Abstract
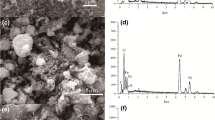
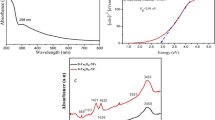
The aim of this present work is to investigate the adsorption capacity, kinetics and mechanism of arsenite ion removal onto beta-Cyclodextrin–Chitosan–Fe3O4 nanocomposite (β-CD–CS–Fe3O4 nanocomposite) from aqueous solutions. Iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4) were synthesized using the co-precipitation method and the nanocomposite was successfully prepared via the solution-blending method. The analysis to determine arsenite ion adsorption was carried out using ICP-MS by varying pH, contact time and arsenite concentration parameters. The sorption of arsenite was found to be dependent on pH, time and arsenite initial concentrations. The adsorption equilibrium was reached in the first 20 min with the maximum uptake of 96%. Adsorption data were fitted well to the Langmuir isotherm describing a monolayer adsorption mechanism and pseudo-second-order models for kinetic study. It was established that the β-CD–CS polymer blend grafted with Fe3O4 nanoparticles enhanced the adsorption capacity because of the complexation abilities of the multiple OH and NH2 groups in the polymer backbone with metal ions. Subsequently, the mechanism of adsorption was investigated by studying the physicochemical properties of the adsorbent and the adsorbed species using the FTIR, TGA, DSC, XRD, SEM and TEM techniques. The characterizations before and after incorporations of the β-CD–CS composite with Fe3O4 nanoparticles showed well-improved properties for better adsorption of arsenite (As(III)) ions.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.J. Nadakavukaren, R.L. Ingermann, G. Jeddeloh, S.J. Falkowski, Seasonal variation of arsenic concentration in well water in Lane County, Oregon. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 33, 264–269 (1984)
A.H. Malik, Z.M. Khan, Q. Mahmood, S. Nasreen, Z.A. Bhatti, Perspectives of low cost arsenic remediation of drinking water in Pakistan and other countries. J. Hazard. Mater. 168, 1–12 (2009)
M. Shih, An overview of arsenic removal by pressure-driven membrane processes. Desalination 172, 85–97 (2005)
Y. Wei, Y. Zheng, J.P. Chen, Enhanced adsorption of arsenate onto a natural polymer-based sorbent by surface atom transfer radical polymerization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 356, 234–239 (2011)
B.K. Mandal, K.T. Suzuki, Arsenic round the world: a review. Talanta 58, 201–235 (2002)
A.H. Smith et al., Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking water. Environ. Health Perspect. 97, 259–267 (1992)
E. Vunain, A.K. Mishra, R.W. Krause, Fabrication, Characterization and application of polymer nanocomposites for arsenic(III) removal from water. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 23, 293–305 (2013)
C.K. Jain, I. Ali, Arsenic: occurrence, toxicity and speciation techniques. Water Res. 34, 4304–4312 (2000)
J.C. Ng, J. Wang, A. Shraim, A global health problem caused by arsenic from natural sources. Chemosphere 52, 1353–1359 (2003)
C.E. Borba, R. Guirardello, E.A. Silva, M.T. Veit, C.R.G. Tavares, Removal of nickel (II) ions from aqueous solution by biosorption in a fixed bed column: experimental and theoretical breakthrough curves. Biochem. Eng. J. 30, 184–191 (2006)
N. Oyaro, O. Juddy, E.N.M. Murago, E. Gitonga, The contents of Pb, Cu, Zn and Cd in meat in Nairobi, Kenya. J. Food. Agric. Environ. 5, 119–121 (2007)
A.T. Paulino et al., Novel adsorbent based on silkworm chrysalides for removal of heavy metals from wastewaters. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 301, 479–487 (2006)
C. Namasivayam, K. Kadirvelu, Uptake of mercury (II) from wastewater by activated carbon from an unwanted agricultural solid by-product: coirpith. Carbon 37, 79–84 (1999)
R. Naseem, S.S. Tahir, Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous/acidic solutions by using bentonite as an adsorbent. Water Res. 35, 3982–3986 (2001)
L. Khezami, R. Capart, Removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution by activated carbons: kinetic and equilibrium studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 123, 223–231 (2005)
J.F. Ferguson, J.F. Ferguson, A review of the arsenic cycle in natural waters. Water Res. 6, 1259–1274 (2000)
P.L. Smedley, D.G. Kinniburgh, A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl. Geochem. 17, 517–568 (2002)
S. Wang, C.N. Mulligan, Occurrence of arsenic contamination in Canada: sources, behavior and distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 366, 701–721 (2006)
