Abstract
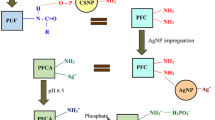
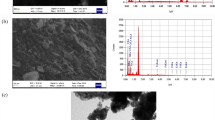
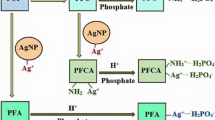
In this study, a novel polyurethane foam (PU) nanocomposite adsorbent based on silane-modified magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4@APTES) is synthesized via a low cost and simple in situ polymerization method for the removal of arsenic ions from aqueous solutions. The chemical structure and surface morphology of the prepared nanoparticles and adsorbent were characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, attenuated total reflection, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry was used to measure the arsenic concentration of the treated solutions. Sorption isotherms models were applied to determine the adsorption mechanism and modeling parameters. The removal capacity of the modified PU foam was at its highest during a contact time of four hours which resulted in a removal capacity of 95%. Kinetic studies were conducted to determine the adsorption capacity and the uptake rate of arsenic. A Pseudo-order model was found to be the best fit model for adsorption. The prepared adsorbent can be separated from the solution by using an external magnet field.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar M, Puri A (2012) Indian J Occup Environ Med 16:40–44
Zhou S, Wang D, Sun H, Chen J, Wu S, Na P (2014) Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1945
Lièvremont D, Bertin PN, Lett MC (2009) Biochimie 91:1229–1237
Malwal D, Gopinath P (2017) Colloid Interface Sci Commun 19:14–19
Zhu J, Wei S, Chen M, Gu H, Rapole SB, Pallavkar S, Ho TC, Hopper J, Guo Z (2013) Adv Powder Technol 24:459–467
Venkateswarlu S, Kumar BN, Prathima B, SubbaRao Y, Jyothi NVV (2014) Arab J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.09.006
Wang J, Xu W, Chen L, Huang X, Liu J (2014) Chem Eng J 251:25–34
Musico YLF, Santos CM, Dalida MLP, Rodrigues DF (2013) J Mater Chem A 1:3789–3796
Yu X, Tong S, Ge M, Zuo J, Cao C, Song W (2013) J Mater Chem A 1:959–965
Sharma M, Kalita P, Garg A, Senapati K (2018) Ecol Environ Sci 8(3):207–210
Cao C, Xiao L, Chen C, Shi X, Cao Q, Gao L (2014) Powder Technol 260:90–97
Hussein FB, Abu-Zahra NH (2016) Water Sci Technol 17:889–896
Hussein FB, Abu-Zahra NH (2016) J Water Process Eng 13:1–5
Hussein FB, Abu-Zahra NHJ (2017) JMMCE 5:298–310
Moghaddam ST, Naimi-Jamal MR (2018) J Thermoplast Compos Mater. https://doi.org/10.1177/0892705718798008
Abu-Zahra N, Gunashekar S (2014) J Res Updates Polym Sci 3:16–25
Gunashekar S, Abu-Zahra N (2016) J Porous Mater 23:801–810
Gunashekar S, Abu-Zahra N (2014) Int J Polym Sci 2014:7
Pandey N, Shukla SK, Singh NB (2017) Nanocomposites 3:47–66
Zhu J, Wei S, Lee IY, Park S, Willis J, Haldolaarachchige N, Young DP, Luoe Z, Guo Z (2012) RSC adv 2:1136–1143
Yang K, Peng H, Wen Y, Li N (2010) Appl Surf Sci 256:3093–3097
Moghaddam ST, Naimi-Jamal MR (2017) 21st International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry Sciforum
Zhou L, Li G, An T, Li Y (2010) Res Chem Intermed 36:277–288
Ramesh A, Hasegawa H, Maki T, Ueda K (2007) Sep Purif Technol 56:90–100
Gong J, Liu T, Wang X, Hu X, Zhang L (2011) Environ Sci Technol 45:6181–6187
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank Dr. Steven Hardcastle at UWM’s Advanced Analysis Facility and Dr. Ana Benko at UWM’s Shimadzu Lab Facility for their support and insights during the characterization and performance analysis of the foam samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamaddoni Moghaddam, S., Naimi-Jamal, M.R., Rohlwing, A. et al. High Removal Capacity of Arsenic from Drinking Water Using Modified Magnetic Polyurethane Foam Nanocomposites. J Polym Environ 27, 1497–1504 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01446-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01446-7