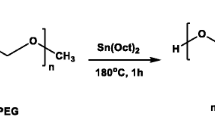
Abstract
Ring opening copolymerization is the most frequently applied reaction for the synthesis of polycaprolactone–polyethylene glycol–polycaprolactone (PCL–PEG–PCL). In this reaction, a number of expensive and toxic organic solvents are being used for the purpose of purification and extraction of the prepared copolymer. Exposure to these organic solvents can cause serious issues to the human health and also impart serious environmental pollution. In the current work, a new, economical and organic solvent free approach was used for the synthesis of triblock copolymer. The results of the current studies confirmed the successful formation of triblock copolymer as revealed by Fourier transform infrared spectra, 13carbon nuclear magnetic resonance (13C-NMR) and proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR). Gel permeation chromatography analysis ensured the homo-distribution of the prepared copolymer. The prepared copolymer was further evaluated as a carrier for the drug loading. Nanomicelles were successfully prepared by the nanoprecipitation technique and exhibited an average size distribution of 42.50 nm and an encapsulation efficiency of 90%. The prepared nanomicelles also exhibited safety at the concentration of 50 µg/ml and a long-term storage stability. All these studies suggested the success of the new simplest and economical method for the synthesis of PCL–PEG–PCL and its subsequent applications as a carrier for fabrication and efficient delivery of hydrophobic drug molecules.
Graphic Abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cabral H, Miyata K, Osada K, Kataoka K (2018) Chem Rev 14:6844–6892
Youn YS, Bae YH (2018) Adv Drug Deliv Rev 130:3–11
Hacker MC, Krieghoff J, Mikos AG (2019) Synthetic polymers. In: Principles of regenerative medicine. Elsevier, New York
Cheng H (2012) An overview of degradable polymers. Degradable polymers and materials: principles and practice. ACS, Washington, DC
Terzopoulou Z, Klonos PA, Kyritsis A, Tziolas A, Avgeropoulos A, Papageorgiou GZ, Bikiaris DN (2019) Polymer 11:1–12
Ganipineni LP, Ucakar B, Joudiou N, Bianco J, Danhier P, Zhao M, Bastiancich C, Gallez B, Danhier F, Preat V (2018) Int J Nanomed 13:4509–4521
Badri W, El Asbahani A, Miladi K, Baraket A, Agusti G, Nazari QA, Errachid A, Fessi H, Elaissari A (2018) J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 3:234–242
Gupta B, Revagade N, Hilborn J (2007) Prog Polym Sci 4:455–482
Guarino V, Gentile G, Sorrentino L, Ambrosio L (2002) EPST 5:1–36
Azevedo M, Reis R, Claase M, Grijpma DW, Feijen J (2003) J Materials Sci Mater Med 2:103–107
Qindeel M, Ahmed N, Khan GM, Rehman AU (2019) Nanomedicine 14:1–20
Sabir F, Asad MI, Qindeel M, Afzal I, Dar MJ, Shah KU, Zeb A, Khan GM, Ahmed N, Din F-U (2019) J Nanomater 2019:1–16
Veronese FM (2005) Pasut G 21:1451–1458
Bunker A (2012) Phys Procedia 34:24–33
Bailon P, Won C-Y (2009) Expert Opin Drug Deliv 1:1–16
Lipka J, Semmler-Behnke M, Sperling RA, Wenk A, Takenaka S, Schleh C, Kissel T, Parak WJ, Kreyling WG (2010) Biomaterials 25:6574–6581
Gong C, Wei X, Wang X, Wang Y, Guo G, Mao Y, Luo F, Qian Z (2010) Nanotechnology 21:215103
Gong C, Shi S, Dong P, Kan B, Gou M, Wang X, Li X, Luo F, Zhao X, Wei Y (2009) Int J Pharm 1–2:89–99
