Abstract
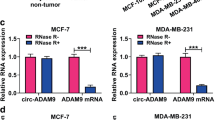
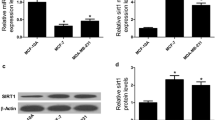
Breast cancer is one of the most common malignancies worldwide. Circular RNAs (CircRNAs) were revealed to be implicated in the development of breast cancer. In this research, we aimed to investigate the role and underlying mechanism of circ_0008500 in the development and radiosensitivity of breast cancer. Using real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) and western blot, we found that hsa_circ_0008500 (circ_0008500) and profilin 2 (PFN2) were increased, while microRNA-758-3p (miR-758-3p) was decreased in breast cancer tissues and cells. Cell viability, the number of colonies, proliferation and apoptosis were detected using CCK-8, colony formation, EdU assays and flow cytometry, respectively. Dual-luciferase reporter and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays were devoted to test the interaction between miR-758-3p and circ_0008500 or PFN2. The results showed that circ_0008500 knockdown inhibited cell growth, and facilitated cell apoptosis and radiosensitivity in breast cancer cells in vitro. Moreover, circ_0008500 regulated PFN2 expression by sponging miR-758-3p. Functionally, circ_0008500 knockdown regulated cell behaviors and radiosensitivity by targeting miR-758-3p to downregulate PFN2 expression in vitro. Additionally, in vivo tumor formation assay and immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay demonstrated that circ_0008500 knockdown enhanced the radiosensitivity and repressed tumor growth in vivo. In conclusion, circ_0008500 inhibition promoted the radiosensitivity and restrained the development of breast cancer by downregulating PFN2 expression via targeting miR-758-3p.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harbeck N, Penault-Llorca F, Cortes J, Gnant M, Houssami N, Poortmans P, et al. Breast cancer Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5(1):66.
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424.
Benvenuto M, Focaccetti C, Izzi V, Masuelli L, Modesti A, Bei R. Tumor antigens heterogeneity and immune response-targeting neoantigens in breast cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021;72:65–75.
DeSantis CE, Ma J, Gaudet MM, Newman LA, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, et al. (2019) Breast cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(6):438–51.
Mahvi DA, Liu R, Grinstaff MW, Colson YL, Raut CP. Local Cancer Recurrence: The Realities, Challenges, and Opportunities for New Therapies. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):488–505.
Zheng R, Yao Q, Xie G, Du S, Ren C, Wang Y, et al. TAT-ODD-p53 enhances the radiosensitivity of hypoxic breast cancer cells by inhibiting Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Oncotarget. 2015;6(19):17417–29.
Sio TT, Joliat GR, Jrebi N. Multidisciplinary approach to uncommon, widely metastatic breast cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(6):846–50.
Anastasiadou E, Jacob LS, Slack FJ. Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18(1):5–18.
Yin Y, Long J, He Q, Li Y, Liao Y, He P, et al. Emerging roles of circRNA in formation and progression of cancer. J Cancer. 2019;10(21):5015–21.
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature. 2013;495(7441):333–8.
Wang J, Du Y, Liu X, Cho WC, Yang Y. MicroRNAs as regulator of signaling networks in metastatic colon cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2015:823620.
Hammond SM. An overview of microRNAs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;87:3–14.
Memczak S, Papavasileiou P, Peters O, Rajewsky N. Identification and characterization of circular RNAs as a new class of putative biomarkers in human blood. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0141214.
Wu D, Jia H, Zhang Z, Li S. Circ-PRMT5 promotes breast cancer by the miR-509–3p/TCF7L2 axis activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. J Gene Med 2021;23(2):e3300.
Du S, Zhang P, Ren W, Yang F, Du C. Circ-ZNF609 Accelerates the Radioresistance of Prostate Cancer Cells by Promoting the Glycolytic Metabolism Through miR-501-3p/HK2 Axis. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:7487–99.
Jin Y, Su Z, Sheng H, Li K, Yang B, Li S. Circ_0086720 knockdown strengthens the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer via mediating the miR-375/SPIN1 axis. Neoplasma. 2021;68(1):96–107.
