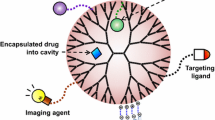
Abstract
Dendrimers are hyper-branched organic compounds characterized via a three-dimensional structure possessing functional groups on the surface. These terminals groups can be simply modified to enhance the functionality of dendrimers and produce biocompatible and versatile products. They are a promising agent for nanomedicine applications because of their unique properties, including nanoscale size, globular shape, and high reactivity, solubility in water, internal cavities, and comfortable synthesis methods. The use of dendrimers as drug delivery systems have received great attention from researchers. Dendrimers can be applied as carriers for different therapeutic agents. They can reduce the toxicity of drugs and increase their efficacy. This review provides a general outline of the structure and types of dendrimers, the synthesis of dendrimers, and applications in the nanomedicine field with emphasis on drug delivery.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Hereby we state that data sharing is not applicable in our submission.
References
C.L. Ventola, Progress in nanomedicine: approved and investigational nanodrugs. Pharm. Ther. 42(12), 742 (2017)
A.K. Rai et al., Dendrimers: a potential carrier for targeted drug delivery system. Pharm. Biol. Eval. 3(3), 275–287 (2016)
A.M. Reddy, P.S. Babu, Dendrimers in antimicrobial therapy—an overview. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 9(3), 322–332 (2016)
M. Stevanović, Biomedical applications of nanostructured polymeric materials, in Nanostructured Polymer Composites for Biomedical Applications. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2019), pp. 1–19
M.J. Dunlop et al., Nanocomposites derived from molybdenum disulfide and an organoiron dendrimer. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 27(1), 84–89 (2017)
K. Rajavelu, P. Rajakumar, Synthesis and DSSC application of donor-acceptor stilbenoid dendrimers with triphenylamine as core and benzothiazole as surface unit. Org. Electron. 56, 192–200 (2018)
R. Bissessur et al., Nanocomposites based on dendrimers and layered molybdenum disulfide. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 30, 4771–4782 (2020)
M. Dabrzalska et al., Phosphorus dendrimers and photodynamic therapy. Spectroscopic studies on two dendrimer-photosensitizer complexes: cationic phosphorus dendrimer with rose Bengal and anionic phosphorus dendrimer with methylene blue. Int. J. Pharm. 492(1–2), 266–274 (2015)
D.R.D. Carmo, L.L. Paim, Investigation about the copper adsorption on the chloropropylsilica gel surface modified with a nanostructured dendrimer DAB-Am-16: an analytical application for determination of copper in different samples. Mater. Res. 16(1), 164–172 (2013)
M.A. Mintzer, M.W. Grinstaff, Biomedical applications of dendrimers: a tutorial. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40(1), 173–190 (2011)
A.A. Joraid et al., Thermal degradation behavior of a new family of organometallic dendrimer. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01444-6
E. Buhleier, " Cascade"-and" nonskid-chain-like" syntheses of molecular cavity topologies. Synthesis 1978(2): 155–158 (1978)
R. Denkewalter, J. Kolc, W. Lukasavage. US Pat. 4289872, 1981. in Chem. Abstr. (1985)
D.A. Tomalia et al., A new class of polymers: starburst-dendritic macromolecules. Polym. J. 17(1), 117–132 (1985)
G.R. Newkome et al., Micelles. Part 1. Cascade molecules: a new approach to micelles. A [27]-arborol. J. Org. Chem. 50(11), 2003–2004 (1985)
C.J. Hawker, J.M. Frechet, Preparation of polymers with controlled molecular architecture. A new convergent approach to dendritic macromolecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112(21), 7638–7647 (1990)
B. Noriega-Luna et al., Applications of dendrimers in drug delivery agents, diagnosis, therapy, and detection. J. Nanomater. 2014, 1–19 (2014)
K. Albrecht, Y. Kasai, K. Yamamoto, The fluorescence and electroluminescence properties of the carbazole–phenylazomethine double layer-type dendrimer. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 19(1), 118–123 (2009)
R.W. Scott, O.M. Wilson, R.M. Crooks, Synthesis, characterization, and applications of dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B. 109(2), 692–704 (2005)
