Abstract
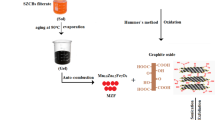
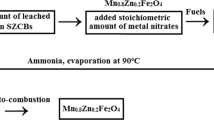
In the present work, the prepared Mn0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 ferrites (MZF) via recycling process of Zn–C batteries and auto-combustion route (using different fuels) were used to synthesize MZF/polypyrroly (PPy) nanocomposites via the in-situ polymerization technique. The core–shell structure formed was confirmed using X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared techniques. The thermogravimetric measurements suggests that the presence of MZF was found to catalyze PPy thermal decomposition and decreasing its thermal stability through increasing its exposed surface. The core–shell structure was found also to vanish the MZF magnetic properties through the insulation effect of the non-magnetic PPy coat. A possible schematic diagram for the core–shell formation mechanism was suggested and discussed. AC-conductivity vs. temperature clearly reveals a metallic behavior of all the samples with a dramatic increase in the MZF conductivities by addition of PPy. The main conduction mechanism was found to be through polarons. The higher dielectric values obtained suggests their use as a microwave absorbing materials besides being a promising candidates in the electromagnetic shielding applications. Generally, we can conclude that, the complete coating of MZF particles with PPy not only greatly influence the magnetic property but also greatly affected and improved the electrical properties. The ferrites’ preparation method was found not to affect the structural, magnetic or electrical properties owing to the core–shell structure formed.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data and materials will be available on demand.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
X. Feng, C. Mao, G. Yang, W. Hou, J.-J. Zhu, Polyaniline/Au composite hollow spheres: synthesis, characterization, and application to the detection of dopamine. Langmuir 22, 4384–4389 (2006)
X. Lu, Y. Yu, L. Chen, H. Mao, H. Gao, J. Wang, W. Zhang, Y. Wei, Aniline dimer–COOH assisted preparation of well-dispersed polyaniline–Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 16, 1660 (2005)
Q. Zhou, G. Shi, Conducting polymer-based catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 2868–2876 (2016)
Z. Li, M. Ye, A. Han, H. Du, Preparation, characterization and microwave absorption properties of NiFe2O4 and its composites with conductive polymer. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 1031–1043 (2016)
K. Krukiewicz, A. Kruk, R. Turczyn, Evaluation of drug loading capacity and release characteristics of PEDOT/naproxen system: effect of doping ions. Electrochim. Acta 289, 218–227 (2018)
M.H. Abdel-Aziz, M. Zwawi, A.F. Al-Hossainy, MSh. Zoromba, Conducting polymer thin film for optoelectronic devices applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 32, 2588–2596 (2021)
K.T. Arul, E. Manikandan, P.P. Murmu, J. Kennedy, M. Henini, Enhanced magnetic properties of polymer-magnetic nanostructures synthesized by ultrasonication. J. Alloys Compd. 720, 395–400 (2017)
K.D. Martinson, V.E. Belyak, D.D. Sakhno, A.A. Ivanov, L.A. Lebedev, L.A. Nefedov, I.B. Panteleev, V.I. Popkov, Solution combustion assisted synthesis of ultra-magnetically soft LiZnTiMn ferrite ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 894, 162554 (2022)
K.D. Martinson, A.A. Ivanov, I.B. Panteleev, V.I. Popkov, Effect of sintering temperature on the synthesis of LiZnMnFe microwave ceramics with controllable electro/magnetic properties. Ceram. Int. 47, 30071–30081 (2021)
J. Azadmanjiri, Preparation of Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles from chemical sol–gel combustion method and the magnetic properties after sintering. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 353, 4170–4173 (2007)
J. Topfer, A. Angermann, Nanocrystalline magnetite and Mn–Zn ferrite particles via the polyol process: synthesis and magnetic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 129, 337–342 (2011)
