Abstract
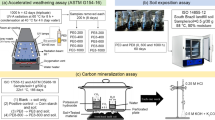
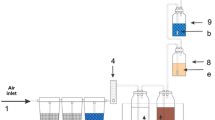
The current paper is aimed at understanding the environmental fate of linear low density polyethylenes (LLDPE) films designed for mulching purposes and loaded with different pro-degradant additives. These were analyzed, upon exposure to natural sunlight for a period intended to mimick a general crop season in the mediterranean region. The selected samples underwent a relatively low extent of degradation as monitored by carbonyl index, molecular weight variation, extractability by solvent, changes in the onset of the decomposition temperature and crystallinity. The tendency to biodegradation of outdoor exposed LLDPE was then assessed under different environmental compartments including soil medium, aqueous medium as well as in axenic culture of white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. That fungus is known to be effective in the degradation of recalcitrant organic materials and plastic items. During the soil burial biodegradation test, lasted for 27 months, samples specimen were withdrawn at time intervals and characterized by means of structural and thermal analysis. These analytical assessments allowed to monitor any progress of oxidative degradation as a direct effect of the incubation in an active microbial environment. Analogous characterizations were carried out at the end of the biodegradation tests in aqueous medium and in P. chrysosporium axenic cultures. Data presented here are in keeping with the initial abiotic oxidation via a free radical chain reaction promoted by a pro-degradant additive acting on hydroperoxides and peroxide moieties present initially in the polymer bulk. This step was followed by a free radical cascade reactions leading to degradation once the oxidation started under relatively mild conditions (sunlight exposure). During the incubation step in soil, the abiotically degraded samples underwent significant variation in the level of oxidation and degradation with respect to the detected starting values. Indications were gained on the synergistic effect of a random fashion microbial metabolization coupled to biotically mediated oxidation of the original abiotically fragmented samples. Similar results were obtained in the biodegradation tests carried out in the aqueous media and in presence of P. chrysosporium axenic cultures. These evidences are suggesting the role of natural occurring microorganisms in promoting both partial oxiditation and degradation of LLDPE samples in combination with contextual mineralization process of the oxidized fragments.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kyrikou I, Demetres B (2007) J Polym Environ 15:125
Briassoulis D (2005) Polym Degrad Stab 88:489
von Elsner B, Briassoulis D, Waaijenberg D et al (2000) J Agr Eng Res 75:1
Dilara PA, Briassoulis D (1998) Polym Test J 17:549
G. Scott (1995) In: Scott G, Gilead D (eds) Introduction to the abiotic degradation of carbon chain polymers. In: Degradable polymers: principles and applications. Chapman & Hall, London
Al-Malaika S, Scott G (1983) In: Allen NS (ed) Degradation and stabilisation of polyolefins. Applied Science Publishers, London
Wiles DM, Scott G (2006) Polym Degrad Stab 91:1581
Billingham NC, Calvert PD, Allen NS (1983) In: Allen NS (ed) Degradation and stabilization of polyolefins. Applied Science Publishers, London
Scott G, Wiles DM (2001) Biomacromolecules 2:615
Scott G (1994) In: Doi Y, Fukuda K (eds) Biodegradable plastics and polymers. Amsterdam, Elsevier, pp 79–91
Scott G, Gilead D (1978) British Patent 1, 588:344
Scott D, Gilead D (1982) In: Scott G (ed) Developments in polymer stabilisation. Applied Science Publishers, London, pp 71–106
Fabbri A (1995) In: Scott G, Gilead D (eds) Degradable polymers: principles and applications, 1st edn. Chapman & Hall, Chapter 10
Guillet JE (1973) US patent 3, pp 753–952
Guillet JE (1973) in: J.E. Guillet ed. Polymers and ecological problems. Polymers with controlled life times. Plenum, New York
Roy PK, Sureka P, Rajagopal C, Chatterejee SN, Choudhary V (2006) Polym Degrad Stab 91:1791
Osawa P, Kurisu N, Nagashima K, Nankano K (1979) J Appl Polym Sci 23:3583
Khabbaz F, Albertsson A-C, Karlsson S (1999) Polym Degrad Stab 63:127
Karlsson S, Hakkarainen M, Albertsson A-C (1997) Macromolecules 30:7721
Roy PK, Surekha P, Rajagopal C, Chatterjee SN, Choudhary V (2005) Polym Degrad Stab 90:577
Setnescu R, Silviu J, Osawa Z (1998) Polym Degrad Stab 60:377
Weiland M, Daro A, David C (1995) Polym Degrad Stab 48:275
Jakubowicz I, Yarahmadi N, Arthurson V (2011) Polym Degrad Stab 96:919
Chiellini E, Corti A, D’Antone S (2007) Polym Degrad Stab 92:1378
Koutny M, Sancelme M, Dabin C, Pichon N, Delort A-M, Lemaire J (2006) Polym Degrad Stab 91:1495
Corti A, Sudhakar M, Vitali M, Imam SH, Chiellini E (2010) Polym Degrad Stab 95:1106
Chiellini E, Corti A, Swift G (2003) Polym Degrad Stab 81:341
ASTM D5272-08 standard practice for outdoor exposure testing of photodegradable plastics, Book of Standards vol. 08.03
Sudhakar M, Doble M, Murthy PS, Venkatesan R (2008) Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 61:203
Leskovics K, Kollár M, Bárczy P (2006) Mater Sci Eng A 419:138
Erlandsson B, Karlsson S, Albertsson A-C (1997) Polym Degrad Stab 55:237
Iiyoshi Y, Tsutsumi Y, Nishida T (1998) J Wood Sci 44:222
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corti, A., Sudhakar, M. & Chiellini, E. Assessment of the Whole Environmental Degradation of Oxo-Biodegradable Linear Low Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) Films Designed for Mulching Applications. J Polym Environ 20, 1007–1018 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-012-0493-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-012-0493-7