B. Klajnert, M. Bryszewska, The interaction of tryptophan and ANS with PAMAM dendrimers. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 7(4), 1087–1094 (2002)
M. Nasr, E. Elmowafy, M.E. Soliman, The evolution of dendrimers to composite dendrimers: a review of the state of the art, in Nanoparticles in Pharmacotherapy. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2019), pp. 217–249
H. Chaudhari et al., Dendrimers: novel carriers for drug delivery. J. Appl. Pharm. Res. 4(1), 01–19 (2016)
C. Loo et al., Immunotargeted nanoshells for integrated cancer imaging and therapy. Nano Lett. 5(4), 709–711 (2005)
X.-Y. Zhang, P.-Y. Zhang, Nanotechnology for multimodality treatment of cancer. Oncol. Lett. 12(6), 4883–4886 (2016)
A.P. Dias et al., Dendrimers in the context of nanomedicine. Int. J. Pharm. 573, 118814 (2020)
D. Li, S. Wen, X. Shi, Dendrimer-entrapped metal colloids as imaging agents. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 7(5), 678–690 (2015)
R. Akki, et al., A novel approach in drug delivery system using dendrimers. Pharma. Innovation J. 8(5), 166–174 (2019)
B. Yavuz et al., In vitro/in vivo evaluation of dexamethasone—PAMAM dendrimer complexes for retinal drug delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 104(11), 3814–3823 (2015)
D. Patton et al., Preclinical safety and efficacy assessments of dendrimer-based (SPL7013) microbicide gel formulations in a nonhuman primate model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50(5), 1696–1700 (2006)
A.P. Sherje et al., Dendrimers: a versatile nanocarrier for drug delivery and targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 548(1), 707–720 (2018)
S.K. Prajapati et al., Dendrimers in drug delivery, diagnosis and therapy: basics and potential applications. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 6(1), 67–92 (2016)
R. Esfand, D.A. Tomalia, Poly(amidoamine)(PAMAM) dendrimers: from biomimicry to drug delivery and biomedical applications. Drug Discov. Today 6(8), 427–436 (2001)
S.K. Parajapati et al., Potential application of dendrimers in drug delivery: a concise review and update. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 6(2), 71–88 (2016)
R. Yang et al., Synthesis of a novel polyamidoamine dendrimer conjugating with alkali blue as a lymphatic tracer and study on the lymphatic targeting in vivo. Drug Deliv. 23(7), 2298–2308 (2016)
F. Abedi-Gaballu et al., PAMAM dendrimers as efficient drug and gene delivery nanosystems for cancer therapy. Appl. Mater. Today 12, 177–190 (2018)
A.O. Idris, Development of Electrochemical Biosensors Based on Carbon Nanoparticles-Dendrimer Derivatives for Carcinoembryonic Antigen and Alpha-Feto Protein Cancer Biomarkers (University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, 2019).
L. Liang, J. Ruiz, D. Astruc, “Click” synthesis of a heterobifunctional ferrocenyl dendrimer with molecular recognition properties and influence of the ferrocenyl redox potential on the formation of gold nanoparticles. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 20(3), 503–510 (2010)
E. Esmaeili et al., Dendrimer functionalized magnetic nanoparticles as a promising platform for localized hyperthermia and magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 234(8), 12615–12624 (2019)
S. Wongin et al., Maintenance of human chondrogenic phenotype on a dendrimer-immobilized surface for an application of cell sheet engineering. BMC Biotechnol. 18(1), 1–11 (2018)
H. Ahmadi, M. Abdollahi, Synthesis and structural characterization of lignin/silica hybrid nanoparticles functionalized with sulfonic acid-terminated polyamidoamine. Wood Sci. Technol. 54(1), 249–268 (2020)
M. Kalomiraki, K. Thermos, N.A. Chaniotakis, Dendrimers as tunable vectors of drug delivery systems and biomedical and ocular applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 11, 1 (2016)
D.K. Hawamdeh, K. Qamhieh, A. Sayyed-Ahmad, Complexation of DNA with nano-cationic dendrimers as nonviral vectors in gene therapy. Technical Report. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.30392.44803
H.J. Hsu et al., Dendrimer-based nanocarriers: a versatile platform for drug delivery. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 9(1), e1409 (2017)
