Abstract
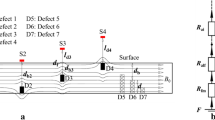
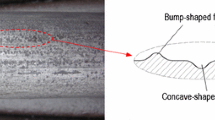
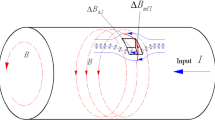
This study focused on the very low-field region of the initial magnetization curve and developed a method to inspect and evaluate reverse side wall-thinning on a ferromagnetic test object by using very low strength magnetized magnetic flux leakage testing. The principle of the method was derived based on the magnetic circuit theory, and a parameter named as differential magnetic-leaking reluctivity was found to be a linear function of the remaining thickness of a ferromagnetic steel plate with thinning on the reverse side. This approach was verified by electromagnetic numerical simulation, and highly sensitive magneto-impedance sensor utilized measurements. Preliminary measurements demonstrated that it is possible to measure and estimate the thicknesses of ferromagnetic plates using very low-level magnetized magnetic flux leakage testing, suggesting the applicability of using this approach to inspect and evaluate over a sufficiently large area reverse side thinning.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
McMaster, R.C., Mclntire, P., Mester, M.L.: Nondestructive Testing Handbook. Vol. 4: Electromagnetic Testing. ASNT, Ohio (1986)
Blitz, J.: Electrical Magnetic Methods of Nondestructive Testing, chapter 3. IOP Publishing, Bristol (1991)
Park, G.S., Park, E.S.: Improvement of the sensor system in magnetic flux leakage-type nondestructive testing (NDT). IEEE Trans. Magn. 38(2), 1277–1280 (2002)
Kikuchi, H., Shimuzu, I., Ara, K., Kamada, Y., Kobayashi, S.: Applicability of Magnetic Flux Leakage Method for Wall Thinning Monitoring in Nuclear Power Plants, Electromagnetic Nondestructive Evaluation (XIV). IOS Press, Amsterdam (2011)
Bisch, A., Dijkstra, F.H., de Raad, J.A.: Magnetic flux and SLOFEC inspection of thick walled components, 15th WCNDT2000. http://www.ndt.net/article/wcndt00/papers/idn352/idn352.htm
Chikazumi, S.: Physics of Ferromagnetism. Vol. 1—Magnetic Properties of Matter. Syokabo, Tokyo (2000)
http://www.aichi-mi.com/e-home/highly-sensitive-magnetometers/type-dm/. Accessed 23 July 2015
Jiles, D.: Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2nd edn. Chapman & Hall, Boca Raton (1998)
http://www.ssil.com/em/EMSolution/ja/index.html. Accessed 23 July 2015
NF Corporation, Bipolar DC Power Supply BP4610 Instruction Manual. http://www.nfcorp.co.jp/english/sup/dl/manual/pp/e_bp4610.pdf
NI PXI/PCI-5922 Specifications. http://www.ni.com/pdf/manuals/374049e.pdf
van Drongelen, W.: Signal Processing for Neuroscientists, chapter 4, p. 55. Academic Press, Cambridge (2008)
Bozorth, R.M.: Ferromagnetism. IEEE Press, New York (2003)
Cheng, W., Saito, Y.: Modeling and analysis of hysteresis by harmonic balance method. J. Appl. Phys. 17, 17D143 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, W. Magnetic Flux Leakage Testing of Reverse Side Wall-Thinning by Using Very Low Strength Magnetization. J Nondestruct Eval 35, 31 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-016-0347-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-016-0347-7