Abstract
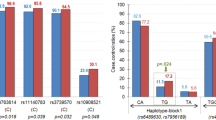
Pathological gambling (PG) is an impulse control disorder that has been considered as a behavioral addiction. Recent studies have suggested the involvement of the dopaminergic system in addictions and impulse control disorders and associations of dopamine receptor genes (DRD1, DRD2, and DRD4) and PG have been reported. In the present study, 140 sib-pairs discordant for the diagnosis of PG (70 males and 70 females on each group) were recruited through the Gambling Outpatient Unit at the Institute of Psychiatry, University of Sao Paulo and were assessed by trained psychiatrists. A family-based association design was chosen to prevent population stratification. All subjects were genotyped for dopamine receptor genes (DRD1 −800 T/C, DRD2 TaqIA RFLP, DRD3 Ser9Gly, DRD4 48bp exon III VNTR, DRD5 (CA) repeat) and the dopamine transporter gene (SCL6A3 40 bp VNTR). Our results suggest the association of PG with DRD1 −800 T/C allele T (P = .03).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.P.A. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-IV), 4th ed. Washington (DC): American Psychiatric Association.
Barr, C. L., Wigg, K. G., Bloom, S., Schachar, R., Tannock, R., Roberts, W., Malone, M., & Kennedy, J. L. (2000a). Further evidence from haplotype analysis for linkage of the dopamine D4 receptor gene and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 96, 262–267.
Barr, C. L., Wigg, K. G., Feng, Y., Zai, G., Malone, M., Roberts, W., Schachar, R., Tannock, R., & Kennedy, J. L. (2000b). Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and the gene for the dopamine D5 receptor. Molecular Psychiatry, 5, 548–551.
Black, D. W., & Moyer, T. (1998). Clinical features and psychiatric comorbidity of subjects with pathological gambling behavior. Psychiatric Services, 49, 1434–1439.
Black, D. W., Monahan, P. O., Temkit, M., & Shaw, M. (2006). A family study of pathological gambling. Psychiatry Research, 141, 295–303.
Black, D. W., Moyer, T., & Schlosser, S. (2003). Quality of life and family history in pathological gambling. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 191, 124–126.
Blanco, C., Moreyra, P., Nunes, E. V., Saiz-Ruiz, J., & Ibanez, A. (2001). Pathological gambling: addiction or compulsion? Seminars in Clinical Neuropsychiatry, 6, 167–176.
Blum, K., Sheridan, P. J., Wood, R. C., Braverman, E. R., Chen, T. J., & Comings, D. E. (1995). Dopamine D2 receptor gene variants: association and linkage studies in impulsive-addictive-compulsive behaviour. Pharmacogenetics, 5, 121–141.
Bobb, A. J., Addington, A. M., Sidransky, E., Gornick, M. C., Lerch, J. P., Greenstein, D. K., Clasen, L. S., Sharp, W. S., Inoff-Germain, G., Wavrant-De Vrieze, F., Arcos-Burgos, M., Straub, R. E., Hardy, J. A., Castellanos, F. X., & Rapoport, J. L. (2005). Support for association between ADHD and two candidate genes: NET1 and DRD1. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 134, 67–72.
Boehnke, M., & Langefeld, C. D. (1998). Genetic association mapping based on discordant sib pairs: the discordant-alleles test. American Journal of Human Genetics, 62, 950–961.
Callegari-Jacques, S. M., Grattapaglia, D., Salzano, F. M., Salamoni, S. P., Crossetti, S. G., Ferreira, M. E., & Hutz, M. H. (2003). Historical genetics: spatiotemporal analysis of the formation of the Brazilian population. American Journal of Human Biology, 15, 824–834.
Cetin, T., Freudenberg, F., Fuchtemeier, M., & Koch, M. (2004). Dopamine in the orbitofrontal cortex regulates operant responding under a progressive ratio of reinforcement in rats. Neuroscience Letters, 370, 114–117.
Cichon, S., Nothen, M. M., Stober, G., Schroers, R., Albus, M., Maier, W., Rietschel, M., Korner, J., Weigelt, B., Franzek, E., Wildenauer, D., Fimmers, R., Propping, P. (1996). Systematic screening for mutations in the 5'-regulatory region of the human dopamine D1 receptor (DRD1) gene in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 67, 424–428.
