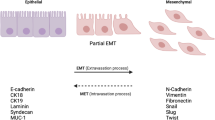
Abstract
Since its initial description, the interconversion between epithelial and mesenchymal cells (designed as epithelial-mesenchymal or mesenchymal-epithelial transition, EMT or MET, respectively) has received special attention since it provides epithelial cells with migratory features. Different studies using cell lines have identified cytokines, intercellular signaling elements and transcriptional factors capable of regulating this process. Particularly, the identification of Snail family members as key effectors of EMT has opened new ways for the study of this cellular process. In this article we discuss the molecular pathways that control EMT, showing a very tight and interdependent regulation. We also analyze the contribution of EMT and Snail genes in the process of tumorigenesis using the mammary gland as cellular model.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- MET:
-
Mesenchymal-epithelial transition
- CDH1:
-
E-Cadherin gene
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylases
- PRC2:
-
Polycomb group of proteins
- SBE:
-
Smad binding element
- SCP:
-
C-terminal domain phosphatase
- Ppa:
-
Partner of Paired
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
- Egr1:
-
Early growth response 1 gene
- MAPK1:
-
Mitogen activated protein kinase 1
- HMGA2:
-
High mobility group A2
- ER-α:
-
Estrogen Receptor α
- CSN2:
-
COP9 signalosome 2
- TEB:
-
Terminal end buds
- FSP:
-
Fibroblast specific protein
References
Hay ED. Theory for epithelial-mesenchymal transformation based on the "fixed cortex" cell motility model. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;14(4):455–7.
Arnoux V, Come C, Kusewitt D, Savagner P. Cutaneous wound healing: a partial and reversible EMT. Rise and fall of epithelial phenotype: Concepts of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. In: Savagner P, editor.: Landes Biosciences; 2004
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell. 2008;133(4):704–15.
Morel AP, Lievre M, Thomas C, Hinkal G, Ansieau S, Puisieux A. Generation of breast cancer stem cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 2008;3(8):e2888.
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R, Thompson EW. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol. 2006;172(7):973–81.
Klymkowsky MW, Savagner P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: a cancer researcher’s conceptual friend and foe. Am J Pathol. 2009;174(5):1588–93.
Perl AK, Wilgenbus P, Dahl U, Semb H, Christofori G. A causal role for E-cadherin in the transition from adenoma to carcinoma. Nature. 1998;392(6672):190–3.
Frixen UH, Behrens J, Sachs M, Eberle G, Voss B, Warda A, et al. E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion prevents invasiveness of human carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1991;113(1):173–85.
Vleminckx K, Vakaet Jr L, Mareel M, Fiers W, van Roy F. Genetic manipulation of E-cadherin expression by epithelial tumor cells reveals an invasion suppressor role. Cell. 1991;66(1):107–19.
Birchmeier W, Behrens J. Cadherin expression in carcinomas: role in the formation of cell junctions and the prevention of invasiveness. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1198(1):11–26.
Ohkubo T, Ozawa M. The transcription factor Snail downregulates the tight junction components independently of E-cadherin downregulation. J Cell Sci. 2004;117(Pt 9):1675–85.
Solanas G, Porta-de-la-Riva M, Agusti C, Casagolda D, Sanchez-Aguilera F, Larriba MJ, et al. E-cadherin controls beta-catenin and NF-kappaB transcriptional activity in mesenchymal gene expression. J Cell Sci. 2008;121(Pt 13):2224–34.
Hennig G, Behrens J, Truss M, Frisch S, Reichmann E, Birchmeier W. Progression of carcinoma cells is associated with alterations in chromatin structure and factor binding at the E-cadherin promoter in vivo. Oncogene. 1995;11(3):475–84.
Hennig G, Lowrick O, Birchmeier W, Behrens J. Mechanisms identified in the transcriptional control of epithelial gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(1):595–602.
Kamei T, Matozaki T, Takai Y. Mechanisms of cell adhesion and migration. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 1999;26(9):1359–66.
Le TL, Yap AS, Stow JL. Recycling of E-cadherin: a potential mechanism for regulating cadherin dynamics. J Cell Biol. 1999;146(1):219–32.
