Abstract
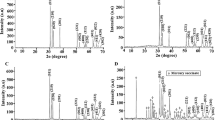
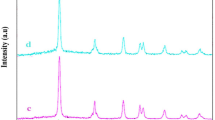
In this paper, the hydrothermal method was utilized for the facile synthesis of copper chromite nanoparticles in the absence (abbreviated as CC1) and presence of citric acid (abbreviated as CC2) and tartaric acid (abbreviated as CC3) as templates. The synthesized nanoparticles were characterized using different tools such as XRD, FT-IR, UV–Vis, FE-SEM, HR-TEM, and BET. The average crystallite size of the CC1, CC2, and CC3 samples is 25.45, 20.26, and 12.75 nm, respectively. The FT-IR spectra show two bands in the range 613–616 cm−1 and 511–514 cm−1, which are characteristic of the spinel copper chromite crystalline structure. The optical energy gaps of the CC1, CC2, and CC3 samples are 1.25, 1.88, and 1.92 eV, respectively. The synthesized nanoparticles were used for the degradation of the acid orange 7 dye under visible light irradiations. The highest % degradation was obtained at pH 2.5 and irradiation time = 40 min. The % degradation of the acid orange 7 dye using CC1, CC2, and CC3 photocatalysts at pH 2.50 and time = 40 min is 87.38, 96.52, and 98.81, respectively. The degradation of the acid orange 7 dye was markedly reduced with the addition of isopropyl alcohol or disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate, confirming that the hydroxyl radicals and holes routes play a fundamental role in the degradation process of the acid orange 7 dye. The degradation of the acid orange 7 dye is slightly affected by the addition of ascorbic acid, confirming a minor concentration of oxygen anion radicals.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Wongkalasin, S. Chavadej, T. Sreethawong, Photocatalytic degradation of mixed azo dyes in aqueous wastewater using mesoporous-assembled TiO2 nanocrystal synthesized by a modified sol–gel process. Colloids Surf. A 384, 519–528 (2011)
N. Turkten, Z. Cinar, Photocatalytic decolorization of azo dyes on TiO2: prediction of mechanism via conceptual DFT. Catal. Today 287, 169–175 (2017)
P. Navarro, J.A. Gabaldón, V.M. Gómez-López, Degradation of an azo dye by a fast and innovative pulsed light/H2O2 advanced oxidation process. Dyes Pigm. 136, 887–892 (2017)
V. Mirkhani, S. Tangestaninejad, M. Moghadam, M.H. Habibi, Iranian chemical society photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes catalyzed by Ag doped TiO2 photocatalyst. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 6, 578–587 (2009)
T.K. Das, S. Ganguly, P. Bhawal, S. Remanan, S. Mondal, N.C. Das, Mussel inspired green synthesis of silver nanoparticles-decorated halloysite nanotube using dopamine: characterization and evaluation of its catalytic activity. Appl. Nanosci. 8, 173–186 (2018)
T.K. Das, S. Ganguly, P. Bhawal, S. Remanan, S. Ghosh, N.C. Das, A facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles decorated silica nanocomposites using mussel inspired polydopamine chemistry and assessment its catalytic activity. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6, 6989–7001 (2018)
S. Ganguly, S. Mondal, P. Das, P. Bhawal, T. Kanti Das, M. Bose, S. Choudhary, S. Gangopadhyay, A.K. Das, N.C. Das, Natural saponin stabilized nano-catalyst as efficient dye-degradation catalyst. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 16, 86–95 (2018)
T.K. Das, S. Remanan, S. Ghosh, S.K. Ghosh, N.C. Das, Efficient synthesis of catalytic active silver nanoparticles illuminated cerium oxide nanotube: a mussel inspired approach. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 15, 100411 (2021)
A. Thiam, M. Zhou, E. Brillas, I. Sirés, Two-step mineralization of tartrazine solutions: study of parameters and by-products during the coupling of electrocoagulation with electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Appl. Catal. B 150–151, 116–125 (2014)
