Abstract
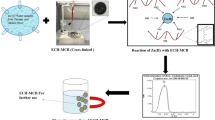
The applicability of magnetic cobalt ferrite entrapped chitosan beads (NH2-CF-CB) in water treatment is of research interest due to its biodegradable and cost-effective production. Amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles are entrapped into chitosan beads which increases the binding sites for pollutants and makes magnetic separation easier. The feasibility of amino-functionalized magnetic chitosan beads was evaluated for malachite green dye and copper (II) ions. The synthesized NH2-CF-CB adsorbent was characterized by the X-ray diffraction (XRD), fourier transform infrared (FTIR), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), Braunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) techniques. The adsorption of malachite green and copper (II) ions followed pseudo second order kinetics, which indicates chemisorption for both the pollutants. The maximum adsorption capacities of 357.16 and 158.73 mg.g−1 on NH2-CF-CB for malachite green and copper (II) ions respectively were evaluated from the Langmuir adsorption isotherm model. The superlative adsorption capacities with reusability and ease of separation characteristics for adsorption of malachite green (organic pollutant) as well as copper (II) ions (inorganic pollutants) make NH2-CF-CB unusual low-cost adsorbent to diminish water pollution concern.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.K. Uddin, A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem. Eng. J. 308, 438–462 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.029
W.S. Chai, J.Y. Cheun, P.S. Kumar, M. Mubashir, Z. Majeed, F. Banat, S.H. Ho, P.L. Show, A review on conventional and novel materials towards heavy metal adsorption in wastewater treatment application. J. Clea. Prod. 296, 126589 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126589
Y. Wen, J. Ma, J. Chen, C. Shen, H. Li, W. Liu, Carbonaceous sulfur-containing chitosan–Fe(III): a novel adsorbent for efficient removal of copper (II) from water. Chem. Eng. J. 259, 372–380 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.08.011
S. Hu, J. Song, F. Zhao, X. Meng, G. Wu, Highly sensitive and selective colorimetric naked-eye detection of Cu2+ in aqueous medium using a hydrazine chemosensor. Sens. Actuators B chem. 215, 241–248 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.03.059
M. Choudhary, R. Kumar, S. Neogi, Activated biochar derived from opuntiaficus-indica for the efficient adsorption of malachite green dye, Cu+2 and Ni+2 from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 392, 122441 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122441
S. Wang, E. Ariyanto, Competitive adsorption of malachite green and Pb ions on natural zeolite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 314, 25–31 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.05.032
M.Y. Zhou, P. Zhang, L.F. Fang, B.K. Zhu, J.L. Wang, J.H. Chen, H.M. Abdallah, A positively charged tight UF membrane and its properties for removing trace metal cations via electrostatic repulsion mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 373, 168–175 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.088
L.G.M. Silva, F.C. Moreira, M.A.P. Cechinel, L.P. Mazur, A.A.U. Souza, S.M.A.G.U. Souza, R.A.R. Boaventura, V.J.P. Vilar, Integration of Fenton’s reaction based processes and cation exchange processes in textile wastewater treatment as a strategy for water reuse. J. Environ. Manage. 272, 111082 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111082
M.B.K. Suhan, S.B. Shuchi, A. Anis, Z. Haque, M.S. Islam, Comparative degradation study of remazol black B dye using electro-coagulation and electro-Fenton process: Kinetics and cost analysis. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 14, 100335 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100335
A. Pohl, Removal of heavy metal ions from water and wastewaters by sulphur containing precipitation agents. Water Air Soil Pollut. 231, 503 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04863-w
S.B. Doltade, Y.J. Yadav, N.L. Jadhav, Industrial wastewater treatment using oxidative integrated approach. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 40, 100–106 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajce.2022.02.004
