Abstract
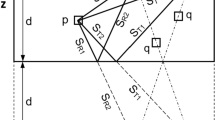
Up to now there is no sufficient technique to detect transverse cracks in austenitic and dissimilar welds which recently are of increasing interest in the integrity surveillance of nuclear power plants as well as in quality control of longitudinally welded pipes. Weld inspection by interpretation of single A-scans will lead to erroneous results due to effects caused by anisotropy and in worst case might leave flaws undetected. Therefore, imaging techniques such as the synthetic aperture focusing technique (SAFT) should be used. If the SAFT algorithm is applied on data taken from austenitic welds, the inhomogeneous, anisotropic structure of these welds has to be taken into account in order to properly attribute amplitudes measured in A-scans to the corresponding coordinates in the region of interest. While this has been investigated in the past, all attempts so far were limited to the imaging of longitudinal cracks which requires a less complicated setup than the imaging of transverse cracks. In this paper we give an outline of our attempts to reconstruct images of transverse cracks in different welds. For this purpose a SAFT program based on ray tracing and a layered structure weld model derived from an empirical model of grain orientations in welds are used. The results of the image reconstruction on experimental data are shown and compared to images obtained by assuming an isotropic homogeneous model. Root reflection and crack tip echo are clearly visible which allows an estimation of size and position of the crack with good accuracy.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spies, M.: Analytical methods for modeling of ultrasonic nondestructive testing of anisotropic media. Ultrasonics 42, 213–219 (2004)
Langenberg, K.J., Hannemann, R., Kaczorowski, T., Marklein, R., Koehler, B., Schurig, C., Walte, F.: Application of modeling techniques for ultrasonic austenitic weld inspection. NDT E Int. 33, 465–480 (2000)
Shlivinski, A., Langenberg, K.J.: Defect imaging with elastic waves in inhomogeneous-anisotropic materials with composite geometries. Ultrasonics 46, 89–104 (2007)
Kröning, M., Bulavinov, A., Reddy, K.M., Walte, F., Dalichow, M.: Improving the inspectability of stainless steel and dissimilar metal welded joints using inverse phase-matching of phased array time-domain signals. In: Proceedings of the 17th WCNDT, Shanghai (2008). Paper 451
Pudikov, S., Bulavinov, A., Pinchuk, R.: Innovative ultrasonic testing (UT) of nuclear components by sampling phased array with 3D visualization of inspection results. In: DGZfP Proceedings BB 125 (8th International Conference on NDE in Relation to Structural Integrity for Nuclear and Pressurised Components 2010), Berlin (2011). Paper Th. 2.C.6
Matthies, K., et al.: Ultraschallprüfung von austenitischen Werkstoffen. DGZfP, Berlin (2009)
Langenberg, K.J., Marklein, R., Mayer, K.: Theoretische Grundlagen der zerstörungsfreien Materialprüfung mit Ultraschall. Oldenburg, München (2009)
Ogilvy, J.A.: Ultrasonic reflection properties of planar defects within austenitic welds. Ultrasonics 26(6), 318–327 (1988)
Spies, M., Rieder, H.: Synthetic aperture focusing of ultrasonic inspection data to enhance the probability of detection in strongly attenuating materials. NDT E Int. 43, 425–431 (2010)
Müller, W., Schmitz, V., Schäfer, G.: Reconstruction by the synthetic aperture focussing technique (SAFT). Nucl. Eng. Des. 94, 393–404 (1986)
Schmitz, V., Chaklov, S., Müller, W.: Experiences with the synthetic aperture focusing technique in the field. Ultrasonics 38, 731–738 (2000)
Spies, M., Jager, W.: Synthetic aperture focusing for defect reconstruction in anisotropic media. Ultrasonics 41, 125–131 (2003)
Silk, M.G.: A computer model for ultrasonic propagation in complex orthotropic structures. Ultrasonics 19(5), 208–212 (1981)
Rokhlin, S.I., Bolland, T.K., Adler, L.: Reflection and refraction of elastic waves on a plane interface between two generally anisotropic media. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 79(4), 906–918 (1986)
