Abstract
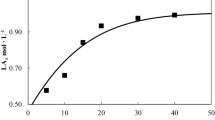
The recycling of used, post-industrial and post-consumer PLA is crucial to reduce both the consumption of renewable resources for the monomer synthesis and the environmental impact related to its production and disposal. Several processes are actually available: among these, there is a particular interest on the chemical recycling of PLA with production of its monomer. The aim of this work is to analyse the PLA dissolution behaviour in different organic solvents (acetone and Ethyl lactate) at different water concentrations in order to optimize the chemical depolymerisation process of PLA. New experimental data are presented and a kinetic model is provided for a first analysis. Preliminary results suggest that acetone based solvents (i.e., acetone water mixtures at various concentrations) are more effective to solubilize the PLA rather than the Ethyl-lactate based solvent. Anyway, an increase of water concentration in the solvent phase, determines both a reduction of the solvent power and a reduction of mass transport coefficient for the two solvents tested.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hakkarainen M (2002) Aliphatic polyesters: abiotic and biotic degradation and degradation products. Adv Polym Sci 157:113
Piemonte V, Gironi F (2011) Bioplastics and petroleum-based plastics: strengths and weaknesses. Energy Source Part A Energy Recover Environ Eff 33:1949–1959
Piemonte V, Gironi F (2012) Bioplastics and GHGs saving: the land use change (LUC) emissions issue. Energy Source Part A Energy Recover Environ Eff 34(21):1995–2003
Piemonte V, Gironi F (2011) Land use change emissions: how green are the bioplastics? Environ Prog Sustain Energy 30(4):685–691
Piemonte V (2011) Bioplastic wastes: the best final disposition for energy saving. J Polym Environ 19:988–994
Gironi F, Piemonte V (2011) Life cycle assessment of PET and PLA bottles for drinking water. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 30(3):459–468
Piemonte V, Sabatini S, Gironi F (2013) Chemical recycling of PLA: a great opportunity towards the sustainable development? J Polym Environ 21(3):640–647
Liang Z, Zhang M, Ni X, Li X, Shen Z (2013) Ring-openingpolymerization of cyclic esters initiated by lithium aggregatecontaining bis(phenolate) and enolate mixed ligands. Inorg Chem Commun 29:145–147
Noda M, Okuyama H (1999) Thermal catalytic depolymerisationof poly(L-lactic acid) oligomer into LL-lactide: effects of Al, Ti, Zn and Zr compounds as catalysts. Chem Pharm Bull 47:467–471
Henton DE, Gruber P, Lunt J, Randall J (2005) Polylactic acidtechnology. In: Mohanty K, Misra M, Drzal LT (eds) Naturalfibers. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Proikakis CS, Mamouzelos NJ, Tarantili PA, Andreopulos AG (2006) Swelling and hydrolytic degradation of poly(d, l-lacticacid) in aqueous solutions. Polym Degrad Stab 91:614–619
Inkinen S (2011) Structural modification of poly(lactic acid) bystep-growth polymerization and Stereocomplexation, Ph.D Thesis, Chemical Engineering Department, Abo Akademi University
Tsuji H, Daimon H, Fujie K (2003) A new strategy for recyclingand preparation of poly(l-lacticacid): hydrolysis in the melt. Biomacromolecules 4:835–840
Tsuji H, Saeki T, Tsukegi T, Daimon H, Fujie K (2008) Comparativestudy on hydrolytic degradation and monomer recoveryof poly(l-lactic acid) in the solid and in the melt. Polym Degrad Stab 93:1956–1963
Brake LD, Subramanian NS (1993) US Patent 5,229,5281993
Brake LD (1993) Recovery of polyhydroxy acids. US Patent 526,461,4
Coszach P, Bogaert JC, Willocq J Chemical recycling of PLA byalcoholysis. WO Patent 2010/118955 A
Xiuyan S, Hui W, Xuequn Y, Fusheng L, Shitao Y, Shiwei L (2014) Hydrolysis of poly(lactic acid) into calcium lactate using ionic liquid [Bmim][OAc] for chemical recycling. Polym Degrad Stab 110:65–70
Plichta A, Lisowska P, Kundys A, Zychewicz A, Debowski M, Florjanczyk Z (2014) Chemical recycling of poly(lactic acid) via controlled degradation with protic (macro)molecules. Polym Degrad Stab 108:288–296
Carne Sanchez A, Collinson SR (2011) The selective recycling of mixed plastic waste of polylactic acid and polyethylene terephthalate by control of process conditions. Eur Polym J 47(10):1970–1976
Codari F, Lazzari S, Soos M, Storti G, Morbidelli M, Moscatelli D (2012) Kinetics of the hydrolytic degradation of poly (lactic acid). Polym Degrad Stab 97:2460e–2466e
Chen GX, Kim HS, Kim ES, Yoon JS (2006) Synthesis of high-molecular-weight poly(l-lactic acid) through the direct condensation polymerization of l-lactic acid in bulk state. Eur Eur 42:468–472
Gruber PR, Hall ES, Kolstad JJ, Iwen ML, Benson RD, Borchardt RL (1992) Continuous process for manufacture of lactide polymers with controlled optical purity. US Patent 514,202,3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gironi, F., Frattari, S. & Piemonte, V. PLA Chemical Recycling Process Optimization: PLA Solubilization in Organic Solvents. J Polym Environ 24, 328–333 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-016-0777-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-016-0777-4