V. Mishra et al., Dendrimer based nanoarchitectures in diabetes management: an overview. Curr. Pharm. Des. 25(23), 2569–2583 (2019)
L. Salvi et al., A synthesis, properties and application as a possible drug delivery systems dendrimers—a review. Asian J. Pharm. Res. Dev. 8(2), 107–113 (2020)
V.P. Chavda, Nanobased nano drug delivery: a comprehensive review, in Applications of Targeted Nano Drugs and Delivery Systems. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2019), pp. 69–92
T. Baig et al., A review about dendrimers: synthesis, types, characterization and applications. Int. J. Adv. Pharm. Biol. Chem 4, 44–59 (2015)
A.S. Ertürk, G. Elmacı, PAMAM dendrimer functionalized manganese ferrite magnetic nanoparticles: microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 28(5), 2100–2107 (2018)
E. Abbasi et al., Dendrimers: synthesis, applications, and properties. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 9(1), 247 (2014)
A. Gothwal et al., Toxicity and biocompatibility aspects of dendrimers, in Pharmaceutical Applications of Dendrimers. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2020), pp. 251–274
C.J. Hawker, K.L. Wooley, J.M. Fréchet, Unimolecular micelles and globular amphiphiles: dendritic macromolecules as novel recyclable solubilization agents. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 12, 1287–1297 (1993)
U. Gupta, O. Perumal, Dendrimers and its biomedical applications, in Natural and Synthetic Biomedical Polymers. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2014), pp. 243–257
X. Xu et al., Cooperative hierarchical self-assembly of peptide dendrimers and linear polypeptides into nanoarchitectures mimicking viral capsids. Angew. Chem. 124(13), 3184–3187 (2012)
K. Sadler, J.P. Tam, Peptide dendrimers: applications and synthesis. Rev. Mol. Biotechnol. 90(3–4), 195–229 (2002)
P. Niederhafner, J. Šebestík, J. Ježek, Peptide dendrimers. J. Pept. Sci. 11(12), 757–788 (2005)
P. Kesharwani et al., Dendrimers in targeting and delivery of drugs, in Nanotechnology-Based Approaches for Targeting and Delivery of Drugs and Genes. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2017), pp. 363–388
A. Pushechnikov, S.S. Jalisatgi, M.F. Hawthorne, Dendritic closomers: novel spherical hybrid dendrimers. Chem. Commun. 49(34), 3579–3581 (2013)
K. Jain et al., Dendrimer toxicity: let’s meet the challenge. Int. J. Pharm. 394(1–2), 122–142 (2010)
P. Antoni et al., Bifunctional dendrimers: from robust synthesis and accelerated one-pot postfunctionalization strategy to potential applications. Angew. Chem. 121(12), 2160–2164 (2009)
S.M. Grayson, J.M. Frechet, Convergent dendrons and dendrimers: from synthesis to applications. Chem. Rev. 101(12), 3819–3868 (2001)
D.A. Tomalia, J.M. Fréchet, Discovery of dendrimers and dendritic polymers: a brief historical perspective. J. Polym. Sci. A 40(16), 2719–2728 (2002)
A.-M. Caminade et al., Synthetic pathways towards phosphorus dendrimers and dendritic architectures. Curr. Org. Chem. 10(18), 2333–2355 (2006)
T. Kawaguchi et al., Double exponential dendrimer growth. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117(8), 2159–2165 (1995)
M. Arseneault, C. Wafer, J.-F. Morin, Recent advances in click chemistry applied to dendrimer synthesis. Molecules 20(5), 9263–9294 (2015)
Z. Iqbal et al., The edge versions of degree-based topological descriptors of dendrimers. J. Cluster Sci. 31(2), 445–452 (2020)
I. Gheorghe, C. Curutiu, L.-M. Ditu, Therapeutic nanostructures: novel approaches, in Materials for Biomedical Engineering. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2019), pp. 1–22
S. ho Hng, Y. Choi, Mesoporous silica-based nanoplatforms for the delivery of photodynamic therapy agents. J. Pharm. Invest. 48(1), 3–17 (2018)
P.K. Pandey et al., Nanogold-core multifunctional dendrimer for pulsatile chemo-, photothermal-and photodynamic-therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 544, 61–77 (2019)
S. Battah et al., Enhanced porphyrin accumulation using dendritic derivatives of 5-aminolaevulinic acid for photodynamic therapy: an in vitro study. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 38(8), 1382–1392 (2006)
K.-F. Xu et al., Cholesterol-modified dendrimers for constructing a tumor microenvironment-responsive drug delivery system. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 5(11), 6072–6081 (2019)
