Abstract
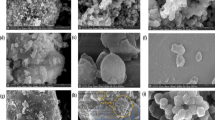
Amino-functionalized magnetic mesoporous microsphere has been successfully synthesized through a two-step coating process of silica on a magnetic core (Fe3O4). In the synthesis process, cetyltrimethyl ammoniumbromide (CTAB) was used as a structure-directing agent and it was removed by combination of solvent extraction and calcination modified processes. In this method, mesoporous silica shell with higher surface area was formed which could facilitate the loading of much more amino groups and the capacity to adsorb more heavy metal ions such as Zn2+ was provided. Different amounts of 3-aminopropyl triethoxysilane (APTES) were examined in order to obtain an optimum amount of amino groups which can be grafted on Fe3O4/SiO2/meso-SiO2 microsphere. The resultant multifunctional microsphere was characterized by field emission scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope, FTIR spectrophotometer, X-ray diffraction, vibration sample magnetometer, thermogravimetric analysis, nitrogen adsorption–desorption and particle size analyzer. Comparing to functionalized amino group on traditional magnetic mesoporous silica, the as-prepared microsphere not only exhibited higher specific surface area (617.31 m2 g−1) but also demonstrated higher adsorption capacity for Zn(II) (270.2703 mg g−1 at 25 °C). Important of all, the adsorbent was simply removed from sample solution by magnetic field and it was regenerated by acid treatment.
Graphical Abstract
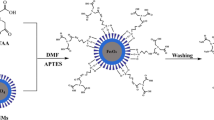
Synthetic route of Fe3O4/SiO2/meso-SiO2–NH2 and its use for Zn(II) ions removal.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Norton, K. Baskaran, T. McKenzie, Biosorption of zinc from aqueous solutions using biosolids. Adv. Environ. Res. 8, 629–635 (2004)
Y.-h. Zhu, S. Yuan, D. Bao, Y.-b. Yin, H.-x. Zhong, X.-b. Zhang, J.-m. Yan, Q. Jiang, Decorating waste cloth via industrial wastewater for tube-type flexible and wearable sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 29, 1603719-n/a (2017)
A.I. Bush, Metals and neuroscience. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 4, 184–191 (2000)
Y. Miller, B. Ma, R. Nussinov, Zinc ions promote alzheimer Aβ aggregationvia population shift of polymorphic states. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 107, 21 (2010)
J.A. Duce, A. Tsatsanis, M.A. Cater, S.A. James, E. Robb, K. Wikhe, S.L. Leong, K. Perez, T. Johanssen et al., Iron-export ferroxidase activity of β-amyloid precursor protein is inhibited by zinc in alzheimer’s disease. Cell 142, 857–867 (2010)
M. del Mar Gómez-Tamayo, A. Macías-García, M.A. Díaz Díez, E.M. Cuerda-Correa, Adsorption of Zn(II) in aqueous solution by activated carbons prepared from evergreen oak (Quercus rotundifolia L.). J. Hazard. Mater. 153, 28–36 (2008)
C. Wang, J. Chen, Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol. Adv. 27, 195–226 (2009)
J. Chen, C. Wang, Removal of Pb2+, Ag+, Cs+ and Sr2+ from aqueous solution by brewery’s waste biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 151, 65–70 (2008)
Z. Elouear, J. Bouzid, N. Boujelben, M. Feki, F. Jamoussi, A. Montiel, Heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions by activated phosphate rock. J. Hazard. Mater. 156, 412–420 (2008)
G. Crini, Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresour. Technol. 97, 1061–1085 (2006)
H. Jiang, P. Chen, S. Luo, X. Luo, X. Tu, Q. Cao, Y. Zhou, W. Zhang, Synthesis of novel biocompatible composite Fe3O4/ZrO2/Chitosan and its application for dye removal. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 23, 393–400 (2013)
E. Cerrahoğlu, A. Kayan, D. Bingöl, New inorganic–organic hybrid materials and their oxides for removal of heavy metal ions: response surface methodology approach. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 27, 427–435 (2017)
E. Vunain, A.K. Mishra, R.W. Krause, Fabrication, characterization and application of polymer nanocomposites for arsenic(iii) removal from water. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 23, 293–305 (2013)
A.S.S. Frank Caruso, G. Michael, M. Helmuth, Magnetic core–shell particles: preparation of magnetite multilayers on polymer latex microspheres. Am. Chem. Soc. 11, 950–953 (1999)
N.H. Desheng Wang, R. Nista, R. Zeev, Superparamagnetic Fe2O3 beads–CdSe/ZnS quantum dots core–shell nanocomposite particles for cell separation. Nano Lett. 4, 409–413 (2004)
