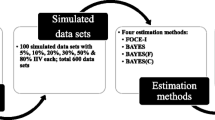
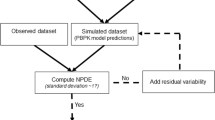
The aim of this study is to present and evaluate an alternative sequential method to perform population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PKPD) analysis. Simultaneous PKPD analysis (SIM) is generally considered the reference method but may be computationally burdensome and time consuming. Evaluation of alternative approaches aims at speeding up the computation time and stabilizing the estimation of the models, while estimating the model parameters with good enough precision. The IPPSE method presented here uses the individual PK parameter estimates and their uncertainty (SE) to propagate the PK information to the PD estimation step, while the IPP method uses the individual PK parameters only and the PPP&D method utilizes the PK data. Data sets (n = 200) with various study designs were simulated according to a one-compartment PK model and a direct Emax PD model. The study design of each dataset was randomly selected. The same PK and PD models were fitted to the simulated observations using the SIM, IPP, PPP&D and IPPSE methods. The performances of the methods were compared with respect to estimation precision and bias, and computation time. Estimated precision and bias for the IPPSE method were similar to that of SIM and PPP&D, while IPP had higher bias and imprecision. Compared with the SIM method, IPPSE saved more computation time (61%) than PPP&D (39%), while IPP remained the fastest method (86% run time saved). The IPPSE method is a promising alternative for PKPD analysis, combining the advantages of the SIM (higher precision and lower bias of parameter estimates) and the IPP (shorter run time) methods.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang L, Beal SL, Sheiner LB (2003) Simultaneous vs. sequential analysis for population PK/PD Data I: best case performance. J Pharmacokin Pharmacodyn 30:387–403
Wade JR, Karlsson MO (1999) Combining PK and PD data during population PKPD analysis, p 8 Abstract 139 [www.page-meeting.org/?abstract=139]
Savic RM, Karlsson MO (2009) Importance of shrinkage in empirical bayes estimates for diagnostics: problems and solutions. AAPS J 11:558–569
Beal S, Sheiner LB, Boeckmann A, Bauer RJ (1989, 2009) NONMEM user’s guides, Icon Development Solutions, Ellicott City, MD, USA
Sheiner L, Wakefield J (1999) Population modelling in drug development. Stat Methods Med Res 8:183–193
Beal S, Sheiner LB, Boeckmann A (1989, 2006) NONMEM user’s guides, Icon Development Solutions, Ellicott City, MD, USA
Lindbom L, Pihlgren P, Jonsson EN (2005) PsN-Toolkit: a collection of computer intensive statistical methods for non-linear mixed effect modeling using NONMEM. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 79:241–257
R Development Core Team (2008) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.R-project.org
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1982) Pharmacokinetics. Marcel Dekker, New York
Mouton JW, Dudley MN, Cars O, Derendorf H, Drusano GL (2005) Standardization of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) terminology for anti-infective drugs: an update. J Antimicrob Chemother 55:601–607
Carnell R (2009) Latin hypercube samples package, http://cran.rproject.org/web/packages/lhs/index.html
Ueckert S, Johansson ÅM, Plan EL, Hooker AC, Karlsson MO (2010) p 19 Abstract 1915 [www.page-meeting.org/?abstract=1915]
Johansson ÅM, Ueckert S, Plan EL, Hooker AC, Karlsson MO (2010) p 19 Abstract 1922[www.page-meeting.org/?abstract=1922]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix A
See Table 4
Appendix B
See Table 5
Appendix C - Extract NONMEM code for PD estimation using the IPPSE method

APPENDIX D - Extract NONMEM code for PD estimation using the PPP&D method

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lacroix, B.D., Friberg, L.E. & Karlsson, M.O. Evaluation of IPPSE, an alternative method for sequential population PKPD analysis. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 39, 177–193 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-012-9240-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-012-9240-x