M.T. McMahon, J.W. Bulte, Two decades of dendrimers as versatile MRI agents: a tale with and without metals. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 10(3), e1496 (2018)
J.K. Patra et al., Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 16(1), 71 (2018)
L.H. Bryant et al., Pharmacokinetics of a high-generation dendrimer–Gd-DOTA. Acad. Radiol. 9(1), S29–S33 (2002)
O.P. Perumal et al., The effect of surface functionality on cellular trafficking of dendrimers. Biomaterials 29(24–25), 3469–3476 (2008)
H.B. Agashe et al., Investigations on the toxicological profile of functionalized fifth-generation poly (propylene imine) dendrimer. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 58(11), 1491–1498 (2006)
S. Zhang et al., Radical dendrimers based on biocompatible oligoethylene glycol dendrimers as contrast agents for MRI. Pharmaceutics 12(8), 772 (2020)
B. Gorain et al., The use of nanoscaffolds and dendrimers in tissue engineering. Drug Discov. Today 22(4), 652–664 (2017)
A. Taheri-Kafrani, H. Shirzadfar, E. Tavassoli-Kafrani, Dendrimers and dendrimers-grafted superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, functionalization, and biological applications in drug delivery systems, in Nano-and Microscale Drug Delivery Systems. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2017), pp. 75–94
S. Shukla et al., Biodegradable polymeric nanostructures in therapeutic applications: opportunities and challenges. RSC Adv. 6(97), 94325–94351 (2016)
K.A. Boduch-Lee et al., Design and synthesis of hydroxyapatite composites containing an mPEG−dendritic poly (l-lysine) star polycaprolactone. Macromolecules 37(24), 8959–8966 (2004)
I. Rajzer, Fabrication of bioactive polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite scaffolds with final bilayer nano-/micro-fibrous structures for tissue engineering application. J. Mater. Sci. 49(16), 5799–5807 (2014)
J.M. Oliveira et al., The osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells cultured with dexamethasone-loaded carboxymethylchitosan/poly (amidoamine) dendrimer nanoparticles. Biomaterials 30(5), 804–813 (2009)
N. Tomar, Dendrimers as nanocarriers in cancer chemotherapy. Anticancer Res. 8, 12 (2019)
J. Hu, K. Hu, Y. Cheng, Tailoring the dendrimer core for efficient gene delivery. Acta Biomater. 35, 1–11 (2016)
M. Gorzkiewicz et al., Application of new lysine-based peptide dendrimers D3K2 and D3G2 for gene delivery: Specific cytotoxicity to cancer cells and transfection in vitro. Bioorg. Chem. 95, 103504 (2020)
J.M. Fréchet, Functional polymers and dendrimers: reactivity, molecular architecture, and interfacial energy. Science 263(5154), 1710–1715 (1994)
P. Kesharwani, K. Jain, N.K. Jain, Dendrimer as nanocarrier for drug delivery. Prog. Polym. Sci. 39(2), 268–307 (2014)
A.S.P. Kumar, S. Latha, P. Selvamani, Dendrimers: multifunctional drug delivery carriers. Int. J. Technol. Res. Engine 2, 1569–1575 (2015)
W.E. Bawarski et al., Emerging nanopharmaceuticals. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 4(4), 273–282 (2008)
D.G. Mullen et al., Design, synthesis, and biological functionality of a dendrimer-based modular drug delivery platform. Bioconjug. Chem. 22(4), 679–689 (2011)
J. Singh et al., Dendrimers in anticancer drug delivery: mechanism of interaction of drug and dendrimers. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 44(7), 1626–1634 (2016)
G.A. Hughes, Nanostructure-mediated drug delivery. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 1(1), 22–30 (2005)
D. Huang, D. Wu, Biodegradable dendrimers for drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 90, 713–727 (2018)
G. Pasut et al., PEG-epirubicin conjugates with high drug loading. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 20(3), 213–230 (2005)
M. Liu, J.M. Fréchet, Designing dendrimers for drug delivery. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 2(10), 393–401 (1999)
W.-D. Jang et al., Bioinspired application of dendrimers: from bio-mimicry to biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 34(1), 1–23 (2009)