Y.D. Lan Jin, J. Hu, C. Wang, Preparation and characterization of core–shell polymer particles with protonizable shells prepared by oxyanionic polymerization. Polym. Sci. A 42, 6081–6088 (2004)
Y.D. Wei Li, W. Zhangxiong, X. Qian, J. Yang, Y. Wang, G. Dong, F. Zhang, B. Tu, D. Zhao, Hydrothermal etching assisted crystallization: a facile route to functional yolk-shell titanate microspheres with ultrathin nanosheets-assembled double shells. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 15830–15833 (2011)
J.G. Wenru Zhao, L. Zhang, H. Chen, J. Shi, Fabrication of uniform magnetic nanocomposite spheres with a magnetic core/mesoporous silica shell structure. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 8916–8917 (2005)
E. Khosroshahi, M.L. Ghazanfari, Synthesis and functionalization of SiO2 coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles with amine groups based on self-assembly. Mater. Sci. Eng. 32, 1043–1049 (2012)
W. Mokaya, R. Jones, Physicochemical characterisation and catalytic activity of primary amine templated aluminosilicate mesoporous catalysts. J. Catal. 172, 211–221 (1997)
R. Hitz, S. Prins, Influence of template extraction on structure, activity, and stability of MCM-41 catalysts. J. Catal. 168, 194–206 (1997)
T. Tanev, P.T.J. Pinnavaia, Mesoporous silica molecular sieves prepared by ionic and neutral surfactant templating: a comparison of physical properties. Chem. Mater. 8, 2068–2079 (1996)
B. Stein, A. Holland, Aluminum-containing mesostructural materials. J. Porous. Mater. 3, 83–92 (1996)
M.T. Keene, R.D. Gougeon, R. Denoyel, R.K. Harris, J. Rouquerol, P.L. Llewellyn, Calcination of the MCM-41 mesophase: mechanism of surfactant thermal degradation and evolution of the porosity. J. Mater. Chem. 9, 2843–2849 (1999)
W.A. Gomes Jr., L.A.M. Cardoso, A.R.E. Gonzaga, L.G. Aguiar, H.M.C. Andrade, Influence of the extraction methods to remove organic templates from Al-MCM-41 molecular sieves. Mater. Chem. Phys. 93, 133–137 (2005)
W. Mokaya, R. Jones, The influence of template extraction on the properties of primary amine templated aluminosilicate mesoporous molecular sieves. J. Mater. Chem. 8, 2819–2826 (1998)
M. Kumar, D.P.S. Rathore, A.K. Singh, Amberlite XAD-2 functionalized with o-aminophenol: synthesis and applications as extractant for copper(II), cobalt(II), cadmium(II), nickel(II), zinc(II) and lead(II). Talanta 51, 1187–1196 (2000)
K.L.Y. Koon Fung Lam, G. McKay, Efficient approach for Cd2+ and Ni2+ removal and recovery using mesoporous adsorbent with tunable selectivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41, 3329 (2007)
J. Li, X. Miao, Y. Hao, J. Zhao, X. Sun, L. Wang, Synthesis, amino-functionalization of mesoporous silica and its adsorption of Cr(VI). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 318, 309–314 (2008)
C. Sun, R. Qu, C. Ji, C. Wang, Y. Sun, Z. Yue, G. Cheng, Preparation and adsorption properties of crosslinked polystyrene-supported low-generation diethanolamine-typed dendrimer for metal ions. Talanta 70, 14–19 (2006)
P. Yang, Z. Quan, Z. Hou, C. Li, X. Kang, Z. Cheng, J. Lin, A magnetic, luminescent and mesoporous core–shell structured composite material as drug carrier. Biomaterials 30, 4786–4795 (2009)
Z. Li, D. Huang, C. Fu, B. Wei, W. Yu, C. Deng, X. Zhang, Preparation of magnetic core mesoporous shell microspheres with C18-modified interior pore-walls for fast extraction and analysis of phthalates in water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 1218, 6232–6239 (2011)
L. Zhao, Y. Chi, Q. Yuan, N. Li, W. Yan, X. Li, Phosphotungstic acid anchored to amino–functionalized core–shell magnetic mesoporous silica microspheres: a magnetically recoverable nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 390, 70–77 (2013)
F. Aboufazeli, H.R.L.Z. Zhad, O. Sadeghi, M. Karimi, E. Najafi, Novel ion imprinted polymer magnetic mesoporous silica nano-particles for selective separation and determination of lead ions in food samples. Food. Chem. 141, 3459–3465 (2013)
W. Li, B. Zhang, X. Li, H. Zhang, Q. Zhang, Preparation and characterization of novel immobilized Fe3O4@SiO2@mSiO2–Pd(0) catalyst with large pore-size mesoporous for Suzuki coupling reaction. Appl. Catal. A 459, 65–72 (2013)
A.S.S. Ibrahim,, A.A. Al-Salamah, A.M. El-Toni, M.A. El-Tayeb, Y.B. Elbadawi, Cyclodextrin glucanotransferase immobilization onto functionalized magnetic double mesoporous core–shell silica nanospheres. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 17, 55–64 (2014)
