Abstract
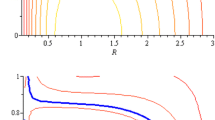
The ITER superconducting magnet systems consists of four main sub-systems: toroidal field (TF) coils, central solenoid coils, poloidal field coils, and correction coils. Like many other ITER systems, the magnet components are supplied in-kind by six domestic agencies. The technical specifications, manufacturing processes and procedures required to fabricate these components are particularly challenging. The management structure and organization to realize this procurement within the tight ITER construction schedule is very complex. On the other hand, toroidal magnetic field ripple in tokamak is an important issue in plasma equilibrium and stability studies. Toroidal magnetic field is created by toroidal torus with finite number of coils, therefore the field has a ripple in torus space. In this paper, we have reviewed the ITER magnetic coils materials, and also we have estimated the amplitude of TF ripples and its dependence to numbers of coils using the “Comsol Multiphysics” software. The calculations which performed for three: 8, 16 and 32 toroidal coils, indicates that increasing the number of toroidal coils lead to reduction of magnetic field ripple and lead to more stable plasma, but diagnostic access to plasma is reduces.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
03 May 2023
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02674-0
References
J. Wesson, Tokamaks, 3rd edn. (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 2004)
J.P. Freidberg, Plasma Physics and Fusion Energy (MIT Press, Cambridge, 2002)
C.C. Petty et al., Nucl. Fusion 44(2), 243 (2004)
M. Spolaore et al., Czech J. Phys. 55(12), 1615–1621 (2005)
P. Devynck et al., Phys. Plasmas 13(10), 102505–102513 (2006)
A. Salar Elahi, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 40, 892–897 (2012)
B. Viatcheslav et al., J. Plasma Fusion Res. 5, 418–423 (2002)
E.Y. Wang et al., Nucl. Fusion 35, 467 (1995)
ChP Ritz et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 59, 1739–1744 (1998)
V.V. Bulanin et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 48, A101 (2006)
J.A.C. Cabral et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 40, 1001 (1998)
C. Silva et al. 17th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference, EX/P1-10 Lyon, France (2002)
A. Salar Elahi, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 38(2), 181–185 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 38(9), 3163–3167 (2010)
M. Emami, M. Ghoranneviss, A. Salar Elahi, A.R. Rad, J. Plasma Phys. 76(1), 1–8 (2009)
A. Salar Elahi, Fusion Eng. Des. 85, 724–727 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, Phys. Scr. 80, 045501 (2009)
A. Salar Elahi, Phys. Scr. 80, 055502 (2009)
A. Salar Elahi, Phys. Scr. 81(5), 055501 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, Phys. Scr. 82, 025502 (2010)
M. Ghoranneviss, A. Salar Elahi, Phys. Scr. 82(3), 035502 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 28(4), 346–349 (2009)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 28(4), 416–419 (2009)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 28(4), 408–411 (2009)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 28(4), 412–415 (2009)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 28(4), 394–397 (2009)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 28(4), 404–407 (2009)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 28(4), 390–393 (2009)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 28(4), 385–389 (2009)
A.R. Rad, M. Ghoranneviss, M. Emami, A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 28(4), 420–426 (2009)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(1), 1–4 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(1), 22–25 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(1), 29–31 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(1), 26–28 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(1), 32–35 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(1), 36–40 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(1), 62–64 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(1), 76–82 (2010)
A.R. Rad, M. Emami, M. Ghoranneviss, A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(1), 73–75 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(1), 83–87 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(1), 88–93 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(3), 209–214 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(3), 232–236 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(3), 251–255 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(3), 279–284 (2010)
M. Ghoranneviss, A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(5), 467–470 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 29(5), 461–465 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, Braz. J Phys. 40(3), 323–326 (2010)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 30(2), 116–120 (2011)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 30(6), 477–480 (2011)
A. Salar Elahi, Fusion Eng. Des. 86, 442–445 (2011)
A. Salar Elahi, J. Fusion Energy 31(2), 191–194 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Mahdavipour, B., Salar Elahi, A. & Ghoranneviss, M. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Tokamak Coils Materials and Toroidal Field Ripples Calculation Using the Comsol Multiphysics. J Inorg Organomet Polym 26, 439–445 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-015-0325-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-015-0325-z