Y. Cheng et al., New insights into the interactions between dendrimers and surfactants: 2. Design of new drug formulations based on dendrimer−surfactant aggregates. J. Phys. Chem. B 113(24), 8339–8346 (2009)
J.J. Michels et al., Well-defined assemblies of adamantyl-terminated poly (propylene imine) dendrimers and β-cyclodextrin in water. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1039/b002689l
V. Mishra, U. Gupta, N. Jain, Surface-engineered dendrimers: a solution for toxicity issues. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 20(2), 141–166 (2009)
H. Yang, W.J. Kao, Dendrimers for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 17(1–2), 3–19 (2006)
M.J. Cloninger, Biological applications of dendrimers. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 6(6), 742–748 (2002)
O. Milhem et al., Polyamidoamine Starburst® dendrimers as solubility enhancers. Int. J. Pharm. 197(1–2), 239–241 (2000)
F. Wang et al., Reducing cytotoxicity while improving anti-cancer drug loading capacity of polypropylenimine dendrimers by surface acetylation. Acta Biomater. 8(12), 4304–4313 (2012)
P. Kolhe et al., Drug complexation, in vitro release and cellular entry of dendrimers and hyperbranched polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 259(1–2), 143–160 (2003)
V. Kabanov et al., Polyelectrolyte behavior of astramol poly (propyleneimine) dendrimers. Macromolecules 31(15), 5142–5144 (1998)
E. Murugan et al., Evaluation of surface acetylated and internally quaternized poly (propylene imine) dendrimer as a biocompatible drug carrier for piroxicam as a model drug. RSC Adv. 5(129), 106461–106475 (2015)
A.K. Patri, J.F. Kukowska-Latallo, J.R. Baker Jr., Targeted drug delivery with dendrimers: comparison of the release kinetics of covalently conjugated drug and non-covalent drug inclusion complex. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 57(15), 2203–2214 (2005)
V. Patel et al., Dendrimers as novel drug-delivery system and its applications, in Drug Delivery Systems. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2020), pp. 333–392
H. Yang, S.T. Lopina, Penicillin V-conjugated PEG-PAMAM star polymers. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 14(10), 1043–1056 (2003)
R. Shukla et al., HER2 specific delivery of methotrexate by dendrimer conjugated anti-HER2 mAb. Nanotechnology 19(29), 295102 (2008)
B.K. Nanjwade et al., Dendrimers: emerging polymers for drug-delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 38(3), 185–196 (2009)
J.B. Wolinsky, M.W. Grinstaff, Therapeutic and diagnostic applications of dendrimers for cancer treatment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 60(9), 1037–1055 (2008)
S.H. Medina, M.E. El-Sayed, Dendrimers as carriers for delivery of chemotherapeutic agents. Chem. Rev. 109(7), 3141–3157 (2009)
A.S. Chauhan, Dendrimers for drug delivery. Molecules 23(4), 938 (2018)
M. Markowicz-Piasecka, E. Mikiciuk-Olasik, Dendrimers in drug delivery, in Nanobiomaterials in Drug Delivery. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2016), pp. 39–74
M. Markowicz et al., Evaluation of poly (amidoamine) dendrimers as potential carriers of iminodiacetic derivatives using solubility studies and 2D-NOESY NMR spectroscopy. J. Biol. Phys. 38(4), 637–656 (2012)
M. Najlah et al., Synthesis, characterization and stability of dendrimer prodrugs. Int. J. Pharm. 308(1–2), 175–182 (2006)
M. Ficker et al., Complexes of indomethacin with 4-carbomethoxy-pyrrolidone PAMAM dendrimers show improved anti-inflammatory properties and temperature-dependent binding and release profile. Mol. Pharm. 15(8), 3573–3582 (2018)
M. Gorzkiewicz et al., Pyrrolidone-modified PAMAM dendrimers enhance anti-inflammatory potential of indomethacin in vitro. Colloids Surf. B 181, 959–962 (2019)
L.D. Pedro-Hernández et al., Synthesis, characterization, and nanomedical applications of conjugates between resorcinarene-dendrimers and ibuprofen. Nanomaterials 7(7), 163 (2017)
J. Manikkath et al., Influence of peptide dendrimers and sonophoresis on the transdermal delivery of ketoprofen. Int. J. Pharm. 521(1–2), 110–119 (2017)
Ł Uram et al., The effect of biotinylated PAMAM G3 dendrimers conjugated with COX-2 inhibitor (celecoxib) and PPARγ agonist (Fmoc-L-Leucine) on human normal fibroblasts, immortalized keratinocytes and glioma cells in vitro. Molecules 24(20), 3801 (2019)