X. Li, W. Zhao, J. Gu, Y. Li, L. Li, D. Niu, J. Shi, Facile synthesis of magnetic core-mesoporous shell structured sub-microspheres decorated with NiO nanoparticles for magnetic recyclable separation of proteins. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 207, 142–148 (2015)
W.-H. Chen, G.-F. Luo, Q. Lei, F.-Y. Cao, J.-X. Fan, W.-X. Qiu, H.-Z. Jia, S. Hong, F. Fang et al., Rational design of multifunctional magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticle for tumor-targeted magnetic resonance imaging and precise therapy. Biomaterials 76, 87–101 (2016)
S. Bao, L. Tang, K. Li, P. Ning, J. Peng, H. Guo, T. Zhu, Y. Liu, Highly selective removal of Zn(II) ion from hot-dip galvanizing pickling waste with amino-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 magnetic nano-adsorbent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 462, 235–242 (2016)
Z. Sun, H. Li, G. Cui, Y. Tian, S. Yan, Multifunctional magnetic core–shell dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres decorated with tiny Ag nanoparticles as a highly active heterogeneous catalyst, Appl. Surf. Sci. 360, 252–262 (2016)
M. Koneracká, P. Kopčanský, M. Antalík, M. Timko, C.N. Ramchand, D. Lobo, R.V. Mehta, R.V. Upadhyay, Immobilization of proteins and enzymes to fine magnetic particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 201, 427–430 (1999)
W. Stöber, A. Fink, E. Bohn, Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 26, 62–69 (1968)
M. Seenuvasan, C.G. Malar, S. Preethi, N. Balaji, J. Iyyappan, M.A. Kumar, K.S. Kumar, Fabrication, characterization and application of pectin degrading Fe3O4–SiO2 nanobiocatalyst. Mater. Sci. Eng. 33, 2273–2279 (2013)
Xu, J.-J., Wang, Z.-L., Xu, D., L.-L. Zhang, X.-B. Zhang, Tailoring deposition and morphology of discharge products towards high-rate and long-life lithium-oxygen batteries. Nat. Commun. 4, 2438 (2013)
J.-J. Xu, Z.-L. Wang, D. Xu, F.-Z. Meng, X.-B. Zhang, 3D ordered macroporous LaFeO3 as efficient electrocatalyst for Li-O2 batteries with enhanced rate capability and cyclic performance. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 2213–2219 (2014)
Y.-B. Yin, J.-J. Xu, Q.-C. Liu, X.-B. Zhang, Macroporous interconnected hollow carbon nanofibers inspired by golden-toad eggs toward a binder-free, high-rate, and flexible electrode. Adv. Mater. 28, 7494–7500 (2016)
Q. Yuan, Y. Chi, N. Yu, Y. Zhao, W. Yan, X. Li, B. Dong, Amino-functionalized magnetic mesoporous microspheres with good adsorption properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 49, 279–284 (2014)
Y. Tang, S. Liang, J. Wang, S. Yu, Y. Wang, Amino-functionalized core-shell magnetic mesoporous composite microspheres for Pb(II) and Cd(II) removal. J. Environ. Sci. 25, 830–837 (2013)
Z. Xu, Y. Feng, X. Liu, M. Guan, C. Zhao, H. Zhang, Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4@SiO2@ poly-l-alanine, peptide brush–magnetic microspheres through NCA chemistry for drug delivery and enrichment of BSA. Colloids Surf. B 81, 503–507 (2010)
L. Wang, Y. Sun, J. Wang, J. Wang, A. Yu, H. Zhang, D. Song, Preparation of surface plasmon resonance biosensor based on magnetic core/shell Fe3O4/SiO2 and Fe3O4/Ag/SiO2 nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 84, 484–490 (2011)
S.N. Abdollahi, M. Naderi, G. Amoabediny, Synthesis and physicochemical characterization of tunable silica–gold nanoshells via seed growth method. Colloids Surf. A 414, 345–351 (2012)
D. Shao, K. Xu, X. Song, J. Hu, W. Yang, C. Wang, Effective adsorption and separation of lysozyme with PAA-modified Fe3O4@silica core/shell microspheres. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 336, 526–532 (2009)
T.S. Sasikala, S. Raman, P. Mohanan, C. Pavithran, M.T. Sebastian, Effect of silane coupling agent on the dielectric and thermal properties of DGEBA-forsterite composites. J. Polym. Res. 18, 811–819 (2010)
P. Xu, H. Wang, R. Tong, Q. Du, W. Zhong, Preparation and morphology of SiO2/PMMA nanohybrids by microemulsion polymerization. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 284, 755–762 (2006)
J. Wang, S. Zheng, Y. Shao, J. Liu, Z. Xu, D. Zhu, Amino-functionalized Fe(3)O(4)@SiO(2) core-shell magnetic nanomaterial as a novel adsorbent for aqueous heavy metals removal. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 349, 293–299 (2010)