R. Verma, A. Asthana, A.K. Singh, S. Prasad, M.A.B.H. Susan, Novel glycine-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles entrapped calcium alginate beads for effective removal of lead. Microchem. J. 130, 168–178 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2016.08.006
T.A. Aragaw, F.M. Bogale, B.A. Aragaw, Iron-based nanoparticles in wastewater treatment: a review on synthesis methods, applications, and removal mechanisms. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 25, 101280 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2021.101280
R. Verma, A. Asthana, A.K. Singh, S. Prasad, An arginine functionalized magnetic nano-sorbent for simultaneous removal of three metal ions from water samples. RSC Adv. 7, 51079 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA09705K
S. Simsek, Z.M. Senol, H.I. Ulusoy, Synthesis and characterization of a composite polymeric material including chelating agent for adsorption of Uranyl ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 338, 437–446 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.05.059
I. Ali, C. Peng, I. Naz, M.A. Amjed, Water purification using magnetic nanomaterials: an overview. Magn. Nanostructures (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16439-3_9
M.E. Mahmouda, M.S. Abdelwahab, E.M. Fathallah, Design of novel nano-sorbents based on nano-magnetic iron oxide–bound-nano-silicon oxide–immobilized-triethylenetetramine for implementation in water treatment of heavy metals. Chem. Eng. J. 223, 318–327 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.02.097
M. Zhang, Z. Zhang, Y. Peng, L. Feng, X. Li, C. Zhao, K. Sarfaraz, Novel cationic polymer modified magnetic chitosan beads for efficient adsorption of heavy metals and dyes over a wide pH range. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 156, 289–301 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.020
Z.M. Şenol, S. Şimşek, Insights into effective adsorption of lead ions from aqueous solutions by using chitosan-bentonite composite beads. J Polym Environ. 30, 3677–3687 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02464-8
F. Karimi, A. Ayati, B. Tanhaei, A.L. Sanati, S. Afshar, A. Kardan, Z. Dabirifar, C. Karaman, Removal of metal ions using a new magnetic chitosan nano-bio-adsorbent; A powerful approach in water treatment. Environ. Res. 203, 111753 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111753
Y. Yu, B. He, H. Gu, Adsorption of bilirubin by amine containingcrosslinked chitosan resins, Art. Cells, Blood Subs, and Immob. Biotech. 28, 307–320 (2000). https://doi.org/10.3109/10731190009119361
P. Coppola, F.G. da Silva, G. Gomide, F.L.O. Paula, A.F.C. Campos, R. Perzynski, C. Kern, J. Depeyrot, R. Aquino, Hydrothermal synthesis of mixed zinc–cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: structural and magnetic properties. J. Nanopart. Res. 18, 138 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3430-1
Z. Chen, B. Peng, J.Q. Xu, X.C. Xiang, D.F. Ren, T.Q. Yang, S.Y. Ma, K. Zhang, Q.M. Chen, A non-surfactant self-templating strategy for mesoporous silica nanospheres: beyond the Stöber method. Nanoscale 12, 3657 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr10939k
T. Gholami, M.S. Niasari, M. Bazarganipour, E. Noori, Synthesis and characterization of spherical silica nanoparticles by modified Stöber process assisted by organic ligand. SuperlatticesMicrostruct. 61, 33–41 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2013.06.004
P. Parand, M. Mohammadi, A.A.S. Akmal, M. Samadpour, M. Dehghani, E. Parvazian, Sequential RTV/(TiO2/SiO2) nanocomposite deposition for suppressing the leakage current in silicone rubber insulators. Appl. Phys. A 126, 333 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03522-5
D. Malwal, P. Gopinath, Silica stabilized magnetic-chitosan beads for removal of arsenic from water. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 19, 14–19 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2017.06.003
J. Wang, S. Zheng, Y. Shao, J. Liu, Z. Xu, D. Zhu, Amino-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 core–shell magnetic nanomaterial as a novel adsorbent for aqueous heavy metals removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 349, 293–299 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.05.010
