Abstract
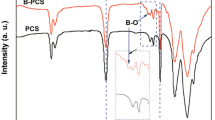
A polycarbosilane precursor of SiC fiber was synthesized at high temperature under high pressure from liquid polysilane (LPS), which was obtained by thermal decomposition of poly(dimethylsilane). The effect of reaction temperature on the Si–H bond content, degree of linearity, Si–Si bond content, molecular weight, molecular weight distribution, elemental composition, softening point, and yield of the polycarbosilane (PCS) was studied spectroscopically (FTIR, UV, 1H-NMR, and 29Si-NMR) and by gel permeation chromatography (GPC). The results showed that the molecular weight, yield and softening point of the PCS increased, the molecular weight distribution broadened, and the Si–Si bond content and degree of linearity decreased when the reaction temperature increased. The Si–H bond content increased when the thermolysis reaction temperature was less than 450°C and decreased when the temperature was over 460°C. Increasing of the reaction temperature affected the composition with a general decrease in the amount of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in the product. A middle molecular weight region of PCS in the GPC appears when the reaction temperature approaches 450°C; and, the as-synthesized PCS was stable with low Si–Si bond content. Synthetically, the conversion process is initially the formation of PCS by thermal decomposition of LPS, which is followed by an increase in molecular weight via condensation of PCS molecules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Schilling SuffixJr. J. P. Wesson T. C. Williams (1983) Ceramic Bull. 62 IssueID8 912 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXls1arsbc%3D
Ch. Zengyong S. Yongcai F. Chunxiang (2002) J. Inorg. Mater. 7 IssueID2 193
M. Birot J. P. Pillot J. Dunogues (1995) Chem. Rev. 95 1443 Occurrence Handle10.1021/cr00037a014 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXmvF2ht70%3D
R. M. Laine F. Babonneau (1993) Chem. Mater. 5 260 Occurrence Handle10.1021/cm00027a007 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXhtlSitr8%3D
S. Yahima Y. Hasegawa J. Hayashi (1978) J. Mater. Sci. 13 2569
Y. Hasegawa K. Okamura (1986) J. Mater. Sci. 21 321 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01144739 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XhtlSmsbc%3D
S. Yongcai W. Ling F. Chunxiang (1997) Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 13 IssueID4 30
H. Q. Ly R. Taylor R. J. Day (2001) J. Mater. Sci. 36 4037 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1017942826657 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmslGrtr0%3D
C. Feng, Doctoral thesis. National University of Defense Technology, 2002
S. Yongcai Sh. Yao F. Chunxiang (1995) Acta Polymerica Sin. 12 IssueID6 753
X. L. Fan, Doctoral thesis. National University of Defense Technology, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, X., Xie, Z., Xiao, J. et al. Influence of Temperature on the Properties of Polycarbosilane. J Inorg Organomet Polym 15, 253–259 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-004-5542-9
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-004-5542-9