X. Zhang, H. Niu, Y. Pan, Y. Shi, Y. Cai, Modifying the surface of Fe3O4/SiO2 magnetic nanoparticles with C18/NH2 mixed group to get an efficient sorbent for anionic organic pollutants. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 362, 107–112 (2011)
S. Hozhabr Araghi, M.H. Entezari, M. Chamsa, Modification of mesoporous silica magnetite nanoparticles by 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane for the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 218, 101–111 (2015)
M. Rosenholm, J., M. Lindén, Towards establishing structure–activity relationships for mesoporous silica in drug delivery applications. J. Control. Release 128, 157–164 (2008)
K.K. Sharma, A. Anan, R.P. Buckley, W. Ouellette, T. Asefa, Toward efficient nanoporous catalysts: controlling site-isolation and concentration of grafted catalytic sites on nanoporous materials with solvents and colorimetric elucidation of their site-isolation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 218–228 (2008)
T. Yokoi, H. Yoshitake, T. Tatsumi, Synthesis of amino-functionalized MCM-41 via direct co-condensation and post-synthesis grafting methods using mono-, di- and tri-amino-organoalkoxysilanes”. J. Mater. Chem. 14, 951–957 (2004)
Z. Lei, Y. Li, X. Wei, A facile two-step modifying process for preparation of poly(SStNa)-grafted Fe3O4/SiO2 particles. J. Solid State Chem. 181, 480–486 (2008)
Y.-M. Hao, C. Man, Z.-B. Hu, Effective removal of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution by amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mat. 184, 392–399 (2010)
M. Monier, D.M. Ayad, Y. Wei, A.A. Sarhan, Adsorption of Cu(II), Co(II), and Ni(II) ions by modified magnetic chitosan chelating resin. J. Hazard. Mat. 177, 962–970 (2010)
M. Mureseanu, A. Reiss, I. Stefanescu, E. David, V. Parvulescu, G. Renard, V. Hulea, Modified SBA-15 mesoporous silica for heavy metal ions remediation. Chemosphere 73, 1499–1504 (2008)
H. Karami, Heavy metal removal from water by magnetite nanorods. Chem. Eng. J. 219, 209–216 (2013)
M. Adeli, Y. Yamini, M. Faraji, Removal of copper, nickel and zinc by sodium dodecyl sulphate coated magnetite nanoparticles from water and wastewater samples. Arab. J. Chem. 10, s514–s521 (2017)
F. Ge, M.-M. Li, H. Ye, B.-X. Zhao, Effective removal of heavy metal ions Cd2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Cu2+ from aqueous solution by polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mat. 211–212, 366–372 (2012)
Y. Zhu, J. Hu, J. Wang, Competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) onto xanthate-modified magnetic chitosan. J. Hazard. Mater. 221–222, 155–161 (2012)
F. An, B. Gao, X. Dai, M. Wang, X. Wang, Efficient removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution using salicylic acid type chelate adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mat. 192, 956–962 (2011)
D. Adamczuk, A. Kołodyńska, Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies on removal of chromium, copper, zinc and arsenic from aqueous solutions onto fly ash coated by chitosan. Chem. Eng. J. 274, 200–212 (2015)
L. Jiang, S. Li, H. Yu, Z. Zou, X. Hou, F. Shen, C. Li, X. Yao, Amino and thiol modified magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes for the simultaneous removal of lead, zinc, and phenol from aqueous solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 369, 398–413 (2016)
S. Lapwanit, T. Trakulsujaritchok, P.N. Nongkhai, Chelating magnetic copolymer composite modified by click reaction for removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 289, 286–295 (2016)
J. Zhang, S. Zhai, S. Li, Z. Xiao, Y. Song, Q. An, G. Tian, Pb(II) removal of Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2 core–shell nanomaterials prepared via a controllable sol–gel process. Chem. Eng. J. 215–216, 461–471 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Ghodratollah Absalan, Professor Masoumi Laboratory, Department of chemistry, collage of science, Shiraz University, for his kind assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kheshti, Z., Hassanajili, S. Novel Multifunctional Mesoporous Microsphere with High Surface Area for Removal of Zinc Ion from Aqueous Solution: Preparation and Characterization. J Inorg Organomet Polym 27, 1613–1626 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-017-0621-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-017-0621-x