Yang J, Weinberg RA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: at the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 2008;14(6):818–29.
Kinch MS, Clark GJ, Der CJ, Burridge K. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the adhesions of ras-transformed breast epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1995;130(2):461–71.
Shtutman M, Levina E, Ohouo P, Baig M, Roninson IB. Cell adhesion molecule L1 disrupts E-cadherin-containing adherens junctions and increases scattering and motility of MCF7 breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66(23):11370–80.
Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, Dominguez D, Monfar M, Baulida J, et al. The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2(2):84–9.
Cano A, Perez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I, Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, et al. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2(2):76–83.
Wang X, Zheng M, Liu G, Xia W, McKeown-Longo PJ, Hung MC, et al. Kruppel-like factor 8 induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition and epithelial cell invasion. Cancer Res. 2007;67(15):7184–93.
Hajra KM, Chen DY, Fearon ER. The SLUG zinc-finger protein represses E-cadherin in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62(6):1613–8.
Comijn J, Berx G, Vermassen P, Verschueren K, van Grunsven L, Bruyneel E, et al. The two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein SIP1 downregulates E-cadherin and induces invasion. Mol Cell. 2001;7(6):1267–78.
Eger A, Aigner K, Sonderegger S, Dampier B, Oehler S, Schreiber M, et al. DeltaEF1 is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin and regulates epithelial plasticity in breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2005;24(14):2375–85.
Perez-Moreno MA, Locascio A, Rodrigo I, Dhondt G, Portillo F, Nieto MA, et al. A new role for E12/E47 in the repression of E-cadherin expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(29):27424–31.
Ellenberger T, Fass D, Arnaud M, Harrison SC. Crystal structure of transcription factor E47: E-box recognition by a basic region helix-loop-helix dimer. Genes Dev. 1994;8(8):970–80.
Vandewalle C, Van Roy F, Berx G. The role of the ZEB family of transcription factors in development and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66(5):773–87.
Vandewalle C, Comijn J, De Craene B, Vermassen P, Bruyneel E, Andersen H, et al. SIP1/ZEB2 induces EMT by repressing genes of different epithelial cell-cell junctions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33(20):6566–78.
Grooteclaes ML, Frisch SM. Evidence for a function of CtBP in epithelial gene regulation and anoikis. Oncogene. 2000;19(33):3823–8.
Grooteclaes M, Deveraux Q, Hildebrand J, Zhang Q, Goodman RH, Frisch SM. C-terminal-binding protein corepresses epithelial and proapoptotic gene expression programs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(8):4568–73.
Shi Y, Sawada J, Sui G, Affar el B, Whetstine JR, Lan F, et al. Coordinated histone modifications mediated by a CtBP co-repressor complex. Nature. 2003;422(6933):735–8.
Alpatov R, Munguba GC, Caton P, Joo JH, Shi Y, Hunt ME, et al. Nuclear speckle-associated protein Pnn/DRS binds to the transcriptional corepressor CtBP and relieves CtBP-mediated repression of the E-cadherin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(23):10223–35.
Nieto MA. The snail superfamily of zinc-finger transcription factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3(3):155–66.
Bolos V, Peinado H, Perez-Moreno MA, Fraga MF, Esteller M, Cano A. The transcription factor Slug represses E-cadherin expression and induces epithelial to mesenchymal transitions: a comparison with Snail and E47 repressors. J Cell Sci. 2003;116(Pt 3):499–511.
Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A. Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(6):415–28.
Vega S, Morales AV, Ocana OH, Valdes F, Fabregat I, Nieto MA. Snail blocks the cell cycle and confers resistance to cell death. Genes Dev. 2004;18(10):1131–43.
Kajita M, McClinic KN, Wade PA. Aberrant expression of the transcription factors snail and slug alters the response to genotoxic stress. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(17):7559–66.
Escriva M, Peiro S, Herranz N, Villagrasa P, Dave N, Montserrat-Sentis B, et al. Repression of PTEN phosphatase by Snail1 transcriptional factor during gamma radiation-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28(5):1528–40.