Comings, D. E., Comings, B. G., Muhleman, D., Dietz, G., Shahbahrami, B., Tast, D., Knell, E., Kocsis, P., Baumgarten, R., Kovacs, B. W. et al. (1991). The dopamine D2 receptor locus as a modifying gene in neuropsychiatric disorders. JAMA, 266, 1793–1800.
Comings, D. E., Gade, R., Wu, S., Chiu, C., Dietz, G., Muhleman, D., Saucier, G., Ferry, L., Rosenthal, R. J., Lesieur, H. R., Rugle, L. J., & MacMurray, P. (1997). Studies of the potential role of the dopamine D1 receptor gene in addictive behaviors. Molecular Psychiatry, 2, 44–56.
Comings, D. E., Gade-Andavolu, R., Gonzalez, N., Wu, S., Muhleman, D., Chen, C., Koh, P., Farwell, K., Blake, H., Dietz, G., MacMurray, J. P., Lesieur, H. R., Rugle, L. J., & Rosenthal, R. J. (2001). The additive effect of neurotransmitter genes in pathological gambling. Clinical Genetics, 60, 107–116.
Comings, D. E., Gonzalez, N., Wu, S., Gade, R., Muhleman, D., Saucier, G., Johnson, P., Verde, R., Rosenthal, R. J., Lesieur, H. R., Rugle, L. J., Miller, W. B., & MacMurray, J. P. (1999). Studies of the 48 bp repeat polymorphism of the DRD4 gene in impulsive, compulsive, addictive behaviors: Tourette syndrome, ADHD, pathological gambling, and substance abuse. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 88, 358–368.
Comings, D. E., Rosenthal, R. J., Lesieur, H. R., Rugle, L. J., Muhleman, D., Chiu, C., Dietz, G., & Gade, R. (1996). A study of the dopamine D2 receptor gene in pathological gambling. Pharmacogenetics, 6, 223–234.
Cook, E. H. Jr., Stein, M. A., Krasowski, M. D., Cox, N. J., Olkon, D. M., Kieffer, J. E., & Leventhal, B. L. (1995). Association of attention-deficit disorder and the dopamine transporter gene. American Journal of Human Genetics, 56, 993–998.
Crockford, D. N., & el-Guebaly, N. (1998). Psychiatric comorbidity in pathological gambling: a critical review. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 43, 43–50.
Crockford, D. N., Goodyear, B., Edwards, J., Quickfall, J., & el-Guebaly, N. (2005). Cue-induced brain activity in pathological gamblers. Biological Psychiatry, 58, 787–795.
Crocq, M. A., Mant, R., Asherson, P., Williams, J., Hode, Y., Mayerova, A., Collier, D., Lannfelt, L., Sokoloff, P., Schwartz, J. C. et al. (1992). Association between schizophrenia and homozygosity at the dopamine D3 receptor gene. Journal of Medical Genetics, 29, 858–860.
Crow, J. (1948). Alternative hypotheses of hybrid vigor. Genetics, 33, 477–487.
Curtis, D. (1997). Use of siblings as controls in case-control association studies. Annals of Human Genetics, 61(Pt 4), 319–333.
Dalley, J. W., Laane, K., Theobald, D. E., Armstrong, H. C., Corlett, P. R., Chudasama, Y., & Robbins, T. W. (2005). Time-limited modulation of appetitive Pavlovian memory by D1 and NMDA receptors in the nucleus accumbens. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 6189–6194.
Daly, G., Hawi, Z., Fitzgerald, M., & Gill, M. (1999). Mapping susceptibility loci in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: preferential transmission of parental alleles at DAT1, DBH and DRD5 to affected children. Molecular Psychiatry, 4, 192–196.
DiMaio, S., Grizenko, N., & Joober, R. (2003). Dopamine genes and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a review. Journal of Psychiatry Neuroscience, 28, 27–38.
Dudbridge, F. (2003). Pedigree disequilibrium tests for multilocus haplotypes. Genetic Epidemiology, 25, 115–121.
