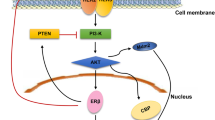
Abstract
After the discovery that depriving certain breast tumors of estrogen promoted tumor regression, therapeutic strategies aimed at depriving tumors of this hormone were developed. The tumorigenic properties of estrogen are regulated through the estrogen receptor-α (ER), making understanding the mechanisms that activate this receptor highly relevant. In addition to estrogen activating the ER, other growth factor pathways, such as the insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), can activate the ER. This review will examine the interaction between these two pathways. Estrogen can activate the growth stimulatory properties of the IGF pathway via ER’s genomic and non-genomic functions. Further, blockade of ER function can inhibit IGF-mediated mitogenesis and blocking IGF action can inhibit estrogen stimulation of breast cancer cells. Collectively, these observations suggest that the two growth regulatory pathways are tightly linked and a more thorough understanding of the mechanism of this crosstalk could lead to improved therapeutic strategies in breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ER:
-
estrogen receptor
- IGF:
-
insulin-like growth factor
- IGF1R:
-
type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor
- EGF:
-
epidermal growth factor
- EGFR:
-
epidermal growth factor receptor
- MAPK:
-
mitogen activated protein kinase
- SRC:
-
steroid receptor co-activator
- IRS:
-
insulin receptor substrate
- ERE:
-
estrogen response element
- SERM:
-
selective estrogen receptor modulator
- PI3K:
-
PI3 kinase
- IGFBP:
-
IGF-binding protein
References
Beatson G. On the treatment of inoperable cases of carcinoma of the mamma: suggestions for a new method of treatment with illustrative cases. Lancet 1896;2:162–7. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)72384-7.
Allen E, Doisy EA. An ovarian hormone: Preliminary reports on its localization, extraction and partial purification and action in test animals. JAMA 1923;81:810–21.
Jensen EV, Jacobson HI. Basic guides to the mechanism of estrogen action. Recent Prog Horm Res 1962;18:387–414.
Green S, Walter P, Kumar V, Krust A, Bornert JM, Argos P, et al. Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature 1986;320:134–9. doi:10.1038/320134a0.
O’Malley BW, Conneely OM. Orphan receptors: in search of a unifying hypothesis for activation. Mol Endocrinol. 1992;6:1359–61. doi:10.1210/me.6.9.1359.
Parker MG. Steroid and related receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993;5:499–504. doi:10.1016/0955-0674(93)90016-J.
Lees JA, Fawell SE, Parker MG. Identification of two transactivation domains in the mouse oestrogen receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17:5477–88. doi:10.1093/nar/17.14.5477.
Kuiper GG, Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA. Cloning of a novel receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:5925–30. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.12.5925.
Osborne CK, Schiff R, Fuqua SA, Shou J. Estrogen receptor: current understanding of its activation and modulation. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:4338s–42s. discussion 411s–2s.
Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell 1989;56:335–44. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7.
Klein-Hitpass L, Ryffel GU, Heitlinger E, Cato AC. A 13 bp palindrome is a functional estrogen responsive element and interacts specifically with estrogen receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16:647–63. doi:10.1093/nar/16.2.647.
Kushner PJ, Agard DA, Greene GL, Scanlan TS, Shiau AK, Uht RM, et al. Estrogen receptor pathways to AP-1. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000;74:311–7. doi:10.1016/S0960-0760(00)00108-4.
Safe S. Transcriptional activation of genes by 17 beta-estradiol through estrogen receptor-Sp1 interactions. Vitam Horm. 2001;62:231–52. doi:10.1016/S0083-6729(01)62006-5.
Song RX, Barnes CJ, Zhang Z, Bao Y, Kumar R, Santen RJ. The role of Shc and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in mediating the translocation of estrogen receptor alpha to the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:2076–81. doi:10.1073/pnas.0308334100.
MacGregor JI, Jordan VC. Basic guide to the mechanisms of antiestrogen action. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;50:151–96.
Paige LA, Christensen DJ, Gron H, Norris JD, Gottlin EB, Padilla KM, et al. Estrogen receptor (ER) modulators each induce distinct conformational changes in ER alpha and ER beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:3999–4004. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.7.3999.
Knowlden JM, Hutcheson IR, Barrow D, Gee JM, Nicholson RI. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer: a supporting role to the epidermal growth factor receptor. Endocrinology 2005;146:4609–18. doi:10.1210/en.2005-0247.
Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Creighton CJ, Qin L, Tsimelzon A, Huang S, et al. Tamoxifen resistance in breast tumors is driven by growth factor receptor signaling with repression of classic estrogen receptor genomic function. Cancer Res. 2008;68:826–33. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2707.
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Ovarian ablation for early breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;CD000485.
Wakeling AE, Dukes M, Bowler J. A potent specific pure antiestrogen with clinical potential. Cancer Res. 1991;51:3867–73.
Pietras RJ. Biologic basis of sequential and combination therapies for hormone-responsive breast cancer. Oncologist 2006;11:704–17. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.11-7-704.
Favoni RE, de Cupis A, Ravera F, Cantoni C, Pirani P, Ardizzoni A, et al. Expression and function of the insulin-like growth factor I system in human non-small-cell lung cancer and normal lung cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1994;56:858–66. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910560618.
Hassan AB, Macaulay VM. The insulin-like growth factor system as a therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2002;13:349–56. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdf096.
Lee AV, Hilsenbeck SG, Yee D. IGF system components as prognostic markers in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998;47:295–302. doi:10.1023/A:1005915420341.
LeRoith D, Roberts CT Jr. Insulin-like growth factors and their receptors in normal physiology and pathological states. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 1993;6:251–5.
Ciampolillo A, De Tullio C, Giorgino F. The IGF-I/IGF-I receptor pathway: implications in the pathophysiology of thyroid cancer. Curr Med Chem 2005;12:2881–91. doi:10.2174/092986705774454715.
Tanno S, Mitsuuchi Y, Altomare DA, Xiao GH, Testa JR. AKT activation up-regulates insulin-like growth factor I receptor expression and promotes invasiveness of human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61:589–93.
Alexia C, Fallot G, Lasfer M, Schweizer-Groyer G, Groyer A. An evaluation of the role of insulin-like growth factors (IGF) and of type-I IGF receptor signalling in hepatocarcinogenesis and in the resistance of hepatocarcinoma cells against drug-induced apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004;68:1003–15. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2004.05.029.
Bonnette SG, Hadsell DL. Targeted disruption of the IGF-I receptor gene decreases cellular proliferation in mammary terminal end buds. Endocrinology 2001;142:4937–45. doi:10.1210/en.142.11.4937.
Kasuya J, Paz IB, Maddux BA, Goldfine ID, Hefta SA, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y. Characterization of human placental insulin-like growth factor-I/insulin hybrid receptors by protein microsequencing and purification. Biochemistry 1993;32:13531–6. doi:10.1021/bi00212a019.
Pandini G, Vigneri R, Costantino A, Frasca F, Ippolito A, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, et al. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor overexpression in breast cancers leads to insulin/IGF-I hybrid receptor overexpression: evidence for a second mechanism of IGF-I signaling. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:1935–44.
Frasca F, Pandini G, Scalia P, Sciacca L, Mineo R, Costantino A, et al. Insulin receptor isoform A, a newly recognized, high-affinity insulin-like growth factor II receptor in fetal and cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:3278–88.
Denley A, Carroll JM, Brierley GV, Cosgrove L, Wallace J, Forbes B, et al. Differential activation of insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 by insulin-like growth factor-activated insulin receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27:3569–77. doi:10.1128/MCB.01447-06.
Power RF, Mani SK, Codina J, Conneely OM, O’Malley BW. Dopaminergic and ligand-independent activation of steroid hormone receptors. Science 1991;254:1636–9. doi:10.1126/science.1749936.
Ignar-Trowbridge DM, Pimentel M, Parker MG, McLachlan JA, Korach KS. Peptide growth factor cross-talk with the estrogen receptor requires the A/B domain and occurs independently of protein kinase C or estradiol. Endocrinology 1996;137:1735–44. doi:10.1210/en.137.5.1735.
Ignar-Trowbridge DM, Teng CT, Ross KA, Parker MG, Korach KS, McLachlan JA. Peptide growth factors elicit estrogen receptor-dependent transcriptional activation of an estrogen-responsive element. Mol Endocrinol. 1993;7:992–8. doi:10.1210/me.7.8.992.
Ignar-Trowbridge DM, Nelson KG, Bidwell MC, Curtis SW, Washburn TF, McLachlan JA, et al. Coupling of dual signaling pathways: epidermal growth factor action involves the estrogen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:4658–62. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.10.4658.