M. Vakili, A. Mojiri, H.M. Zwain, J. Yuan, A.S. Giwa, W. Wang, F. Gholami, X. Guo, G. Cagnettag, Gang Yu, Effect of beading parameters on cross-linked chitosan adsorptive properties. React. Funct. Polym. 144, 104354 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2019.104354
A. Kamari, W. Saime, W. Ngah, L.K. Liew, Chitosan and chemically modified chitosan beads for acid dyes sorption. J. Environ. Sci. 21, 296–302 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62267-6
N.P. Raval, P.U. Shah, N.K. Shah, Nanoparticles loaded biopolymer as effective adsorbent for adsorptive removal of malachite green from aqueous solution. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 1, 69–81 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41101-016-0004-0
S. Chowdhury, R. Mishra, P. Saha, P. Kushwaha, Adsorption thermodynamics, kinetics and isosteric heat of adsorption of malachite green onto chemically modified rice husk. Desalination 265, 159–168 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.07.047
Z.M. Şenol, A chitosan-based composite for adsorption of uranyl ions; mechanism, isothems, kinetics and thermodynamics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 183, 1640–1648 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.130
Y. Zhu, Y. Zheng, W. Wang, A. Wang, Highly efficient adsorption of Hg(II) and Pb(II) onto chitosan-basedgranular adsorbent containing thiourea groups. J. Water Process. Eng. 7, 218–226 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2015.06.010
A.R. Kula, H. Koyuncub, Adsorption of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution by native and activated bentonite: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. J. Hazard. Mater. 179, 332–339 (2010)
S.P. Markandeya, G.C. Shukla, Kisku, Linear and non-linear kinetic modeling for adsorption of disperse dye in batch process. Res. J. Environ. Toxicol. (2015). https://doi.org/10.3923/rjet.2015.320.331
S. Simsek, S. Kaya, Z.M. Senol, H.I. Ulusoy, K.P. Katin, A. Özer, N. Altunay, A. Brahmia, Theoretical and experimental insights about the adsorption of uranyl ion on a new designed Vermiculite-Polymer composite. J. Mol. Liq. 352, 118727 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.118727
N.K. Amin, Removal of direct blue-106 dye from aqueous solution using new activated carbons developed from pomegranate peel: Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 165, 52–62 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.067
A.O. Dada, A.P. Olalekan, A.M. Olatunya, O. Dada, Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of Zn2+ unto phosphoric acid modified rice husk, IOSR. J. Appl. Chem. 3, 38–45 (2012). https://doi.org/10.9790/5736-0313845
V.M. Muinde, J.M. Onyari, B. Wamalwa, J.N. Wabomba, Adsorption of malachite green dye from aqueous solutions using mesoporous chitosan–zinc oxide composite material. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2, 115–125 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enceco.2020.07.005
Y.C. Sharma, Adsorption characteristics of a low-cost activated carbon for the reclamation of colored effluents containing malachite green. J. Chem. Eng. Data 56, 478–484 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/je1008922
Z. Bekci, C. Ozveri, YSeki, K. Yurdakoc, Sorption of malachite green on chitosan bead. J. Hazard. Mater. 154, 254–261 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.021
B.H. Hameeda, M.I.E. Khaiary, Kinetics and equilibrium studies of malachite green adsorption on rice straw-derived char. J. Hazard. Mater. 153, 701–708 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.019
Equilibrium and kinetic studies and process design, E. Bulut, M. O.zacar, I. A. Sengil, Adsorption of malachite green onto bentonite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 115, 234–246 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.01.039
Y. Onal, C.A. Basar, C.S. Ozdemir, Investigation kinetics mechanisms of adsorption malachite green onto activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 146, 194–203 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.006
B.H. Hameeda, M.I.E. Khaiary, Equilibrium, kinetics and mechanism of malachite green adsorption on activated carbon prepared from bamboo by K2CO3 activation and subsequent gasification with CO2. J Hazard Mater. 157, 344–351 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.12.105