Kudo-Saito C, Shirako H, Takeuchi T, Kawakami Y. Cancer metastasis is accelerated through immunosuppression during Snail-induced EMT of cancer cells. Cancer Cell. 2009;15(3):195–206.
Peinado H, Ballestar E, Esteller M, Cano A. Snail mediates E-cadherin repression by the recruitment of the Sin3A/histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1)/HDAC2 complex. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(1):306–19.
Herranz N, Pasini D, Diaz VM, Franci C, Gutierrez A, Dave N, et al. Polycomb complex 2 is required for E-cadherin repression by the Snail1 transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28(15):4772–81.
Langer EM, Feng Y, Zhaoyuan H, Rauscher 3rd FJ, Kroll KL, Longmore GD. Ajuba LIM proteins are snail/slug corepressors required for neural crest development in Xenopus. Dev Cell. 2008;14(3):424–36.
Nibu Y, Zhang H, Levine M. Interaction of short-range repressors with Drosophila CtBP in the embryo. Science. 1998;280(5360):101–4.
Vincent T, Neve EP, Johnson JR, Kukalev A, Rojo F, Albanell J, et al. A SNAIL1-SMAD3/4 transcriptional repressor complex promotes TGF-beta mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(8):943–50.
Stemmer V, de Craene B, Berx G, Behrens J. Snail promotes Wnt target gene expression and interacts with beta-catenin. Oncogene. 2008;27(37):5075–80.
Zhou BP, Deng J, Xia W, Xu J, Li YM, Gunduz M, et al. Dual regulation of Snail by GSK-3beta-mediated phosphorylation in control of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6(10):931–40.
Dominguez D, Montserrat-Sentis B, Virgos-Soler A, Guaita S, Grueso J, Porta M, et al. Phosphorylation regulates the subcellular location and activity of the snail transcriptional repressor. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(14):5078–89.
Wu Y, Evers BM, Zhou BP. Small C-terminal domain phosphatase enhances snail activity through dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(1):640–8.
MacPherson MR, Molina P, Souchelnytskyi S, Wernstedt C, Martin-Perez J, Portillo F, et al. Phosphorylation of serine 11 and serine 92 as new positive regulators of human Snail1 function: potential involvement of casein kinase-2 and the cAMP-activated kinase protein kinase A. Mol Biol Cell. 2009;21(2):244–53.
Yang Z, Rayala S, Nguyen D, Vadlamudi RK, Chen S, Kumar R. Pak1 phosphorylation of snail, a master regulator of epithelial-to-mesenchyme transition, modulates snail’s subcellular localization and functions. Cancer Res. 2005;65(8):3179–84.
Peinado H, Iglesias de la Cruz MC, Olmeda D, Csiszar K, Fong KS, Vega S, et al. A molecular role for lysyl oxidase-like 2 enzyme in snail regulation and tumor progression. EMBO J. 2005;24(19):3446–58.
Vinas-Castells R, Beltran M, Valls G, Gomez I, Garcia JM, Montserrat-Sentis B, et al. The hypoxia-controlled FBXL14 ubiquitin ligase targets SNAIL1 for proteasome degradation. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(6):3794–805.
Hemavathy K, Guru SC, Harris J, Chen JD, Ip YT. Human Slug is a repressor that localizes to sites of active transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20(14):5087–95.
Vernon AE, LaBonne C. Slug stability is dynamically regulated during neural crest development by the F-box protein Ppa. Development. 2006;133(17):3359–70.
Wang SP, Wang WL, Chang YL, Wu CT, Chao YC, Kao SH, et al. p53 controls cancer cell invasion by inducing the MDM2-mediated degradation of Slug. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(6):694–704.
Kataoka H, Murayama T, Yokode M, Mori S, Sano H, Ozaki H, et al. A novel snail-related transcription factor Smuc regulates basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor activities via specific E-box motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28(2):626–33.
Wu WS, Heinrichs S, Xu D, Garrison SP, Zambetti GP, Adams JM, et al. Slug antagonizes p53-mediated apoptosis of hematopoietic progenitors by repressing puma. Cell. 2005;123(4):641–53.