Katzenellenbogen BS, Norman MJ. Multihormonal regulation of the progesterone receptor in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells: interrelationships among insulin/insulin-like growth factor-I, serum, and estrogen. Endocrinology 1990;126:891–8.
Katzenellenbogen BS. Estrogen receptors: bioactivities and interactions with cell signaling pathways. Biol Reprod. 1996;54:287–93. doi:10.1095/biolreprod54.2.287.
Lee AV, Weng CN, Jackson JG, Yee D. Activation of estrogen receptor-mediated gene transcription by IGF-I in human breast cancer cells. J Endocrinol. 1997;152:39–47. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1520039.
Panno ML, Salerno M, Pezzi V, Sisci D, Maggiolini M, Mauro L, et al. Effect of oestradiol and insulin on the proliferative pattern and on oestrogen and progesterone receptor contents in MCF-7 cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1996;122:745–9. doi:10.1007/BF01209122.
El-Tanani MK, Green CD. Two separate mechanisms for ligand-independent activation of the estrogen receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1997;11:928–37. doi:10.1210/me.11.7.928.
Bunone G, Briand PA, Miksicek RJ, Picard D. Activation of the unliganded estrogen receptor by EGF involves the MAP kinase pathway and direct phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1996;15:2174–83.
Kato S, Endoh H, Masuhiro Y, Kitamoto T, Uchiyama S, Sasaki H, et al. Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science 1995;270:1491–4. doi:10.1126/science.270.5241.1491.
Tremblay GB, Tremblay A, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Labrie F, et al. Cloning, chromosomal localization, and functional analysis of the murine estrogen receptor beta. Mol Endocrinol. 1997;11:353–65. doi:10.1210/me.11.3.353.
Simoncini T, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Brazil DP, Ley K, Chin WW, Liao JK. Interaction of oestrogen receptor with the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature 2000;407:538–41. doi:10.1038/35035131.
Ruan W, Catanese V, Wieczorek R, Feldman M, Kleinberg DL. Estradiol enhances the stimulatory effect of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) on mammary development and growth hormone-induced IGF-I messenger ribonucleic acid. Endocrinology 1995;136:1296–302. doi:10.1210/en.136.3.1296.
Richards RG, DiAugustine RP, Petrusz P, Clark GC, Sebastian J. Estradiol stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and insulin receptor substrate-1 in the uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:12002–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.21.12002.
Stewart AJ, Johnson MD, May FE, Westley BR. Role of insulin-like growth factors and the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor in the estrogen-stimulated proliferation of human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:21172–8.
Kleinman D, Karas M, Roberts CT Jr, LeRoith D, Phillip M, Segev Y, et al. Modulation of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) receptors and membrane-associated IGF-binding proteins in endometrial cancer cells by estradiol. Endocrinology 1995;136:2531–7. doi:10.1210/en.136.6.2531.
Figueroa JA, Sharma J, Jackson JG, McDermott MJ, Hilsenbeck SG, Yee D. Recombinant insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 inhibits IGF-I, serum, and estrogen-dependent growth of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 1993;157:229–36. doi:10.1002/jcp.1041570204.
Samani AA, Yakar S, LeRoith D, Brodt P. The role of the IGF system in cancer growth and metastasis: overview and recent insights. Endocr Rev. 2007;28:20–47. doi:10.1210/er.2006-0001.
Freiss G, Rochefort H, Vignon F. Mechanisms of 4-hydroxytamoxifen anti-growth factor activity in breast cancer cells: alterations of growth factor receptor binding sites and tyrosine kinase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990;173:919–26. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(05)80873-3.
Wakeling AE, Newboult E, Peters SW. Effects of antioestrogens on the proliferation of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 1989;2:225–34.
Lee AV, Jackson JG, Gooch JL, Hilsenbeck SG, Coronado-Heinsohn E, Osborne CK, et al. Enhancement of insulin-like growth factor signaling in human breast cancer: estrogen regulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 expression in vitro and in vivo. Mol Endocrinol. 1999;13:787–96. doi:10.1210/me.13.5.787.
Lee AV, Darbre P, King RJ. Processing of insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II) by human breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1994;99:211–20. doi:10.1016/0303-7207(94)90010-8.
Osborne CK, Coronado EB, Kitten LJ, Arteaga CI, Fuqua SA, Ramasharma K, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II): a potential autocrine/paracrine growth factor for human breast cancer acting via the IGF-I receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1989;3:1701–9.