Ł Uram et al., Biotinylated PAMAM G3 dendrimer conjugated with celecoxib and/or Fmoc-l-Leucine and its cytotoxicity for normal and cancer human cell lines. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 124, 1–9 (2018)
J. Manikkath et al., Low frequency ultrasound and PAMAM dendrimer facilitated transdermal delivery of ketoprofen. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 41, 334–343 (2017)
B. Huang et al., Dendrimer-coupled sonophoresis-mediated transdermal drug-delivery system for diclofenac. Drug Des. Dev. Therapy 9, 3867 (2015)
A.J. Perisé-Barrios et al., Improved efficiency of ibuprofen by cationic carbosilane dendritic conjugates. Mol. Pharm. 13(10), 3427–3438 (2016)
A.S. Ertürk, M.U. Gürbüz, EDA Çekirdekli Amin, TRIS ve Karboksil Sonlu PAMAM Dendrimerleri Kullanarak Ketoprofenin Çözünürlüğünü Geliştirme. Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü Dergisi 22(2), 768–773 (2018)
S. Al-Azzawi et al., Dendrimeric poly (Epsilon-Lysine) delivery systems for the enhanced permeability of flurbiprofen across the blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19(10), 3224 (2018)
A. D’Emanuele, D. Attwood, Dendrimer–drug interactions. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 57(15), 2147–2162 (2005)
P. Singh et al., Folate and folate− PEG− PAMAM dendrimers: synthesis, characterization, and targeted anticancer drug delivery potential in tumor bearing mice. Bioconjug. Chem. 19(11), 2239–2252 (2008)
D. Chandrasekar et al., Folate coupled poly (ethyleneglycol) conjugates of anionic poly (amidoamine) dendrimer for inflammatory tissue specific drug delivery. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 82(1), 92–103 (2007)
R.I. Castro, O. Forero-Doria, L. Guzman, Perspectives of dendrimer-based nanoparticles in cancer therapy. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências 90(2), 2331–2346 (2018)
S. Kim et al., Engineered polymers for advanced drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 71(3), 420–430 (2009)
G. Pasut, F. Veronese, Polymer–drug conjugation, recent achievements and general strategies. Prog. Polym. Sci. 32(8–9), 933–961 (2007)
S.G. Sampathkumar, K.J. Yarema, in Dendrimers in Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis, Nanotechnologies for the Life Sciences (Wiley, 2007)
Y. Yue et al., Synthesis and characterization of G5 PAMAM dendrimer containing daunorubicin for targeting cancer cells. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 35(2), 343–349 (2012)
J.R. Baker, Dendrimer-based nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Hematology 2009(1), 708–719 (2009)
M. Marcinkowska et al., Multicomponent conjugates of anticancer drugs and monoclonal antibody with PAMAM dendrimers to increase efficacy of HER-2 positive breast cancer therapy. Pharm. Res. 36(11), 154 (2019)
D. Yoyen-Ermis et al., Tumor-induced myeloid cells are reduced by gemcitabine-loaded PAMAM dendrimers decorated with anti-Flt1 antibody. Mol. Pharm. 15(4), 1526–1533 (2018)
M. Marcinkowska et al., Conjugate of PAMAM dendrimer, doxorubicin and monoclonal antibody—trastuzumab: the new approach of a well-known strategy. Polymers 10(2), 187 (2018)
S.A. Torres-Pérez, M. del Pilar Ramos-Godínez, E. Ramón-Gallegos, Glycosylated one-step PAMAM dendrimers loaded with methotrexate for target therapy in breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 58, 101769 (2020)
D.-D. Chang et al., Click synthesis of glycosylated porphyrin-cored PAMAM dendrimers with specific recognition and thermosensitivity. J. Polym. Res. 25(12), 257 (2018)
A. Sharma et al., Effect of mannose targeting of hydroxyl PAMAM dendrimers on cellular and organ biodistribution in a neonatal brain injury model. J. Control. Release 283, 175–189 (2018)
H. Kulhari et al., Trastuzumab-grafted PAMAM dendrimers for the selective delivery of anticancer drugs to HER2-positive breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 1–13 (2016)
H. Kulhari et al., Optimization of carboxylate-terminated poly (amidoamine) dendrimer-mediated cisplatin formulation. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 41(2), 232–238 (2015)
H. Bhatt, B. Ghosh, S. Biswas, Cell-penetrating peptide and α-tocopherol-conjugated poly (amidoamine) dendrimers for improved delivery and anticancer activity of loaded paclitaxel. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 3(5), 3157–3169 (2020)