J. Ding, X.Y. Liu, J. Wang, Y. Shi, Ultrafine ferrite particles prepared by coprecipitation/mechanical milling. Mater. Lett. 44, 19–22 (2000)
Z.X. Yue, W.Y. Guo, J. Zhou, Z.L. Gui, L.T. Li, Synthesis of nanocrystilline ferrites by sol–gel combustion process: the influence of pH value of solution. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 270, 216–223 (2004)
K. Praveena, K. Sadhana, S.R. Murthy, Elastic behaviour of microwave hydrothermally synthesized nanocrystalline. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 1096–1103 (2012)
A. Kosak, D. Markovec, M. Drofenik, A. Znidarsic, In situ synthesis of magnetic MnZn-ferrite nanoparticles using reverse microemulsions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 272, 1542–1544 (2004)
G. Xi, Y. Li, Y. Liu, Study on preparation of manganese–zinc ferrites using spent Zn–Mn batteries. Mater. Lett. 58, 1164–1167 (2004)
J. Nan, D. Han, M. Cui, M. Yang, L. Pan, Recycling spent zinc manganese dioxide batteries through synthesizing Zn–Mn ferrite magnetic materials. J. Hazard. Mater. B 133, 257–261 (2006)
G. Xi, L. Yang, M. Lu, Study on preparation of nanocrystalline ferrites using spent alkaline Zn–Mn batteries. Mater. Lett. 60, 3582–3585 (2006)
P. Chang-hong, B. Ben-shuai, C. Yi-feng, Study on the preparation of Mn–Zn soft magnetic ferrite powders from waste Zn–Mn dry batteries. Waste Manag. 28, 326–332 (2008)
T. Kim, G. Senanayake, J. Kang, J. Sohn, K. Rhee, S. Lee, S. Shin, Reductive acid leaching of spent zinc–carbon batteries and oxidative precipitation of Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. Hydrometallurgy 96, 154–158 (2009)
P. Hu, D. Pan, S. Zhang, J. Tian, A.A. Volinsky, Mn–Zn soft magnetic ferrite nanoparticles synthesized from spent alkaline Zn–Mn batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 3991–3994 (2011)
M.A. Gabal, E.A. Al-Harthy, Y.M. Al Angari, A. Awad, A.A. Al-Juaid, A.M. Abdel-Daiem, A. Saeed, Recovery of Mn0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 from Zn–C battery: auto-combustion synthesizes, characterization, and electro-magnetic properties. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 100, 526–537 (2021)
Y. Li, R. Yi, A. Yan, L. Deng, K. Zhou, X. Liu, Facile synthesis and properties of ZnFe2O4 and ZnFe2O4/polypyrrole core–shell nanoparticles. Solid State Sci. 11, 1319–1324 (2009)
P. Karthikeyan, S.S.D. Elanchezhiyan, S. Meenakshi, C.M. Park, Magnesium ferrite-reinforced polypyrrole hybrids as an effective adsorbent for the removal of toxic ions from aqueous solutions: preparation, characterization, and adsorption experiments. J. Hazard. Mater. 408, 124892 (2021)
J. Guo, X. Li, Z. Chen, J. Zhu, X. Mai, R. Wei, K. Sun, H. Liu, Y. Chen, N. Naik, Z. Guo, Magnetic NiFe2O4/polypyrrole nanocomposites with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 108, 64–72 (2022)
X. Ren, J. Wang, H. Yin, Y. Tang, H. Fan, H. Yuan, S. Cui, L. Huang, Hierarchical CoFe2O4@PPy hollow nanocubes with enhanced microwave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 575, 151752 (2022)
L. Jiang, C. Dong, B. Jin, Z. Wen, Q. Jiang, ZnFe2O4@PPy core–shell structure for high-rate lithium-ion storage. J. Electroanal. Chem. 851, 113442 (2019)
M.A. Chougulea, S.G. Pawara, P.R. Godsea, R.N. Mulika, S. Senb, V.B. Patil, Synthesis and characterization of polypyrrole (PPy) thin films. Soft Nanosci. Lett. 1, 6–10 (2011)
U.O. Aigbe, R. Das, W.H. Ho, V. Srinivasu, A. Maity, A novel method for removal of Cr(VI) using polypyrrole magnetic nanocomposite in the presence of unsteady magnetic fields. Sep. Purif. Technol. 194, 377–387 (2018)
I. Seo, M. Pyo, G. Cho, Micrometer to nanometer patterns of polypyrrole thin films via microphase separation and molecular mask. Langmuir 18, 7253–7257 (2002)
J. Luo, Y. Xu, H. Mao, Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of rare earth ions (Sm3+, Er3+) doped strontium ferrite and its nanocomposites with polypyrrole. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 381, 365–371 (2015)