Huynh H, Yang X, Pollak M. Estradiol and antiestrogens regulate a growth inhibitory insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 autocrine loop in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 1996;271:1016–21. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.2.1016.
Nickerson T, Huynh H, Pollak M. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 induces apoptosis in MCF7 breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;237:690–3. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.7089.
Mathieu M, Vignon F, Capony F, Rochefort H. Estradiol down-regulates the mannose-6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor-II receptor gene and induces cathepsin-D in breast cancer cells: a receptor saturation mechanism to increase the secretion of lysosomal proenzymes. Mol Endocrinol. 1991;5:815–22.
Figueroa JA, Jackson JG, McGuire WL, Krywicki RF, Yee D. Expression of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in human breast cancer correlates with estrogen receptor status. J Cell Biochem. 1993;52:196–205. doi:10.1002/jcb.240520211.
Stewart AJ, Westley BR, May FE. Modulation of the proliferative response of breast cancer cells to growth factors by oestrogen. Br J Cancer. 1992;66:640–8.
Salerno M, Sisci D, Mauro L, Guvakova MA, Ando S, Surmacz E. Insulin receptor substrate 1 is a target for the pure antiestrogen ICI 182,780 in breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 1999;81:299–304. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19990412)81:2<299::AID-IJC21>3.0.CO;2-8.
Dubik D, Shiu RP. Mechanism of estrogen activation of c-myc oncogene expression. Oncogene 1992;7:1587–94.
Morishita S, Niwa K, Ichigo S, Hori M, Murase T, Fujimoto J, et al. Overexpressions of c-fos/jun mRNA and their oncoproteins (Fos/Jun) in the mouse uterus treated with three natural estrogens. Cancer Lett. 1995;97:225–31. doi:10.1016/0304-3835(95)03979-7.
Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL. Cell cycle control by steroid hormones. Semin Cancer Biol. 1994;5:381–9.
Razandi M, Pedram A, Greene GL, Levin ER. Cell membrane and nuclear estrogen receptors (ERs) originate from a single transcript: studies of ERalpha and ERbeta expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1999;13:307–19. doi:10.1210/me.13.2.307.
Kahlert S, Nuedling S, van Eickels M, Vetter H, Meyer R, Grohe C. Estrogen receptor alpha rapidly activates the IGF-1 receptor pathway. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:18447–53. doi:10.1074/jbc.M910345199.
Zhang Z, Kumar R, Santen RJ, Song RX. The role of adapter protein Shc in estrogen non-genomic action. Steroids 2004;69:523–9. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2004.05.012.
Klijn JG, Blamey RW, Boccardo F, Tominaga T, Duchateau L, Sylvester R. Combined tamoxifen and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) agonist versus LHRH agonist alone in premenopausal advanced breast cancer: a meta-analysis of four randomized trials. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:343–53.
Baum M, Budzar AU, Cuzick J, Forbes J, Houghton JH, Klijn JG, et al. Anastrozole alone or in combination with tamoxifen versus tamoxifen alone for adjuvant treatment of postmenopausal women with early breast cancer: first results of the ATAC randomised trial. Lancet 2002;359:2131–9. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09088-8.
Mackey J, et al. Trastuzumab prolongs progression-free survival in hormone-dependent and HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2006;100:S5. abstract 3.
Lisztwan J, Pornon A, Chen B, Chen S, Evans DB. The aromatase inhibitor letrozole and inhibitors of insulin-like growth factor I receptor synergistically induce apoptosis in in vitro models of estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10:R56. doi:10.1186/bcr2113.
Osborne R. Commercial interest waxes for IGF-1 blockers. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:719–20. doi:10.1038/nbt0708-719.
Cohen BD, Baker DA, Soderstrom C, Tkalcevic G, Rossi AM, Miller PE, et al. Combination therapy enhances the inhibition of tumor growth with the fully human anti-type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody CP-751,871. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:2063–73. doi:10.1158/1078–0432.CCR-04-1070.
Creighton CJ, Casa A, Lazard Z, Huang S, Tsimelzon A, Hilsenbeck SG, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I activates gene transcription programs strongly associated with poor breast cancer prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4078–85.
Yee D. Can the insulin-like growth factors regulate breast cancer growth? Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1992;22:3–5. doi:10.1007/BF01833328.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fagan, D.H., Yee, D. Crosstalk Between IGF1R and Estrogen Receptor Signaling in Breast Cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 13, 423–429 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-008-9098-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-008-9098-0