Dudbridge, F. (2006). UNPHASED user guide. Technical Report 2006/5. MRC Biostatistics Unit. Cambridge, UK.
Eisen, S. A., Lin, N., Lyons, M. J., Scherrer, J. F., Griffith, K., True, W. R., Goldberg, J., & Tsuang, M. T. (1998). Familial influences on gambling behavior: an analysis of 3359 twin pairs. Addiction, 93, 1375–1384.
Fiorillo, C. D., Tobler, P. N., & Schultz, W. (2003). Discrete coding of reward probability and uncertainty by dopamine neurons. Science, 299, 1898–1902.
Goudriaan, A. E., Oosterlaan, J., de Beurs, E., & Van den Brink, W. (2004). Pathological gambling: a comprehensive review of biobehavioral findings. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Review, 28, 123–141.
Grandy, D. K., Zhang, Y., & Civelli, O. (1993). PCR detection of the TaqA RFLP at the DRD2 locus. Human Molecular Genetics, 2, 2197.
Grant, J. E., & Kim, S. W. (2002). Gender differences in pathological gamblers seeking medication treatment. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 43, 56–62.
Heinz, A., Goldman, D., Jones, D. W., Palmour, R., Hommer, D., Gorey, J. G., Lee, K. S., Linnoila, M., & Weinberger, D. R. (2000). Genotype influences in vivo dopamine transporter availability in human striatum. Neuropsychopharmacology, 22, 133–139.
Hill, S. Y., Zezza, N., Wipprecht, G., Xu, J., & Neiswanger, K. (1999). Linkage studies of D2 and D4 receptor genes and alcoholism. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 88, 676–685.
Ibanez, A., Blanco, C., de Castro, I. P., Fernandez-Piqueras, J., & Saiz-Ruiz, J. (2003). Genetics of pathological gambling. Journal of Gambling Studies, 19, 11–22.
Ishiguro, H., Arinami, T., Saito, T., Akazawa, S., Enomoto, M., Mitushio, H., Fujishiro, H., Tada, K., Akimoto, Y., Mifune, H., Shioduka, S., Hamaguchi, H., Toru, M., & Shibuya, H. (1998). Association study between the -141C Ins/Del and TaqI A polymorphisms of the dopamine D2 receptor gene and alcoholism. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 22, 845–848.
Jacobsen, L. K., Staley, J. K., Zoghbi, S. S., Seibyl, J. P., Kosten, T. R., Innis, R. B., & Gelernter, J. (2000). Prediction of dopamine transporter binding availability by genotype: a preliminary report. American Journal of Psychiatry, 157, 1700–1703.
Jonsson, E. G., Nothen, M. M., Grunhage, F., Farde, L., Nakashima, Y., Propping, P., & Sedvall, G. C. (1999). Polymorphisms in the dopamine D2 receptor gene and their relationships to striatal dopamine receptor density of healthy volunteers. Molecular Psychiatry, 4, 290–296.
Kelley, A. E. (2004). Ventral striatal control of appetitive motivation: role in ingestive behavior and reward-related learning. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 27, 765–776.
Kim, S. W., & Grant, J. E. (2001). Personality dimensions in pathological gambling disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Research, 104, 205–212.
Kuntsi, J., McLoughlin, G., & Asherson, P. (2006). Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neuromolecular Medicine, 8, 461–484.
LaHoste, G. J., Swanson, J. M., Wigal, S. B., Glabe, C., Wigal, T., King, N., & Kennedy, J. L. (1996). Dopamine D4 receptor gene polymorphism is associated with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Molecular Psychiatry, 1, 121–124.
Lange, C., & Laird, N. M. (2002). Power calculations for a general class of family-based association tests: dichotomous traits. American Journal of Human Genetics, 71, 575–584.
Lichter, J. B., Barr, C. L., Kennedy, J. L., Van Tol, H. H., Kidd, K. K., & Livak, K. J. (1993). A hypervariable segment in the human dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4) gene. Human Molecular Genetics, 2, 767–773.