Zhang T, Wu DM, Deng SH, Han R, Liu T, Li J, et al. RNAseq profiling of circRNA expression in radiation-treated A549 cells and bioinformatics analysis of radiation-related circRNA-miRNA networks. Oncol Lett. 2020;20(2):1557–66.
Bakhtari N, Mozdarani H, Salimi M, Omranipour R. Association study of miR-22 and miR-335 expression levels and G2 assay related inherent radiosensitivity in peripheral blood of ductal carcinoma breast cancer patients. Neoplasma. 2021;68(1):190–9.
Perez-Anorve IX, Gonzalez-De la Rosa CH, Soto-Reyes E, Beltran-Anaya FO, Del Moral-Hernandez O, Salgado-Albarran M, et al. New insights into radioresistance in breast cancer identify a dual function of miR-122 as a tumor suppressor and oncomiR. Mol Oncol. 2019;13(5):1249–67.
Zhang X, Li Y, Wang D, Wei X. miR-22 suppresses tumorigenesis and improves radiosensitivity of breast cancer cells by targeting Sirt1. Biol Res. 2017;50(1):27.
Sun Q, Liu T, Yuan Y, Guo Z, Xie G, Du S, et al. MiR-200c inhibits autophagy and enhances radiosensitivity in breast cancer cells by targeting UBQLN1. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(5):1003–12.
Xu JZ, Shao CC, Wang XJ, Zhao X, Chen JQ, Ouyang YX, et al. circTADA2As suppress breast cancer progression and metastasis via targeting miR-203a-3p/SOCS3 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(3):175.
Hu Y, Song Q, Zhao J, Ruan J, He F, Yang X, et al. Identification of plasma hsa_circ_0008673 expression as a potential biomarker and tumor regulator of breast cancer. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020;34(9):e23393.
Xu Z, Li P, Fan L, Wu M. The Potential Role of circRNA in Tumor Immunity Regulation and Immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2018;9:9.
Yu CY, Kuo HC. The emerging roles and functions of circular RNAs and their generation. J Biomed Sci. 2019;26(1):29.
Yu D, Li Y, Ming Z, Wang H, Dong Z, Qiu L, et al. Comprehensive circular RNA expression profile in radiation-treated HeLa cells and analysis of radioresistance-related circRNAs. PeerJ 2018;6:e5011.
Chen Y, Yuan B, Wu Z, Dong Y, Zhang L, Zeng Z. Microarray profiling of circular RNAs and the potential regulatory role of hsa_circ_0071410 in the activated human hepatic stellate cell induced by irradiation. Gene. 2017;629:35–42.
Pan G, Mao A, Liu J, Lu J, Ding J, Liu W. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0061825 (circ-TFF1) contributes to breast cancer progression through targeting miR-326/TFF1 signalling. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(2):e12720.
Zhang XY, Mao L. Circular RNA Circ_0000442 acts as a sponge of MiR-148b-3p to suppress breast cancer via PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Gene. 2021;766:145113.
Zhao X, Dong W, Luo G, Xie J, Liu J, Yu F. Silencing of hsa_circ_0009035 Suppresses Cervical Cancer Progression and Enhances Radiosensitivity through MicroRNA 889–3p-Dependent Regulation of HOXB7. Mol Cell Biol. 2021;41(6):e0063120.
Cai F, Li J, Zhang J, Huang S. Knockdown of Circ_CCNB2 Sensitizes Prostate Cancer to Radiation Through Repressing Autophagy by the miR-30b-5p/KIF18A Axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2019.3538.
Li L, Jiang Z, Zou X, Hao T. Exosomal circ_IFT80 Enhances Tumorigenesis and Suppresses Radiosensitivity in Colorectal Cancer by Regulating miR-296-5p/MSI1 Axis. Cancer Manag Res. 2021;13:1929–41.
Wang L, Peng X, Lu X, Wei Q, Chen M, Liu L. Inhibition of hsa_circ_0001313 (circCCDC66) induction enhances the radio-sensitivity of colon cancer cells via tumor suppressor miR-338-3p: Effects of cicr_0001313 on colon cancer radio-sensitivity. Pathol Res Pract. 2019;215(4):689–96.