L. Kőrösi, B. Bognár, S. Bouderias, A. Castelli, A. Scarpellini, L. Pasquale, M. Prato, Highly-efficient photocatalytic generation of superoxide radicals by phase-pure rutile TiO2 nanoparticles for azo dye removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 493, 719–728 (2019)
N. Divya, A. Bansal, A.K. Jana, Photocatalytic degradation of azo dye orange II in aqueous solutions using copper-impregnated titania. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 10, 1265–1274 (2013)
R. Kumar Sonwani, S. Pandey, S. Kumar Yadav, B. Shekhar Giri, V. Katiyar, R. Sharan Singh, B. Nath Rai, Construction of integrated system for the treatment of acid orange 7 dye from wastewater: optimization and growth kinetic study. Bioresour. Technol. 337, 125478 (2021)
H. Jafari-Arvari, S.S. Saei-Dehkordi, S. Farhadian, Evaluation of interactions between food colorant, tartrazine, and Apo-transferrin using spectroscopic analysis and docking simulation. J. Mol. Liq. 339, 116715 (2021)
B. Er Demirhan, H.E. Şatana Kara, B. Demirhan, One-step green aqueous synthesis of blue light emitting copper nanoclusters for quantitative determination of food color Ponceau 4R. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 417, 113356 (2021)
K. Hamidian, A. Najafidoust, A. Miri, M. Sarani, Photocatalytic performance on degradation of acid orange 7 dye using biosynthesized un-doped and Co doped CeO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 138, 111206 (2021)
S. Silvestri, M.G. Gonçalves, P.A. Da Silva Veiga, T.T.D.S. Matos, P. Peralta-Zamora, A.S. Mangrich, TiO2 supported on Salvinia molesta biochar for heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of Acid Orange 7 dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 7, 102879 (2019)
D. Sivaraj, K. Vijayalakshmi, M. Srinivasan, P. Ramasamy, Graphene oxide reinforced bismuth titanate for photocatalytic degradation of azo dye (DB15) prepared by hydrothermal method. Ceram. Int. 47, 25074–25080 (2021)
E.A. Abdelrahman, R.M. Hegazey, Y.H. Kotp, A. Alharbi, Facile synthesis of Fe2O3 nanoparticles from Egyptian insecticide cans for efficient photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and crystal violet dyes. Spectrochim. Acta A 222, 117195 (2019)
A. Alharbi, E.A. Abdelrahman, Efficient photocatalytic degradation of malachite green dye using facilely synthesized hematite nanoparticles from Egyptian insecticide cans. Spectrochim. Acta A 226, 117612 (2020)
R.M. Hegazey, E.A. Abdelrahman, Y.H. Kotp, A.M. Hameed, A. Subaihi, Facile fabrication of hematite nanoparticles from Egyptian insecticide cans for efficient photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 1652–1661 (2020)
M.R. Al-Mamun, S. Kader, M.S. Islam, M.Z.H. Khan, Photocatalytic activity improvement and application of UV-TiO2 photocatalysis in textile wastewater treatment: a review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 7, 103248 (2019)
S. Velázquez-Martínez, S. Silva-Martínez, C.A. Pineda-Arellano, A. Jiménez-González, I. Salgado-Tránsito, A.A. Morales-Pérez, M.I. Peña-Cruz, Modified sol–gel/hydrothermal method for the synthesis of microsized TiO2 and iron-doped TiO2, its characterization and solar photocatalytic activity for an azo dye degradation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 359, 93–101 (2018)
N.H. Mohtor, M.H.D. Othman, S.A. Bakar, T.A. Kurniawan, H. Dzinun, M.N.A.M. Norddin, Z. Rajis, Synthesis of nanostructured titanium dioxide layer onto kaolin hollow fibre membrane via hydrothermal method for decolourisation of reactive black 5. Chemosphere 208, 595–605 (2018)
W. Yuan, X. Liu, L. Li, Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of cubic-like CuCr2O4 for dye degradation under visible light irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 319, 350–357 (2014)
B. Paul, B. Bhuyan, D.D. Purkayastha, S.S. Dhar, S. Behera, Facile synthesis of spinel CuCr2O4 nanoparticles and studies of their photocatalytic activity in degradation of some selected organic dyes. J. Alloys Compd. 648, 629–635 (2015)