M.M. Ghosh, J.R. Yuan, Adsorption of inorganic arsenic and organoarsenicals on hydrous oxides. Environ. Prog. 6, 150–157 (1987)
D. Van Halem, S.A. Van Bakker, G.L. Amy, J.C. Dijk, Arsenic in drinking water: a worldwide water quality concern for water supply companies. Drink. Water Eng. Sci. 2, 29–34 (2009)
B. Al-rashdi, C. Somerfield, N. Hilal, Heavy metals removal using adsorption and nanofiltration techniques and nanofiltration techniques. Sep. Purif. Rev. 40, 209–259 (2016)
Ö Arar, Ü Yüksel, N. Kabay, M. Yüksel, Removal of Cu2+ ions by a micro-flow electrodeionization (EDI) system. Desalination 277, 296–300 (2011)
H. Modin, K.M. Persson, A. Andersson, M. Praagh, Van, Removal of metals from landfill leachate by sorption to activated carbon, bone meal and iron fines. J. Hazard. Mater. 189, 749–754 (2011)
H.K. Hansen, C. Gutie, L.M. Ottosen, Electrochemical peroxidation as a tool to remove arsenic and copper from smelter wastewater. J. Appl. Electrochem. 40, 1031–1038 (2010)
D. Adrian, Review paper a review of potentially low-cost sorbents for heavy metals. Water Res. 33, 2469–2479 (1999)
S. Babel, T.A. Kurniawan, Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 97, 219–243 (2003)
B.A. Veen, J.C.M. Van Der Uitdehaag, B.W. Dijkstra, Engineering of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase reaction and product specificity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1543, 336–360 (2000)
J. Szejtli, Past, present, and future of cyclodextrin research. Pure Appl. Chem. 76, 1825–1845 (2004)
F. Hapiot, S. Tilloy, E. Monflier, Cyclodextrins as supramolecular hosts for organometallic complexes. Chem. Rev. 106, 768–781 (2006)
Y. Chang, D. Chen, Preparation and adsorption properties of monodisperse chitosan-bound Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for removal of Cu(II) ions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 283, 446–451 (2005)
M. Liao, D. Chen, Fast and efficient adsorption/desorption of protein by a novel magnetic nano-adsorbent. Biotechnol. Lett. 24, 1913–1917 (2002)
M. Liao, D. Chen, Preparation and characterization of a novel magnetic. J. Mater. Chem. 12, 3654–3659 (2002)
Y. Sun, Preparation and magnetic properties of spindle porous iron nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 44, 961–965 (2009)
A. Kumar, M. Gupta, Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26, 3995–4021 (2005)
D.J. Greenland et al., Adsorption of polyvinyl alcohols by montmorillonite. J. Colloid. Sci. 18, 647–664 (1963)
A.K. Mishra, A.K. Sharma, Synthesis of γ-cyclodextrin/chitosan composites for the efficient removal of Cd(II) from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 49, 504–512 (2011)
M. Sugimoto, M. Morimotob, H. Sashiwab, H. Saimotob, Y. Shigemasabl, Carbohydrate polymers preparation and characterization of water-soluble chitin and chitosan derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 36, 49–59 (1998)
P.P. Dhawade, R.N. Jagtap, Characterization of the glass transition temperature of chitosan and its oligomers by temperature modulated differential scanning calorimetry. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 3, 1372–1382 (2012)
A. Gupta, V.S. Chauhan, N. Sankararamakrishnan, Preparation and evaluation of iron–chitosan composites for removal of As(III) and As(V) from arsenic contaminated real life groundwater. Water Res. 43, 3862–3870 (2009)
A. Zayed et al., Fe3O4/cyclodextrin polymer nanocomposites for selective heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater. Carbohydr. Polym. 91, 322–332 (2013)
D. Depan, B. Girase, J.S. Shah, R.D.K. Misra, Structure process and property relationship of the polar graphene oxide-mediated cellular response and stimulated growth of osteoblasts on hybrid chitosan network structure nanocomposite scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 7, 3432–3445 (2011)
L. Fan, C. Luo, M. Sun, H. Qiu, X. Li, Synthesis of magnetic β-cyclodextrin–chitosan/graphene oxide as nanoadsorbent and its application in dye adsorption and removal. Colloids Surf. B 103, 601–607 (2013)
L. Chen et al., Physicochemical and engineering aspects studies and comparison of the liquid adsorption and surface properties of α-, β- and γ-cyclodextrins by FTIR and capillary rise method. Colloids Surf. A 411, 69–73 (2012)
S. Ghosh, A.Z.M. Badruddoza, M.S. Uddin, K. Hidajat, Adsorption of chiral aromatic amino acids onto carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin bonded Fe3O4/SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 354, 483–492 (2011)
