Abstract
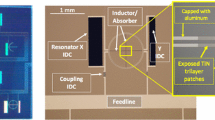
The context of this study is the development of polarisation sensitive detectors in view of future Cosmic Microwave Background experiments. Our goal is to demonstrate the possibility to make a mm-wave polarisation analyser at 150 GHz using Lumped Element Kinetic Inductance Detectors (LEKIDs). Although LEKIDs are very attractive for the relative ease of fabrication, they have an intrinsic optical response which is weakly polarisation-senstive, i.e. orthogonal linear polarisations are absorbed with comparable efficiencies (with a separation typically not exceeding few dB). To overcome this difficulty, we achieve a polarised response by means of small (\(\sim \lambda \times \lambda \)) superconducting Nb wire-grids. Each grid is deposited on the rear side of the 300 micron Si substrate, on which 20 nm Al resonators are patterned, so that each pixel may in principle respond as an independent polarisation analyser. Simulations show encouraging results, with a deep (-20 dB) rejection of the unwanted polarisation. Although what we present here is not yet a polarimeter, this pilot study allows us to address some relevant questions that may be crucial in view of a full polarimetric architecture development. In particular, our first prototypes will allow to assess the behaviour of small grids, the interaction between adjacent polarised pixels, and to choose the most suitable resonator geometry. What we present here are preliminary design results about devices which are currently being realised, and soon ready for optical response characterisation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Doyle, P. Mauskopf, J. Naylon, A. Porch, C. Duncombe, JLTP 151, 530–536 (2008)
A. Monfardini et al., ApJS 194, 24 (2011)
J. Hubmayr et al., IEEE Trans. on Appl. Supercond 23, 3 (2013)
B. Johnson et al., this Special Issue LTD15 in J. Low Temp. Phys
L.J. Van der Pauw, Philips Res. Repts 13, 1–9 (1958)
S. Withington, C.Y. Tham, G. Yassin, SPIE 4855, 49–62 (2003)
D.T. Chuss, E.J. Wollack, S.H. Moseley, S. Withington, G. Saklatvala, PASP 120, 430–438 (2008)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support from the UnivEarthS Labex program of Sorbonne Paris Cité (ANR-10-LABX-0023 and ANR-11-IDEX-0005-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tartari, A., Belier, B., Calvo, M. et al. A mm-Wave Polarisation Analyser Using LEKIDs: Strategy and Preliminary Numerical Results. J Low Temp Phys 176, 524–529 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-013-1055-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-013-1055-7