Conacci-Sorrell M, Simcha I, Ben-Yedidia T, Blechman J, Savagner P, Ben-Ze’ev A. Autoregulation of E-cadherin expression by cadherin-cadherin interactions: the roles of beta-catenin signaling, Slug, and MAPK. J Cell Biol. 2003;163(4):847–57.
Arnoux V, Nassour M, L’Helgoualc’h A, Hipskind RA, Savagner P. Erk5 controls Slug expression and keratinocyte activation during wound healing. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19(11):4738–49.
Grotegut S, von Schweinitz D, Christofori G, Lehembre F. Hepatocyte growth factor induces cell scattering through MAPK/Egr-1-mediated upregulation of Snail. EMBO J. 2006;25(15):3534–45.
Thuault S, Tan EJ, Peinado H, Cano A, Heldin CH, Moustakas A. HMGA2 and Smads co-regulate SNAIL1 expression during induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(48):33437–46.
Palmer MB, Majumder P, Green MR, Wade PA, Boss JM. A 3′ enhancer controls snail expression in melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67(13):6113–20.
Peiro S, Escriva M, Puig I, Barbera MJ, Dave N, Herranz N, et al. Snail1 transcriptional repressor binds to its own promoter and controls its expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(7):2077–84.
Freeman M. Feedback control of intercellular signalling in development. Nature. 2000;408(6810):313–9.
Sakai D, Suzuki T, Osumi N, Wakamatsu Y. Cooperative action of Sox9, Snail2 and PKA signaling in early neural crest development. Development. 2006;133(7):1323–33.
Moreno-Bueno G, Cubillo E, Sarrio D, Peinado H, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Villa S, et al. Genetic profiling of epithelial cells expressing E-cadherin repressors reveals a distinct role for Snail, Slug, and E47 factors in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2006;66(19):9543–56.
Robert G, Gaggioli C, Bailet O, Chavey C, Abbe P, Aberdam E, et al. SPARC represses E-cadherin and induces mesenchymal transition during melanoma development. Cancer Res. 2006;66(15):7516–23.
Huber MA, Azoitei N, Baumann B, Grunert S, Sommer A, Pehamberger H, et al. NF-kappaB is essential for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in a model of breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest. 2004;114(4):569–81.
Julien S, Puig I, Caretti E, Bonaventure J, Nelles L, van Roy F, et al. Activation of NF-kappaB by Akt upregulates Snail expression and induces epithelium mesenchyme transition. Oncogene. 2007;26(53):7445–56.
Barbera MJ, Puig I, Dominguez D, Julien-Grille S, Guaita-Esteruelas S, Peiro S, et al. Regulation of Snail transcription during epithelial to mesenchymal transition of tumor cells. Oncogene. 2004;23(44):7345–54.
Bachelder RE, Yoon SO, Franci C, de Herreros AG, Mercurio AM. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is an endogenous inhibitor of Snail transcription: implications for the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol. 2005;168(1):29–33.
Kuphal S, Poser I, Jobin C, Hellerbrand C, Bosserhoff AK. Loss of E-cadherin leads to upregulation of NFkappaB activity in malignant melanoma. Oncogene. 2004;23(52):8509–19.
Jamora C, Lee P, Kocieniewski P, Azhar M, Hosokawa R, Chai Y, et al. A signaling pathway involving TGF-beta2 and snail in hair follicle morphogenesis. PLoS Biol. 2005;3(1):e11.
Dhasarathy A, Kajita M, Wade PA. The transcription factor snail mediates epithelial to mesenchymal transitions by repression of estrogen receptor-alpha. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21(12):2907–18.
Fujita N, Jaye DL, Kajita M, Geigerman C, Moreno CS, Wade PA. MTA3, a Mi-2/NuRD complex subunit, regulates an invasive growth pathway in breast cancer. Cell. 2003;113(2):207–19.
De Craene B, van Roy F, Berx G. Unraveling signalling cascades for the Snail family of transcription factors. Cell Signal. 2005;17(5):535–47.
Guaita S, Puig I, Franci C, Garrido M, Dominguez D, Batlle E, et al. Snail induction of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in tumor cells is accompanied by MUC1 repression and ZEB1 expression. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(42):39209–16.