Lowe, N., Kirley, A., Hawi, Z., Sham, P., Wickham, H., Kratochvil, C. J., Smith, S. D. et al. (2004). Joint analysis of the DRD5 marker concludes association with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder confined to the predominantly inattentive and combined subtypes. American Journal of Human Genetics, 74, 348–356.
Lundstrom, K., & Turpin, M. P. (1996). Proposed schizophrenia-related gene polymorphism: expression of the Ser9Gly mutant human dopamine D3 receptor with the Semliki Forest virus system. Biochemical Biophysical Research Communications, 225, 1068–1072.
Martin, E. R., Monks, S. A., Warren, L. L., & Kaplan, N. L. (2000). A test for linkage and association in general pedigrees: the pedigree disequilibrium test. American Journal of Human Genetics, 67, 146–154.
Martins, S. S., Tavares, H., da Silva Lobo, D. S., Galetti, A. M., & Gentil, V. (2004). Pathological gambling, gender, and risk-taking behaviors. Addict Behaviors, 29, 1231–1235.
Minowa, M. T., Minowa, T., Monsma, F. J. Jr., Sibley, D. R., & Mouradian, M. M. (1992). Characterization of the 5' flanking region of the human D1A dopamine receptor gene. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 89, 3045–3049.
Misener, V. L., Luca, P., Azeke, O., Crosbie, J., Waldman, I., Tannock, R., Roberts, W., Malone, M., Schachar, R., Ickowicz, A., Kennedy, J. L., & Barr, C. L. (2004). Linkage of the dopamine receptor D1 gene to attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Molecular Psychiatry, 9, 500–509.
Nazarian, A., Russo, S. J., Festa, E. D., Kraish, M., & Quinones-Jenab, V. (2004). The role of D1 and D2 receptors in the cocaine conditioned place preference of male and female rats. Brain Research Bulletin, 63, 295–299.
Neville, M. J., Johnstone, E. C., & Walton, R. T. (2004). Identification and characterization of ANKK1: a novel kinase gene closely linked to DRD2 on chromosome band 11q23.1. Human Mutation, 23, 540–545.
Oliveira, M., Silva, A., & Silveira, D. (1999). Um programa assistencial para o transtorno de jogo patológico. Bol Psiquiatria, 32, 25.
Pato, C. N., Macciardi, F., Pato, M. T., Verga, M., & Kennedy, J. L. (1993). Review of the putative association of dopamine D2 receptor and alcoholism: a meta-analysis. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 48, 78–82.
Payton, A., Holmes, J., Barrett, J. H., Hever, T., Fitzpatrick, H., Trumper, A. L., Harrington, R., McGuffin, P., O’Donovan, M., Owen, M., Ollier, W., Worthington, J., & Thapar, A. (2001). Examining for association between candidate gene polymorphisms in the dopamine pathway and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a family-based study. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 105, 464–470.
Perez de Castro, I., Ibanez, A., Torres, P., Saiz-Ruiz, J., & Fernandez-Piqueras, J. (1997). Genetic association study between pathological gambling and a functional DNA polymorphism at the D4 receptor gene. Pharmacogenetics, 7, 345–348.
Petry, N. M., Stinson, F. S., & Grant, B. F. (2005). Comorbidity of DSM-IV pathological gambling and other psychiatric disorders: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 66, 564–574.
Potenza, M. N., Steinberg, M. A., Skudlarski, P., Fulbright, R. K., Lacadie, C. M., Wilber, M. K., Rounsaville, B. J., Gore, J. C., & Wexler, B. E. (2003). Gambling urges in pathological gambling: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Archives of General Psychiatry, 60, 828–836.
Potenza, M. N., Xian, H., Shah, K., Scherrer, J. F., & Eisen, S. A. (2005). Shared genetic contributions to pathological gambling and major depression in men. Archives of General Psychiatry, 62, 1015–1021.
Sanchez, C. J., Bailie, T. M., Wu, W. R., Li, N., & Sorg, B. A. (2003). Manipulation of dopamine d1-like receptor activation in the rat medial prefrontal cortex alters stress- and cocaine-induced reinstatement of conditioned place preference behavior. Neuroscience, 119, 497–505.
