Abstract
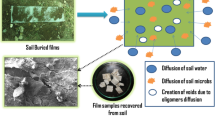
Mesua ferrea L. seed oil (MFLSO) modified polyurethanes blends with epoxy and melamine formaldehyde (MF) resins have been studied for biodegradation with two techniques, namely microbial degradation (broth culture technique) and natural soil burial degradation. In the former technique, rate of increase in bacterial growth in polymer matrix was monitored for 12 days via a visible spectrophotometer at the wavelength of 600 nm using McFarland turbidity as the standard. The soil burial method was performed using three different soils under ambient conditions over a period of 6 months to correlate with natural degradation. Microorganism attack after the soil burial biodegradation of 180 days was realized by the measurement of loss of weight and mechanical properties. Biodegradation of the films was also evidenced by SEM, TGA and FTIR spectroscopic studies. The loss in intensity of the bands at ca. 1735 cm−1 and ca. 1050 cm−1 for ester linkages indicates biodegradation of the blends through degradation of ester group. Both microbial and soil burial studies showed polyurethane/epoxy blends to be more biodegradable than polyurethane/MF blends. Further almost one step degradation in TG analysis suggests degradation for both the blends to occur by breakage of ester links. The biodegradation of the blends were further confirmed by SEM analyses. The study reveals that the modified MFLSO based polyurethane blends deserve the potential to be applicable as “green binders” for polymer composite and surface coating applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weng L, Lu Y, Zhang L (2000) Biomacromolecules 5:1046
Tighzert L, Lu Y, Dole P, Erre D (2005) Polymer 46:9863
Goswami TH, Maity MM (1998) Polym Degrad Stab 61:355
Dutta S, Karak N (2005) Prog Org Coat 53:147
Dutta S, Karak N (2006) Polym Int 55:49
Konwer D, Taylor SE (1989) J Am Oil Chem Soc 66:223
Halim A, El-Sayed MM, Mahmond WM, Davis EM, Coughlin RW (1996) Int Biodet Biodeg 37:69
Darby RT, Kaplan AM (1968) Appl Microbiol 16:900
Yakabe Y, Kitano M (1994) In: Doi Y, Fukuda K, Yakabe Y (eds) Biodegradable polymers and plastics. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 331
Huang SJ (1985) In: Masrk HF, Kroschwitz JI (eds) Encyclopedia of polymer science and engineering. Wiley, New York, pp 220–223
Jana T, Roy BC, Maity S (2000) Polym Degrad Stab 69:79
Solaro R, Corti A, Chiellini E (1998) J Environ Polym Degrad 6:203
Pantake M (1996) In: Heintz E, Sand W, Fleming HC (eds) Microbially influenced corrosion of materials–scientific and technological aspects. Springer, Berlin, pp 379–381
Calmon A, Guillaume S, Maurel VB, Feuilloley P, Silvestre F (1999) J Environ Polym Degrad 7:157
Edwin L, Ashraf PM (2006) Int Biodet Biodeg 57:31
Nakajima-Kambe T, Shigeno-Akustu Y, Nomura N, Onuma F, Nakahara T (1999) Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:134
Dutta S, Karak N (2007) Pigment Res Technol 36:74
Ash RJ, Mauck B, Morgan M (2002) Emerg Infect Dis 8:713
Klugman KP, Friedland IR, Bradley JS (1995) Antimicrob Agents Chemother 39:1988
Lee SI, Yu SC, Lee YS (2001) Polym Degrad Stab 72:81
Mergaert J, Anderson C, Wouters A, Swings J (1994) J Environ Polym Degrad 2:177
Gorna K, Polowinski S, Gogolewski S (2002) J Polym Sci A 40:156
Quian ZY, Li S, He Y, Liu XB (2004) Polym Degrad Stab 84:41
Akmal D, Azizan MN, Majid MIA (2003) Polym Degrad Stab 80:513
Halim A, El-Sayed MM, Mahmond WM, Davis EM, Coughlin RW (1996) Int Biodet Biodeg 37:61
Feldman D, Banu D (2005) J Polym Environ 13:287
Dutta S, Karak N (2005) Euras Chem Technol J 7:251
Dyer JR (1991) Applications of absorption spectroscopy of organic compounds. Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi
Silverstein RM, Webster FX (1998) Spectroscopic identification of organic compounds. Wiley, New York
Sarkar S, Adhikari B (2007) Ind J Chem Technol 14:221
Szycher M (1999) Szycher’s handbook of polyurethanes. CRC Press, Boca Ranton
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude and thanks to the major research project assistance given by DST, India through the grant No. SR/S3/ME/13/2005-SERC-Engg, dated 9th April, 2007. Authors are thankful to Mr. Pronob Gogoi of the department of Environmental Sciences, Tezpur University for his active help in choicing and collecting of soils. Authors are also grateful to Dr. Kishore Baruah and Mr. Rotan Boruah Dept. of Physics, Tezpur University, Assam for offering helping hand during SEM analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dutta, S., Karak, N., Saikia, J.P. et al. Biodegradation of Epoxy and MF Modified Polyurethane Films Derived from a Sustainable Resource. J Polym Environ 18, 167–176 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-010-0161-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-010-0161-8