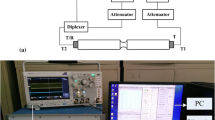
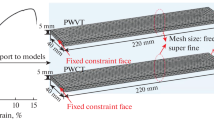
Abstract
Fatigue damage and micro-cracks growth have been proved to be closely related to the nonlinear effect of ultrasonic Lamb waves propagation in materials. In this paper, the relationship among fatigue life, length and width of micro-cracks, and the acoustic nonlinearity parameter was established. The variation of the acoustic nonlinearity parameter caused by fatigue damage was analyzed based on micro-cracks growth. Considering the multimodal nature of nonlinear Lamb waves, we selected the low-frequency mode pairs S0–s0 and S1–s2 to evaluate fatigue damage in 7075 aluminum alloy plates. Both FE simulations and experiments show that the mode pair S1–s2 is more suitable than S0–s0 for the assessment of fatigue damage. It was found that with increasing fatigue cycles, the relative acoustic nonlinearity parameter A2/A12 firstly increases because the micro-cracks length extends while the micro-cracks width does not change much. The relative acoustic nonlinearity parameter A2/A12 reaches its peak at about 60% of the fatigue life. Then the relative acoustic nonlinearity parameter A2/A12 decreases because of the rapid increase in the micro-cracks width. Our findings clarify the mountain-shape curve between the relative acoustic nonlinearity parameter A2/A12 and the fatigue cycles.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meyendorf, N.G., Rosner, H., Kramb, V., et al.: Thermo-acoustic fatigue characterization. Ultrasonics 40(1–8), 427–434 (2002)
Cantrell, J.H.: Substructural organization, dislocation plasticity and harmonic generation in cyclically stressed wavy slip metals. Proc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 460(2043), 757–780 (2004)
Sagar, S.P., Das, S., Parida, N., et al.: Non-linear ultrasonic technique to assess fatigue damage in structural steel. Scr. Mater. 55(2), 199–202 (2006)
Baby, S., Kowmudi, B.N., Omprakash, C.M., et al.: Creep damage assessment in titanium alloy using a nonlinear ultrasonic technique. Scr. Mater. 59(8), 818–821 (2008)
Cantrell, J.H., Salama, K.: Acoustoelastic characterisation of materials. Int. Mater. Rev. 36(1), 125–145 (1991)
Jhang, K.Y., Kim, K.C.: Evaluation of material degradation using nonlinear acoustic effect. Ultrasonics 37(1), 39–44 (1999)
Deng, M.X., Xiang, Y.X., Liu, L.B.: Time-domain analysis and experimental examination of cumulative second-harmonic generation by primary lamb wave propagation. J. Appl. Phys. 109(11), 1829–1836 (2011)
Liu, M.G., Kim, J.Y., Jacobs, L., et al.: Experimental study of nonlinear rayleigh wave propagation in shot-peened aluminum plates-feasibility of measuring residual stress. NDT and E Int. 44(1), 67–74 (2011)
Doerr, C., Lakocy, A., Kim, J.Y., et al.: Evaluation of the heat-affected zone (haz) of a weld joint using nonlinear rayleigh waves. Mater. Lett. 190, 221–224 (2017)
Shen, Y., Cesnik, C.E.: Modeling of nonlinear interactions between guided waves and fatigue cracks using local interaction simulation approach. Ultrasonics. 74, 106123 (2017)
Wang, Y., Guan, R., Lu, Y.: Nonlinear lamb waves for fatigue damage identification in frp-reinforced steel plates. Ultrasonics 80, 87–95 (2017)
Yang, Y., Ng, C.T., Kotousov, A., et al.: Second harmonic generation at fatigue cracks by low-frequency Lamb waves: experimental and numerical studies. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 99, 760–773 (2018)
Jhang, K.Y.: Nonlinear ultrasonic techniques for nondestructive assessment of micro damage in material: a review. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 10(1), 123–135 (2009)
Chillara, V.K., Lissenden, C.J.: Review of nonlinear ultrasonic guided wave nondestructive evaluation: theory, numerics, and experiments. Opt. Eng. 55(1), 011002.1–011002.15 (2016)
Broda, D., Staszewski, W.J., Martowicz, A., et al.: Modelling of nonlinear crack–wave interactions for damage detection based on ultrasound-a review. J. Sound Vib. 333(4), 1097–1118 (2014)
