Abstract
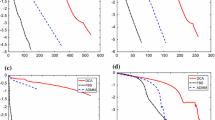
In this paper, we consider the linearly constrained \(\ell _1\)–\(\ell _2\) minimization, and we propose an accelerated Bregman method for solving this minimization problem. The proposed method is based on the extrapolation technique, which is used in accelerated proximal gradient methods proposed by Nesterov and others, and on the equivalence between the Bregman method and the augmented Lagrangian method. A convergence rate of \(\mathcal{O }(\frac{1}{k^2})\) is proved for the proposed method when it is applied to solve a more general linearly constrained nonsmooth convex minimization problem. We numerically test our proposed method on a synthetic problem from compressive sensing. The numerical results confirm that our accelerated Bregman method is faster than the original Bregman method.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baraniuk, R.: Compressive sensing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 24, 118–121 (2007)
Barzilai, J., Borwein, J.: 1988 Two point step size gradient methods. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 8, 141–148 (1988)
Beck, A., Teboulle, M.: Fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2, 183–202 (2009)
Boyd, S., Vandenberghe, L.: Convex Optimization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Bunea, R., She, Y., Ombao, H., Gongvatana, A., Devlin, K., Cohen, R.: Penalized least squares regression methods and applications to neuroimaging. NeuroImage 55, 1519–1527 (2011)
Cai, J., Osher, S., Shen, Z.: Convergence of the linearized Bregman iteration for \(\ell _1\)-norm minimization. Math. Comput. 78, 2127–2136 (2009)
Cai, J., Osher, S., Shen, Z.: Linearized Bregman iterations for compressed sensing. Math. Comput. 78, 1515–1536 (2009)
Candés, E., Romberg, J.: \(\ell _1\)-MAGIC : recovery of sparse signals via convex programming. Technical Report, Caltech (2005)
Candés, E., Romberg, J., Tao, T.: Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52, 489–509 (2006)
Candés, E., Tao, T.: Decoding by linear programming. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 51, 4203–4215 (2005)
Candés, E., Tao, T.: Near optimal signal recovery from random projections: Universal encoding strategies? IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52, 5406–5425 (2006)
Candés, E., Wakin, M.: An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 21, 21–30 (2008)
Chen, S., Donoho, D., Saunders, M.: Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 20, 33–61 (1999)
Cho, S., Kim, H., Oh, S., Kim, K., Park, T.: Elastic-net regularization approaches for genome-wide association studies of rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Proc. 3, S25 (2009)
De Mol, C., De Vito, E., Rosasco, L.: Elastic net regularization in learning theory. J. Complex. 25, 201–230 (2009)
Friedlander, M., Tseng, P.: Exact regularization of convex programs. SIAM J. Opt. 18, 1326–1350 (2007)
Friedman, J., Hastie, T., Hofling, H., Tibshirani, R.: Pathwise coordinate optimization. Ann. Appl. Stat. 1, 302–332 (2007)
Hale, E., Yin, W., Zhang, Y.: Fixed-point continuation applied to compressed sensing: Implementation and numerical experiments. J. Comput. Math. 28, 170–194 (2010)
He, B. and Yuan, X. : The acceleration of augmented Lagrangian method for linearly constrained optimization. optimization online. http://www.optimization-online.org/DB_FILE/2010/10/2760.pdf (2010).
Hestenes, M.: Multiplier and gradient methods. J. Opt. Theory Appl. 4, 303–320 (1969)
Hiriart-Urruty, J.-B., Lemarechal, C.: Convex Analysis and Minimization Algorithms: Part 1: Fundamentals. Springer, New York (1996)
Huang, B., Ma, S., Goldfarb, D.: Accelerated linearized Bregman method. J. Sci. Comput. (2012). doi: 10.1007/s10915-012-9592-9
Li, Q., Lin, N.: The Bayesian elastic net. Bayesian. Analysis 5, 151–70 (2010)
Liu, D., Nocedal, J.: On the limited memory method for large scale optimization. Math. Program. B 45, 503–528 (1989)
Nesterov, Y.: A method of solving a convex programming problem with convergence rate \({\cal O}(\frac{1}{k^2})\). Sov. Math. Doklady 27, 372–376 (1983)
Osher, S., Burger, M., Goldfarb, D., Xu, J., Yin, W.: An iterative regularization method for total variation-based image restoration. SIAM J. Multiscale Model. Simul. 4, 460–489 (2005)
Osher, S., Mao, Y., Dong, B., Yin, W.: Fast Linearized Bregman iteration for compressive sensing and sparse denoising. Commun. Math. Sci. 8, 93–111 (2010)
Rockafellar, R.T., Wets, R.J.-B.: Variational Analysis. Springer, New York (1998)
Saunders, M. : PDCO. Matlab software for convex optimization. Technical report, Stanford University. http://www.stanford.edu/group/SOL/software/pdco.html (2002)
Sra, S., Tropp. J. A.: Row-action methods for compressive sensing, vol 3. In ICASSP, Toulouse, pp. 868–871 (2006).
Van den Breg, E., Friedlander, M.P.: Probing the pareto frontier for basis pursuit solutions. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 31, 890–912 (2009)
Yang, Y., Moller, M., Osher, S. : A dual split Bregman method for fast L1 minimization. Math. Comput. (to appear)
Yin, W.: Analysis and generalizations of the linearized Bregman method. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 3, 856–877 (2010)
Yin, W., Osher, S., Goldfarb, D., Darbon, J.: Bregman iterative algorithms for \(\ell _1\)-minimization with applications to compressive sensing. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 1, 143–168 (2008)
Zuo, H., Hastie, T.: Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 67, 301–320 (2005)
Acknowledgments
Sangwoon Yun and Hyenkyun Woo were supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology(2012R1A1A1006406 and 2010-0510-1-3 respectively). Myungjoo Kang was supported by the NRF funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology(2012001766).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, M., Yun, S., Woo, H. et al. Accelerated Bregman Method for Linearly Constrained \(\ell _1\)–\(\ell _2\) Minimization. J Sci Comput 56, 515–534 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-013-9686-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-013-9686-z