Feng R, Song Z, Zhai G (2012) Int J Nanomed 7:4089
Pazarceviren E, Erdemli O, Keskin D, Tezcaner A (2017) J Biomater Appl 8:1148–1168
Mohanty AK, Jana U, Manna PK, Mohanta GP (2015) Prog Biomater 2–4:89–100
Zhou S, Deng X, Yang H (2003) Biomaterials 20:3563–3570
Pereira ADF, Pereira LGR, Barbosa LADO, Fialho SL, Pereira BG, Patricio PSDO, Pinto FCH, Da Silva GR (2013) Drug Deliv 3–4:168–179
Rostamizadeh K, Manafi M, Nosrati H, Manjili HK, Danafar H (2018) New J Chem 8:5937–5945
Zhang Y, Zhuo R (2005) Biomaterials 33:6736–6742
Liu CB, Gong CY, Huang MJ, Wang JW, Pan YF, Zhang YD, Li GZ, Gou ML, Wang K, Tu MJ (2008) J Biomed Mater Res B 1:165–175
Li R, Li X, Xie L, Ding D, Hu Y, Qian X, Yu L, Ding Y, Jiang X, Liu B (2009) Int J Pharm 1:158–166
Baker EL (1988) Annu Rev Public Health 1:223–232
Dick FD (2006) Occup Environ Med 3:221–226
Spencer PS, Schaumburg HH (1985) Scand J Work Environ Health 21:53–60
Seedorff L, Olsen E (1990) Ann Occup Hyg 4:371–378
Huang J, Kato K, Shibata E, Asaeda N, Takeuchi Y (1994) Nerve-specific marker proteins as indicators of organic solvent neurotoxicity. In Neurobehavioral methods and effects in occupational and environmental health. Elsevier, New York
Qindeel M, Ahmed N, Sabir F, Khan S, Ur-Rehman A (2019) Drug Dev Ind Pharm 4:629–641
Moya ML, Lopez-López M, Lebron JA, Ostos FJ, Perez D, Camacho V, Beck I, Merino-Bohorquez V, Camean M, Madinabeitia N (2019) Pharmaceutics 2:69
Begas E, Papandreou C, Tsakalof A, Daliani D, Papatsibas G, Asprodini E (2014) J Chromatogr Sci 7:590–595
Zhao J, Zhang X, Sun X, Zhao M, Yu C, Lee RJ, Sun F, Zhou Y, Li Y, Teng L (2018) Eur J Pharm Biopharm 12:39–47
Guney A, Gardiner C, McCormack A, Malda J, Grijpma D (2018) Bioengineering 4:99
Danafar H (2017) Jundishapur J Nat Pharm Prod 12:1
Piao L, Dai Z, Deng M, Chen X, Jing X (2003) Polymer 7:2025–2031
Hwang MJ, Suh JM, Bae YH, Kim SW, Jeong B (2005) Biomacromol 2:885–890
Alami-Milani M, Zakeri-Milani P, Valizadeh H, Salehi R, Jelvehgari M (2018) IJBMS 2:153
Brandt JV, Piazza RD, dos Santos CC, Vega-Chacon J, Amantea BE, Pinto GC, Magnani M, Piva HL, Tedesco AC, Primo FL (2019) Colloids Surf B 6:228–234
Dong P, Wang X, Gu Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, Gong C, Luo F, Guo G, Zhao X, Wei Y (2010) Colloids Surf A 1–3:128–134
Manjili HK, Malvandi H, Mousavi MS, Attari E, Danafar H (2018) Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 5:926–936
Acknowledgements
The financial support to accomplish this research by Higher Education Commission of Pakistan is gratefully acknowledged. Maimoona Qindeel was supported by Indigenous Scholarship granted by Higher Education Commission of Pakistan. The authors also acknowledge Mr. Mulazim Hussain Asim for his help regarding chemicals. Department of Microbiology and Department of Chemistry, Quaid-i-Azam University is gratefully acknowledged for support in analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qindeel, M., Ahmed, N., Shah, K.U. et al. New, Environment Friendly Approach for Synthesis of Amphiphilic PCL–PEG–PCL Triblock Copolymer: An Efficient Carrier for Fabrication of Nanomicelles. J Polym Environ 28, 1237–1251 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01683-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01683-1