H. Cao, J. He, L. Deng, X. Gao, Fabrication of cyclodextrin-functionalized superparamagnetic Fe3O4/amino-silane core–shell nanoparticles via layer-by-layer method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 7974–7980 (2009)
M.F. Canbolat, A. Celebioglu, T. Uyar, Biointerfaces drug delivery system based on cyclodextrin-naproxen inclusion complex incorporated in electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibers. Colloids Surf. B 115, 15–21 (2014)
H. Wang et al., Chemical β-cyclodextrin/Fe3O4 hybrid magnetic nano-composite modified glassy carbon electrode for tryptophan sensing. Sens. Actuators B 163, 171–178 (2012)
X.I.N. Qu, A. Wirse, Structural change and swelling Mechanism of pH-sensitive hydrogels based on chitosan and D, L-lactic acid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 74, 3186–3192 (1999)
A. Albertsson, X.I.N. Qu, A. Wirse, Synthesis and characterization of pH-sensitive hydrogels based on chitosan and D, L-lactic acid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 74, 3193–3202 (1999)
L. Cui, Z. Zhang, E. Sun, X. Jia, Effect of β-cyclodextrin complexation on solubility and enzymatic conversion of naringin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 3, 14251–14261 (2012)
J. Li, B. Chen, X. Wang, S. Hong, Preparation and characterization of inclusion complexes formed by biodegradable poly(ε-caprolactone)–poly(tetrahydrofuran)–poly(ε-caprolactone) triblock copolymer and cyclodextrins. Polymer 45, 1777–1785 (2004)
N. Tabary, M.J. Garcia-fernandez, F. Danède, M. Descamps, B. Martel, Determination of the glass transition temperature of cyclodextrin polymers. Carbohydr. Polym. 148, 172–180 (2016)
K. Sakurai, T. Maegawa, T. Takahashi, Glass transition temperature of chitosan and miscibility of chitosan/poly (N-vinyl pyrrolidone) blends. Polymer 41, 7051–7056 (2000)
E. Demirbas, M. Kobya, E. Senturk, T. Ozkan, Adsorption kinetics for the removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solutions on the activated carbons prepared from agricultural wastes. Water SA 30, 533–540 (2004)
M. Kobya, E. Demirbas, Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by activated carbon prepared from apricot stone. Bioresour. Technol. 96, 1518–1521 (2005)
G. Karthikeyan, N.M. Andal, K. Anbalagan, Adsorption studies of iron (III) on chitin. J. Chem. Sci. 117, 663–672 (2005)
Z. Aksu, E. Balibek, Chromium (VI) biosorption by dried Rhizopus arrhizus: effect of salt (NaCl) concentration on equilibrium and kinetic parameters. J. Hazard. Mater. 145, 210–220 (2007)
P. Baskaralingam, M. Pulikesi, V. Ramamurthi, S. Sivanesan, Modified hectorites and adsorption studies of a reactive dye. Appl. Clay Sci. 37, 207–214 (2007)
P. Baskaralingam, M. Pulikesi, D. Elango, V. Ramamurthi, S. Sivanesan, Adsorption of acid dye onto organobentonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 128, 138–144 (2006)
H.C. Zhao, Adsorption study for removal of Congo red anionic dye using organo-attapulgite. J. Adsorpt. 15, 381–389 (2009)
A.K.Z. Bouberka, F.S.M. Kameche, Z. Derriche, Adsorption study of an industrial dye by an organic clay. J. Adsorpt. 13, 149–158 (2007)
G. Crini, Kinetic and equilibrium studies on the removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption onto a cyclodextrin polymer. Dyes Pigm. 77, 415–426 (2008)
Y.S. Ho, G. Mckay, Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 34, 451–465 (1999)
L. Li et al., Adsorbent for chromium removal based on graphene oxide functionalized with magnetic cyclodextrin–chitosan. Colloids Surf. B 107, 76–83 (2013)
G. Crini, H.N. Peindy, F. Gimbert, C. Robert, Removal of CI basic green 4 (Malachite green) from aqueous solutions by adsorption using cyclodextrin-based adsorbent: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 53, 97–110 (2007)
Y. Feng, J. Gong, G. Zeng, Q. Niu, H. Zhang, Adsorption of Cd(II) and Zn(II) from aqueous solutions using magnetic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 162, 487–494 (2010)
Y. Zhou, C. Branford-white, H. Nie, L. Zhu, Biointerfaces adsorption mechanism of Cu2+ from aqueous solution by chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles modified with α-ketoglutaric acid. Colloids Surf. B 74, 244–252 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsiepe, J.T., Mamba, B.B., Inamuddin et al. Fe3O4–β-cyclodextrin–Chitosan Bionanocomposite for Arsenic Removal from Aqueous Solution. J Inorg Organomet Polym 28, 467–480 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-017-0741-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-017-0741-3