Zhu, W.J., Xiang, Y.X., Liu, C.J., et al.: Fatigue damage evaluation using nonlinear lamb waves with quasi phase-velocity matching at low frequency. Materials. 11(10), 1920 (2018)
Metya, A.K., Ghosh, M., Parida, N., et al.: Effect of tempering temperatures on nonlinear lamb wave signal of modified 9cr-1Mo steel. Mater. Charact. 107, 14–22 (2015)
Xiang, Y.X., Deng, M.X., Xuan, F.Z.: Creep damage characterization using nonlinear ultrasonic guided wave method: a mesoscale model. J. Appl. Phys. 115(4), 273 (2014)
Jhang, K.Y.: Applications of Nonlinear Ultrasonics to the NDE of Material Degradation. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 47(3), 540–548 (2000)
Kim, C.S., Kim, Y.H., Kim, I.H.: Ultrasonic linear and nonlinear parameters in cyclically deformed Cu and Cu-35Zn alloy. Key Eng. Mater. 297–300(Pt3), 2134–2139 (2005)
Deng, M.X., Pei, J.F.: Assessment of accumulated fatigue damage in solid plates using nonlinear Lamb wave approach. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(12), 273–277 (2007)
Sagar, S.P., Metya, A.K., Ghosh, M., et al.: Effect of microstructure on non-linear behavior of ultrasound during low cycle fatigue of pearlitic steels. Mater. ence Eng. A 528(6), 2895–2898 (2011)
Steven, V.B., Kong, C.W., Francis, R.L.: Experimental investigation of second-harmonic lamb wave generation in additively manufactured aluminum. J. Nondestr. Eval. Diagn. Progn. Eng. Syst. 1(4), 041003 (2018)
Pruell, C., Kim, J.Y., Qu, J., et al.: Evaluation of fatigue damage using nonlinear guided waves. Smart Mater. Struct. 18(3), 035003 (2009)
Jin, H.S., Yan, J.J., Li, W.B., et al.: Monitoring of fatigue crack propagation by damage index of ultrasonic guided waves calculated by various acoustic features. Appl. Sci. 9(20), 4254 (2019)
Jingpin, J., Xiangji, M., Cunfu, H., Bin, W.: Nonlinear lamb wave-mixing technique for micro-crack detection in plates. Ndt & E Int. 85, 63–71 (2017)
Wan, X., Zhang, Q., Xu, G., et al.: Numerical simulation of nonlinear lamb waves used in a thin plate for detecting buried micro-cracks. Sensors 15(5), 8528–8546 (2014)
Shen, Y.F., Wang, J.Z., Xu, W.: Nonlinear features of guided wave scattering from rivet hole nucleated fatigue cracks considering the rough contact surface condition. Smart Mater. Struct. 27(10), 105044 (2018)
Wang, J.W., Shen, Y.F., Rao, D.Y., et al.: An instantaneous-baseline multi-indicial nonlinear ultrasonic resonance spectral correlation technique for fatigue crack detection and quantification. Nonlinear Dyn. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-06128-x
Liu, P.P., Jang, J.H., Yang, S.Y., et al.: Fatigue crack detection using dual laser induced nonlinear ultrasonic modulation. Opt. Lasers Eng. 110, 420–430 (2018)
Viktorov, I.A.: Rayleigh and Lamb Waves: Physical Theory and Applications. Plenum Press, New York (1967)
Li, W.B., Cho, Y.H., Achenbach, J.D.: Detection of thermal fatigue in composites by second harmonic Lamb waves. Smart Mater. Struct. 21(8), 85019–85026 (2012)
Sun, M.X., Xiang, Y.X., Deng, M.X., et al.: Scanning non-collinear wave mixing for nonlinear ultrasonic detection and localization of plasticity. NDT E Int. 93, 1–6 (2018)
Zhu, W.J., Xiang, Y.X., Liu, C.J., et al.: A feasibility study on fatigue damage evaluation using nonlinear Lamb waves with group-velocity mismatching. Ultrasonics 90, 18–22 (2018)
Matlack, K.H., Kim, J.Y., Jacobs, L.J., et al.: Experimental characterization of efficient second harmonic generation of lamb wave modes in a nonlinear elastic isotropic plate. J. Appl. Phys. 109(1), 2141 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 12025403, 12004114, U1930202, and 518353003), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2020M671015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, T., Zhu, W., Ma, C. et al. Influence of cyclic-loading induced fatigue micro-crack growth on generation of nonlinear ultrasonic Lamb waves. J Nondestruct Eval 40, 62 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-021-00792-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-021-00792-8