R. Peymanfar, H. Ramezanalizadeh, Sol–gel assisted synthesis of CuCr2O4 nanoparticles: an efficient visible-light driven photocatalyst for the degradation of water pollutions. Optik (Stuttg) 169, 424–431 (2018)
S. Mobini, F. Meshkani, M. Rezaei, Surfactant-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of CuCr2O4 spinel catalyst and its application in CO oxidation process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 5, 4906–4916 (2017)
S.S. Acharyya, S. Ghosh, S. Adak, D. Tripathi, R. Bal, Fabrication of CuCr2O4 spinel nanoparticles: a potential catalyst for the selective oxidation of cycloalkanes via activation of Csp3-H bond. Catal. Commun. 59, 145–150 (2015)
E.A. Abdelrahman, A. Alharbi, A. Subaihi, A.M. Hameed, M.A. Almutairi, F.K. Algethami, H.M. Youssef, Facile fabrication of novel analcime/sodium aluminum silicate hydrate and zeolite Y/faujasite mesoporous nanocomposites for efficient removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous media. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 7900–7914 (2020)
H.M. Aly, M.E. Moustafa, E.A. Abdelrahman, Influence of aluminum source on the synthesis of nanosized ZSM-5 zeolite. Der Chem. Sin. 4, 68–72 (2013)
E.A. Abdelrahman, D.A. Tolan, M.Y. Nassar, A tunable template-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxysodalite zeolite nanoparticles using various aliphatic organic acids for the removal of zinc(II) ions from aqueous media. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 29, 229–247 (2019)
E.A. Abdelrahman, R.M. Hegazey, A. Alharbi, Facile synthesis of mordenite nanoparticles for efficient removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous media. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30, 1369–1383 (2020)
K.E. Jelfs, B. Slater, D.W. Lewis, D.J. Willock, The Role of Organic Templates in Controlling Zeolite Crystal Morphology (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2991(07)81047-0
S. Kaur, V. Singh, TiO2 mediated photocatalytic degradation studies of Reactive Red 198 by UV irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 141, 230–236 (2007)
J. Nishio, M. Tokumura, H.T. Znad, Y. Kawase, Photocatalytic decolorization of azo-dye with zinc oxide powder in an external UV light irradiation slurry photoreactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 138, 106–115 (2006)
M. Pirsaheb, K. Karimi, B. Shahmoradi, M. Moradi, Y. Vasseghian, E.N. Dragoi, Photocatalyzed degradation of acid orange 7 dye under sunlight and ultraviolet irradiation using Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Desalin. Water Treat. 165, 321–331 (2019)
S.A. Ong, O.M. Min, L.N. Ho, Y.S. Wong, Comparative study on photocatalytic degradation of mono azo dye acid orange 7 and methyl orange under solar light irradiation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 223, 5483–5493 (2012)
S. Kokate, S. Gupta, V.G. Kopuri, H. Prakash, Energy efficient photocatalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate by g-C3N4 under 400 nm LED irradiation for degradation of Acid Orange 7. Chemosphere (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132099
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Princess Nourah Bint Abdulrahman University, through the Research Groups Program Grant No. (RGP-1440-0003)(3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest for this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Wasidi, A.S., AlZahrani, I.I.S., Thawibaraka, H.I. et al. Facile Hydrothermal Synthesis of Copper Chromite Nanoparticles for Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Acid Orange 7 Dye. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 443–454 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02113-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02113-y