Beltran M, Puig I, Pena C, Garcia JM, Alvarez AB, Pena R, et al. A natural antisense transcript regulates Zeb2/Sip1 gene expression during Snail1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Genes Dev. 2008;22(6):756–69.
Palmer HG, Gonzalez-Sancho JM, Espada J, Berciano MT, Puig I, Baulida J, et al. Vitamin D(3) promotes the differentiation of colon carcinoma cells by the induction of E-cadherin and the inhibition of beta-catenin signaling. J Cell Biol. 2001;154(2):369–87.
Yook JI, Li XY, Ota I, Hu C, Kim HS, Kim NH, et al. A Wnt-Axin2-GSK3beta cascade regulates Snail1 activity in breast cancer cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8(12):1398–406.
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S, Itzykson RA, Come C, et al. Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell. 2004;117(7):927–39.
Wu Y, Deng J, Rychahou PG, Qiu S, Evers BM, Zhou BP. Stabilization of snail by NF-kappaB is required for inflammation-induced cell migration and invasion. Cancer Cell. 2009;15(5):416–28.
Hinck L, Silberstein GB. Key stages in mammary gland development: the mammary end bud as a motile organ. Breast Cancer Res. 2005;7(6):245–51.
Kouros-Mehr H, Werb Z. Candidate regulators of mammary branching morphogenesis identified by genome-wide transcript analysis. Dev Dyn. 2006;235(12):3404–12.
Elston CW, Ellis IO. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 1991;19(5):403–10.
Halachmi S, DeMarzo AM, Chow NH, Halachmi N, Smith AE, Linn JF, et al. Genetic alterations in urinary bladder carcinosarcoma: evidence of a common clonal origin. Eur Urol. 2000;37(3):350–7.
Saegusa M, Hashimura M, Kuwata T, Okayasu I. Requirement of the Akt/beta-catenin pathway for uterine carcinosarcoma genesis, modulating E-cadherin expression through the transactivation of slug. Am J Pathol. 2009;174(6):2107–15.
Derksen PW, Liu X, Saridin F, van der Gulden H, Zevenhoven J, Evers B, et al. Somatic inactivation of E-cadherin and p53 in mice leads to metastatic lobular mammary carcinoma through induction of anoikis resistance and angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2006;10(5):437–49.
Moll R, Mitze M, Frixen UH, Birchmeier W. Differential loss of E-cadherin expression in infiltrating ductal and lobular breast carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1993;143(6):1731–42.
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406(6797):747–52.
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(19):10869–74.
Dontu G, El-Ashry D, Wicha MS. Breast cancer, stem/progenitor cells and the estrogen receptor. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2004;15(5):193–7.
Cho KB, Cho MK, Lee WY, Kang KW. Overexpression of c-myc induces epithelial mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Lett. 2010 Feb 7, [Epub ahead of print] doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2010.01.013
Smith AP, Verrecchia A, Faga G, Doni M, Perna D, Martinato F, et al. A positive role for Myc in TGFbeta-induced Snail transcription and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene. 2009;28(3):422–30.
Storci G, Sansone P, Trere D, Tavolari S, Taffurelli M, Ceccarelli C, et al. The basal-like breast carcinoma phenotype is regulated by SLUG gene expression. J Pathol. 2008;214(1):25–37.
Sarrio D, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Hardisson D, Cano A, Moreno-Bueno G, Palacios J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer relates to the basal-like phenotype. Cancer Res. 2008;68(4):989–97.
Williams DJ, Cohen C, To TV, Page AJ, Lawson D, Sussman ZM, et al. Triple-negative breast carcinoma in women from Vietnam and the United States: characterization of differential marker expression by tissue microarray. Hum Pathol. 2009;40(8):1176–81.
Nakshatri H, Srour EF, Badve S. Breast cancer stem cells and intrinsic subtypes: controversies rage on. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009;4(1):50–60.
DiMeo TA, Anderson K, Phadke P, Fan C, Perou CM, Naber S, et al. A novel lung metastasis signature links Wnt signaling with cancer cell self-renewal and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2009;69(13):5364–73.