S.V.K. Rompicharla et al., Octa-arginine modified poly (amidoamine) dendrimers for improved delivery and cytotoxic effect of paclitaxel in cancer. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 46(sup2), 847–859 (2018)
K. Tokarczyk, B. Jachimska, Characterization of G4 PAMAM dendrimer complexes with 5-fluorouracil and their interactions with bovine serum albumin. Colloids Surf. A 561, 357–363 (2019)
C. Song et al., Efficient co-delivery of microRNA 21 inhibitor and doxorubicin to cancer cells using core–shell tecto dendrimers formed via supramolecular host–guest assembly. J. Mater. Chem. B 8(14), 2768–2774 (2020)
D.F. Argenta, S.M. Martelli, T. Caon, Dendrimer as a platform for drug delivery in the skin, in Materials for Biomedical Engineering. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2019), pp. 331–367
R.V. Movliya, P.M. Patel, Role of dendrimer in drug solubilisation—a review. Drug Deliv. Lett. 9(4), 265–276 (2019)
S. Svenson, D.A. Tomalia, Dendrimers in biomedical applications—reflections on the field. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 64, 102–115 (2012)
V.K. Yellepeddi, H. Ghandehari, Pharmacokinetics of oral therapeutics delivered by dendrimer-based carriers. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 16(10), 1051–1061 (2019)
J.D.A.K. Twibanire, T.B. Grindley, Polyester dendrimers: smart carriers for drug delivery. Polymers 6(1), 179–213 (2014)
K.M. Kitchens et al., Transport of poly (amidoamine) dendrimers across Caco-2 cell monolayers: influence of size, charge and fluorescent labeling. Pharm. Res. 23(12), 2818–2826 (2006)
V.K. Yellepeddi et al., Pediatric oral formulation of dendrimer-N-acetyl-l-cysteine conjugates for the treatment of neuroinflammation. Int. J. Pharm. 545(1–2), 113–116 (2018)
H.S. Sardo et al., A review on 5-aminosalicylic acid colon-targeted oral drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 558, 367–379 (2019)
R. Jevprasesphant et al., Engineering of dendrimer surfaces to enhance transepithelial transport and reduce cytotoxicity. Pharm. Res. 20(10), 1543–1550 (2003)
A. D’emanuele et al., The use of a dendrimer-propranolol prodrug to bypass efflux transporters and enhance oral bioavailability. J. Control. Release 95(3), 447–453 (2004)
M.G. Lancina III., H. Yang, Dendrimers for ocular drug delivery. Can. J. Chem. 95(9), 897–902 (2017)
T.F. Vandamme, L. Brobeck, Poly (amidoamine) dendrimers as ophthalmic vehicles for ocular delivery of pilocarpine nitrate and tropicamide. J. Control. Release 102(1), 23–38 (2005)
P.N. Desai, H. Yang, Synthesis and characterization of photocurable polyionic hydrogels. MRS Online Proc. Lib. Arch. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-1095-EE05-05
U. Kandekar et al., Dendrimers: novel drug nanocarriers. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2(5), 1086 (2011)
S. Bai, C. Thomas, F. Ahsan, Dendrimers as a carrier for pulmonary delivery of enoxaparin, a low-molecular weight heparin. J. Pharm. Sci. 96(8), 2090–2106 (2007)
M. Nasr et al., PAMAM dendrimers as aerosol drug nanocarriers for pulmonary delivery via nebulization. Int. J. Pharm. 461(1–2), 242–250 (2014)
L.M. Kaminskas et al., Pulmonary administration of a doxorubicin-conjugated dendrimer enhances drug exposure to lung metastases and improves cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 183, 18–26 (2014)
U.J. Chigbo, A.E. Ugochukwu, D.F. John, Dendrimers: a novel tool for drug delivery and targeting. Univers. J. Pharm. Res. 2(3), (2017). https://doi.org/10.22270/ujpr.v2i3.RW5
A. Castonguay et al., Dendrimers as bactericides. New J. Chem. 36(2), 199–204 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This manuscript was supported by Pharmacotherapy Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Bagyattallah University of Medical Sciences, and Tehran Iran.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikzamir, M., Hanifehpour, Y., Akbarzadeh, A. et al. Applications of Dendrimers in Nanomedicine and Drug Delivery: A Review. J Inorg Organomet Polym 31, 2246–2261 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-01925-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-01925-2