Ogilvy, J.A.: Computerized ultrasonic ray tracing in austenitic steel. NDT Int. 18(2), 67–77 (1985)
Ogilvy, J.A.: A layered media model for ray propagation in anisotropic inhomogeneous materials. Appl. Math. Model. 14, 237–247 (1990)
Ogilvy, J.A.: Ultrasonic beam profiles and beam propagation in an austenitic weld using a theoretical ray tracing model. Ultrasonics 24(6), 337–347 (1986)
Ogilvy, J.A.: On the use of focused beams in austenitic welds. Br. J. Non-Destr. Test. 29(4), 238–246 (1987)
Harker, A.H., Ogilvy, J.A.: Coherent wave propagation in inhomogeneous materials: a comparison of theoretical models. Ultrasonics 29(3), 235–244 (1991)
Spies, M.: Modeling of transducer fields in inhomogeneous anisotropic materials using Gaussian beam superposition. NDT E Int. 33, 155–162 (2000)
Moysan, J., Apfel, A., Corneloup, G., Chassignole, B.: Modelling the grain orientation of austenitic stainless steel multipass welds to improve ultrasonic assessment of structural integrity. Int. J. Press. Vessels Piping 80, 77–85 (2003)
Moysan, J., Apfel, A., Corneloup, G., Chassignole, B.: Simulations of the influence of the grains orientations on ultrasounds. In: Proceedings of the 16th WCNDT, Montreal (2004). Paper 414
Apfel, A., Moysan, J., Corneloup, G., Fouquet, T., Chassignole, B.: Coupling an ultrasonic propagation code with a model of the heterogeneity of multipass welds to simulate ultrasonic testing. Ultrasonics 43, 447–456 (2005)
Connolly, G.D., Lowe, M.J.S., Temple, J.A.G., Rokhlin, S.I.: Correction of ultrasonic array images to improve reflector sizing and location in inhomogeneous materials using a ray-tracing model. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 127(5), 2802–2812 (2010)
Spencer, G.H., Murty, M.V.R.K.: General ray-tracing procedure. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 41, 672–678 (1961)
Schmitz, V., Walte, F., Chaklov, S.V.: 3D ray tracing in austenite materials. NDT E Int. 32, 201–213 (1999)
Spies, M., Rieder, H., Dillhöfer, A., Dugan, S.: Abbildung und Größenbestimmung von Spannungskorrosionsrissen in austenitischen Komponenten mittels Synthetischer Apertur Fokus Technik. In: Berichtsband DGZfP-Jahrestagung 2011, Bremen (2011). Paper Di. 3.A.1
Munikoti, V., Brekow, G., Tessaro, U., Erhard, A.: Ultrasonic testing for transverse discontinuities in dissimilar welds: theoretical and experimental results. Mater. Eval. 62(11), 1148–1153 (2004)
Kolkoori, S., Rahman, M.U., Prager, J.: Effect of columnar grain orientation on ultrasonic plane wave energy reflection and transmission behaviour in anisotropic austenitic weld materials. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 31(3), 253–269 (2012)
Bazulin, A.E., Bazulin, E.G., Koval, D.A.: Application of the TANDEM scheme for reconstructing flaw images by the SAFT method. Russ. J. Nondestruct. Test. 45(7), 452–463 (2009)
Schenk, G., Völz, U., Dohse, E., Bauer, L.: COMPASXL—outstanding number of channels with a new phased array system. In: Proceedings of ECNDT, Berlin, vol. 11, pp. 25–29 (2006)
Kitze, J., Prager, J., Boehm, R., Völz, U., Montag, H.J.: SAFT—reconstruction in ultrasonic immersion technique using phased array transducers. In: Review of Progress in QNDE AIP Conf. Proc., Burlington, vol. 1430, pp. 825–832 (2012)
Vandermeulen, W., Scibetta, M., Leenaers, A., Schuurmans, J., Gérard, R.: Measurement of the young modulus anisotropy of a reactor pressure vessel cladding. J. Nucl. Mater. 372, 249–255 (2008)
Rinkevich, A.B., Smorodinskii, Y.G.: Elastic waves in an inhomogeneous austenite plate in the model of a transversely isotropic medium. Russ. J. Nondestruct. Test. 37(7), 475–495 (2001)
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out at the Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung; BAM), Berlin, Germany supported by the GRS (Gesellschaft für Anlagen- und Reaktorsicherheit).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Höhne, C., Kolkoori, S., Rahman, MU. et al. SAFT Imaging of Transverse Cracks in Austenitic and Dissimilar Welds. J Nondestruct Eval 32, 51–66 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-012-0159-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-012-0159-3