S.J. Aitcheson, J. Arnett, K.R. Murray, J. Zhang, Removal of aquaculture therapeutants by carbon adsorption: 1 Equilibrium adsorption behaviour of single components. Aquaculture 183, 269–284 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00304-X
W.S.W. Ngah, N.F.M. Ariff, A. Hashim, M.A.K.M. Hanafiah, Malachite green adsorption onto chitosan coated bentonite beads: isotherms, kinetics and mechanism. Clean—Soil, Air, Water 38, 394–400 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.200900251
W.S.W. Ngah, S. Fatinathan, Adsorption characterization of Pb(II) and Cu(II) ions onto chitosan-tripolyphosphate beads: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Manage. 91, 958–969 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.12.003
X. Hu, Y. Liu, H. Wang, A. Chen, G. Zeng, S. Liu, Y. Guo, X. Hu, T. Li, Y. Wang, L. Zhou, S. Liu, Removal of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution using sulfonated magnetic graphene oxide composite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 108, 189–195 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.02.011
Y. Chen, B. Pan, H. Li, W. Zhang, L. Lv, J. Wu, Selective removal of Cu(II) ions by using cation-exchange resin-supported polyethyleneimine (PEI) nanoclusters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 3508–3513 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/es100341x
M. Monier, D.M. Ayad, Y. Wei, A.A. Sarhan, Adsorption of Cu(II), Co(II), and Ni(II) ions by modified magnetic chitosan chelating resin. J. Hazard. Mater. 177, 962–970 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.012
F. Liu, K. Zhou, Q. Chen, A. Wang, W. Chen, Application of magnetic ferrite nanoparticles for removal of Cu(II) from copper ammonia wastewater. J. Alloys Compd 773, 140–149 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.240
D. Kong, N. Qiao, H. Liu, J. Du, N. Wang, Z. Zhou, Z. Ren, Fast and efficient removal of copper using sandwich-like graphene oxide composite imprinted materials. Chem. Eng. J. 326, 141–150 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.05.140
L. Lv, N. Chen, C. Feng, J. Zhanga, M. Li, Heavy metal ions removal from aqueous solution by xanthate-modified cross-linked magnetic chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) particles. RSC Adv. 7, 27992 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra02810e
J. He, K. Zhang, S. Wu, X. Cai, K. Chen, Y. Li, B. Sun, Y. Jia, F. Meng, Z. Jin, L. Kong, J. Liu, Performance of novel hydroxyapatite nanowires in treatment of fluoride contaminated water. J. Hazard. Mater. 303, 119–130 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.10.028
Y. Li, J. He, K. Zhang, T. Liu, Y. Hu, X. Chen, C. Wang, X. Huang, L. Kong, J. Liua, Super rapid removal of copper, cadmium and lead ions from water by NTA-silica gel. RSC Adv. 9, 397–407 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra08638a
C.S. Sundaram, N. Viswanathan, S. Meenakshi, Defluoridation chemistry of synthetic hydroxyapatite at nano scale: equilibrium and kinetic studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 115, 206–215 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.048
Funding
We are thankful to UGC-DAE-CSR, Indore for providing financial support (CSR-IC-BL-67/CRS-184–2016-17/848 and CSR-IC-BL-38/CRS-135–2014-15/123). We are also thankful to Shri R. K. Sharma, RRCAT, Indore for providing experimental facility. Authors are also thankful to DST for providing DST-FIST grant SR/FST/CSI-279/2016(C). We are thankful to Biorender.com for providing platform to draw graphical abstract.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SPS: Data curation, Investigation, Writing—Original draft preparation. AVW: Data Validation, Methodology. AKS: Investigation, Formal analysis. SPZ: Supervision, Conceptualization, Validation, Writing—Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sahare, S.P., Wankhade, A.V., Sinha, A.K. et al. Modified Cobalt Ferrite Entrapped Chitosan Beads as a Magnetic Adsorbent for Effective Removal of Malachite Green and Copper (II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions. J Inorg Organomet Polym 33, 266–286 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02491-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02491-x