Ji C, Hu J, Wang X, Zheng W, Deng X, Song H, et al. Hsa_circ_0053063 inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation via hsa_circ_0053063/hsa-miR-330-3p/PDCD4 axis. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(7):9627–45.
Zhang HD, Jiang LH, Hou JC, Zhou SY, Zhong SL, Zhu LP, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0072995 promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion through sponge for miR-30c-2-3p. Epigenomics. 2018;10(9):1229–42.
Liu Y, Lu C, Zhou Y, Zhang Z, Sun L. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0008039 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and migration by regulating miR-432-5p/E2F3 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;502(3):358–63.
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495(7441):384–8.
Xie H, Wang J, Wang B. Circular RNA Circ_0003221 Promotes Cervical Cancer Progression by Regulating miR-758-3p/CPEB4 Axis. Cancer Manag Res. 2021;13:5337–50.
Hu X, Li Y, Kong D, Hu L, Liu D, Wu J. Long noncoding RNA CASC9 promotes LIN7A expression via miR-758-3p to facilitate the malignancy of ovarian cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(7):10800–8.
Wu X, Chen B, Shi H, Zhou J, Zhou F, Cao J, et al. miR-758-3p suppresses human bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting NOTCH2. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(5):4273–8.
Wu Y, Liu Y. miR-758-3p Inhibits Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma and Predicts Favorable Prognosis. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:9285–95.
Zhang XH, Li BF, Ding J, Shi L, Ren HM, Liu K, et al. LncRNA DANCR-miR-758-3p-PAX6 Molecular Network Regulates Apoptosis and Autophagy of Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:4073–84.
Cai Y, Yu X, Hu S, Yu J. A brief review on the mechanisms of miRNA regulation. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2009;7(4):147–54.
Pandey DK, Chaudhary B. Evolutionary expansion and structural functionalism of the ancient family of profilin proteins. Gene. 2017;626:70–86.
Cui XB, Zhang SM, Xu YX, Dang HW, Liu CX, Wang LH, et al. PFN2, a novel marker of unfavorable prognosis, is a potential therapeutic target involved in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Transl Med. 2016;14(1):137.
Jiang M, Qiu N, Xia H, Liang H, Li H, Ao X. Long noncoding RNA FOXD2AS1/miR1505p/PFN2 axis regulates breast cancer malignancy and tumorigenesis. Int J Oncol. 2019;54(3):1043–52.
Liu J, Wu Y, Wang Q, Liu X, Liao X, Pan J. Bioinformatic analysis of PFN2 dysregulation and its prognostic value in head and neck squamous carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2018;14(5):449–59.
Zhao ZY, Zhao YC, Liu W. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 regulates the progression and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells via miR-140-5p/PFN2 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(22):9781–92.
Ling Y, Cao Q, Liu Y, Zhao J, Zhao Y, Li K, et al. Profilin 2 (PFN2) promotes the proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of triple negative breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer. 2021;28(2):368–78.
Zhao Y, Zhong R, Deng C, Zhou Z. Circle RNA circABCB10 Modulates PFN2 to Promote Breast Cancer Progression, as Well as Aggravate Radioresistance Through Facilitating Glycolytic Metabolism Via miR-223-3p. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2021;36(6):477–90.
Kim HS, Kim SC, Kim SJ, Park CH, Jeung HC, Kim YB, et al. Identification of a radiosensitivity signature using integrative metaanalysis of published microarray data for NCI-60 cancer cells. BMC Genomics. 2012;13:348.
Funding
This study was supported by Scientific Research Fund Project of Hebei Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission. (No. 20201103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no financial conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, D., Shen, D., Liu, Z. et al. Circ_0008500 Knockdown Improves Radiosensitivity and Inhibits Tumorigenesis in Breast Cancer Through the miR-758-3p/PFN2 Axis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 27, 37–52 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-022-09514-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-022-09514-w