C. Zhang, Q. Li, Y. Ye, Preparation and characterization of polypyrrole/nano-SrFe12O19 composites by in situ polymerization method. Synth. Met. 159, 1008–1013 (2009)
Y. Wang, L. Li, J. Jiang, H. Liu, H. Qiu, F. Xu, Conductivity and magnetic properties of Zn0.6Cu0.4Cr0.5La0.04Fe1.46O4/PPy composites prepared by in situ inverse microemulsion polymerization. React. Funct. Polym. 68, 1587–1593 (2008)
P. Qiao, B. Zhao, Z. Nan, Facile fabrication of ZnLa0.02Fe1.98O4/PPy and application inwater treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 178, 1476–1482 (2013)
S.T. Assar, H.F. Abosheiasha, E.H. El-Ghazzawy, Preparation and study of some physical properties of Co–Ni–Li ferrite/polypyrrole nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compd. 802, 553–561 (2019)
T. Qi, Z. Yao, J. Zhou, H. Lin, P. Liu, Y. Lei, Y. Zuo, Interfacial polymerization preparation of polyaniline fibers/Co0.2Ni0.4Zn0.4Fe2O4 urchin-like composite with superior microwave absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 769, 669–677 (2018)
R.D. Waldron, Infrared spectra of ferrites. Phys. Rev. 99, 1727–1735 (1955)
E. Jakab, E. Meszaros, M. Omastova, Thermal decomposition of polypyrrole. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 88, 515–521 (2007)
J. Tang, K. Wang, Y. Lu, N. Liang, X. Qin, G. Tian, D. Zhang, S. Feng, H. Yue, Mesoporous core–shell structure NiFe2O4@polypyrrole micro-rod with efficient electromagnetic wave absorption in C, X, Ku wavebands. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 514, 167268 (2020)
B.I. Kharisov, H.V. Rasika Dias, O.V. Kharissova, Mini-review: ferrite nanoparticles in the catalysis. Arab. J. Chem. 12, 1234–1246 (2019)
M.A. Gabal, N.G. Al-Zahrani, Y.M. Al Angari, A.A. Al-Juaid, M.A. Abdel-Fadeel, S.R. Alharbi, R.M. El-Shishtawy, CoFe2O4/MWCNTs nano-composites structural, thermal, magnetic, electrical properties and dye removal capability. Mater. Res. Exp. 6, 105059 (2019)
I.M. Resta, J.M. Selles, M. Lanus-Mendez-Elizalde, P.S. Antonel, F.V. Molina, Polypyrrole-CoFe2O4 nanocomposites: polymer influence on magnetic behavior and particle effects on polymer conduction. Polym. Compos. 39, 4617–4627 (2018)
J. Stejskal, Conducting polymer–silver composites. Chem. Pap. 67, 814–848 (2013)
H. Kuzmany, M. Mehring, S. Roth, Electronic Properties of Conjugated Polymers (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1987)
Y. Xie, X. Hong, Y. Gao, M. Li, J. Liu, J. Wang, J. Lu, Synthesis and characterization of La/Nd-doped barium-ferrite/polypyrrole nanocomposites. Synth. Met. 162, 677–681 (2012)
J.A. Khan, M. Qasim, B.R. Singh, S. Singh, M. Shoeb, W. Khan, D. Das, A.H. Naqvi, Synthesis and characterization of structural, optical, thermal and dielectric properties of polyaniline/CoFe2O4 nanocomposites with special reference to photocatalytic activity. Spectrochim. Acta A 109, 313–321 (2013)
H. Deligoz, A. Baykal, E.E. Tanrıverdi, Z. Durmus, M.S. Toprak, Synthesis, structural and electrical properties of triethylene glycol (TREG) stabilized Mn0.2Co0.8Fe2O4 NPs. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 537–543 (2012)
M.B. Mohamed, K. El-Sayed, Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of (PANI)–Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe1.5Cr0.5O4 nanocomposite. Compos. B 56, 270–278 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Consent for Publication
By submitting the manuscript, the authors understand that the material presented in this manuscript has not been published before, nor has it been submitted for publication to another journal. The corresponding author attests that this study has been approved by all the co-authors concerned.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gabal, M.A., Al-Harthy, E.A., Al Angari, Y.M. et al. Synthesis, Structural, Magnetic and High-Frequency Electrical Properties of Mn0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4/Polypyrrole Core–Shell Composite Using Waste Batteries. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 1975–1987 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02241-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02241-z