Ansieau S, Bastid J, Doreau A, Morel AP, Bouchet BP, Thomas C, et al. Induction of EMT by twist proteins as a collateral effect of tumor-promoting inactivation of premature senescence. Cancer Cell. 2008;14(1):79–89.
Come SE, Buzdar AU, Arteaga CL, Bissell MJ, Brown MA, Ellis MJ, et al. Proceedings of the third international conference on recent advances and future directions in endocrine manipulation of breast cancer: conference summary statement. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(1 Pt 2):327S–30S.
Franci C, Takkunen M, Dave N, Alameda F, Gomez S, Rodriguez R, et al. Expression of Snail protein in tumor-stroma interface. Oncogene. 2006;25(37):5134–44.
Franci C, Gallen M, Alameda F, Baro T, Iglesias M, Virtanen I, et al. Snail1 protein in the stroma as a new putative prognosis marker for colon tumours. PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5595.
Herschkowitz JI, Simin K, Weigman VJ, Mikaelian I, Usary J, Hu Z, et al. Identification of conserved gene expression features between murine mammary carcinoma models and human breast tumors. Genome Biol. 2007;8(5):R76.
Trimboli AJ, Fukino K, de Bruin A, Wei G, Shen L, Tanner SM, et al. Direct evidence for epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68(3):937–45.
Jechlinger M, Grunert S, Tamir IH, Janda E, Ludemann S, Waerner T, et al. Expression profiling of epithelial plasticity in tumor progression. Oncogene. 2003;22(46):7155–69.
Liu M, Casimiro MC, Wang C, Shirley LA, Jiao X, Katiyar S, et al. p21CIP1 attenuates Ras- and c-Myc-dependent breast tumor epithelial mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell-like gene expression in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(45):19035–9.
Chen YC, Chen YW, Hsu HS, Tseng LM, Huang PI, Lu KH, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 is a putative marker for cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;385(3):307–13.
Kurrey NK, Jalgaonkar SP, Joglekar AV, Ghanate AD, Chaskar PD, Doiphode RY, et al. Snail and slug mediate radioresistance and chemoresistance by antagonizing p53-mediated apoptosis and acquiring a stem-like phenotype in ovarian cancer cells. Stem Cells. 2009;27(9):2059–68.
Moody SE, Perez D, Pan TC, Sarkisian CJ, Portocarrero CP, Sterner CJ, et al. The transcriptional repressor Snail promotes mammary tumor recurrence. Cancer Cell. 2005;8(3):197–209.
Brabletz T, Jung A, Spaderna S, Hlubek F, Kirchner T. Opinion: migrating cancer stem cells—an integrated concept of malignant tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(9):744–9.
Rowe RG, Li XY, Hu Y, Saunders TL, Virtanen I, Garcia de Herreros A, et al. Mesenchymal cells reactivate Snail1 expression to drive three-dimensional invasion programs. J Cell Biol. 2009;184(3):399–408.
Ota I, Li XY, Hu Y, Weiss SJ. Induction of a MT1-MMP and MT2-MMP-dependent basement membrane transmigration program in cancer cells by Snail1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(48):20318–23.
Karnoub AE, Dash AB, Vo AP, Sullivan A, Brooks MW, Bell GW, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2007;449(7162):557–63.
Chua KN, Ma J, Thiery JP. Targeted therapies in control of EMT in carcinoma and fibrosis. Drug Discov Today. 2008;4:261–7.
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K, Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA, et al. Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening. Cell. 2009;138(4):645–59.
Acknowledgements
We thank Rosa Viñas for her help in the correction of this manuscript. Research in AGH laboratory is funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science (SAF2006-00339), Fundació La Marató, Instituto Carlos III (RD06/0020/0040) and Generalitat de Catalunya (2009SGR121). Research in PS laboratory is supported by institutional funds (INSERM U896), by Foundation de France (2009 006685) and Ligue Nationale contra le Cancer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Herreros, A.G., Peiró, S., Nassour, M. et al. Snail Family Regulation and Epithelial Mesenchymal Transitions in Breast Cancer Progression. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 15, 135–147 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-010-9179-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-010-9179-8