Scherrer, J. F., Xian, H., Shah, K. R., Volberg, R., Slutske, W., & Eisen, S. A. (2005). Effect of genes, environment, and lifetime co-occurring disorders on health-related quality of life in problem and pathological gamblers. Archives of General Psychiatry, 62, 677–683.
Self, D. W. (2004). Regulation of drug-taking and -seeking behaviors by neuroadaptations in the mesolimbic dopamine system. Neuropharmacology, 47 (Suppl 1) 242–255.
Shaffer, H. J., & Hall, M. N. (2001). Updating and refining prevalence estimates of disordered gambling behaviour in the United States and Canada. Canadian Journal of Public Health, 92, 168–172.
Shaffer, H. J., & Korn, D. A. (2002). Gambling and related mental disorders: a public health analysis. Annual Review of Public Health, 23, 171–212.
Slutske, W. S., Eisen, S., True, W. R., Lyons, M. J., Goldberg, J., & Tsuang, M. (2000). Common genetic vulnerability for pathological gambling and alcohol dependence in men. Archives of General Psychiatry, 57, 666–673.
Slutske, W. S., Eisen, S., Xian, H., True, W. R., Lyons, M. J., Goldberg, J., & Tsuang, M. (2001). A twin study of the association between pathological gambling and antisocial personality disorder. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 110, 297–308.
Spielman, R. S., & Ewens, W. J. (1998). A sibship test for linkage in the presence of association: the sib transmission/disequilibrium test. American Journal of Human Genetics, 62, 450–458.
Tahir, E., Yazgan, Y., Cirakoglu, B., Ozbay, F., Waldman, I., & Asherson, P. J. (2000). Association and linkage of DRD4 and DRD5 with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in a sample of Turkish children. Molecular Psychiatry, 5, 396–404.
Tavares, H., Gentil, V., Oliveira, C., & Tavares, A. (1999). Jogadores patologicos, uma revisao: psicopatologia, quadro clinico e tratamento. Revista de Psiquiatria clinica, 26, 179–187.
Tavares, H., Martins, S. S., Lobo, D. S., Silveira, C. M., Gentil, V., & Hodgins, D. C. (2003). Factors at play in faster progression for female pathological gamblers: an exploratory analysis. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 64, 433–438.
Tiihonen, J., Kuikka, J., Bergstrom, K., Hakola, P., Karhu, J., Ryynanen, O. P., & Fohr, J. (1995). Altered striatal dopamine re-uptake site densities in habitually violent and non-violent alcoholics. Nature Medicine, 1, 654–657.
Tran, A. H., Tamura, R., Uwano, T., Kobayashi, T., Katsuki, M., & Ono, T. (2005). Dopamine D1 receptors involved in locomotor activity and accumbens neural responses to prediction of reward associated with place. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 2117–2122.
van Dyck, C. H., Malison, R. T., Jacobsen, L. K., Seibyl, J. P., Staley, J. K., Laruelle, M., Baldwin, R. M., Innis, R. B., & Gelernter, J. (2005). Increased dopamine transporter availability associated with the 9-repeat allele of the SLC6A3 gene. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 46, 745–751.
Van Tol, H. H., Bunzow, J. R., Guan, H. C., Sunahara, R. K., Seeman, P., Niznik, H. B., & Civelli, O. (1991). Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D4 receptor with high affinity for the antipsychotic clozapine. Nature, 350, 610–614.
Van Tol, H. H., Wu, C. M., Guan, H. C., Ohara, K., Bunzow, J. R., Civelli, O., Kennedy, J., Seeman, P., Niznik, H. B., & Jovanovic, V. (1992). Multiple dopamine D4 receptor variants in the human population. Nature, 358, 149–152.
Vanyukov, M. M., Moss, H. B., Gioio, A. E., Hughes, H. B., Kaplan, B. B., & Tarter, R. E. (1998). An association between a microsatellite polymorphism at the DRD5 gene and the liability to substance abuse: pilot study. Behavior Genetics, 28, 75–82.
Wing, J. K., Babor, T., Brugha, T., Burke, J., Cooper, J. E., Giel, R., Jablenski, A., Regier, D., & Sartorius, N. (1990). Schedules for clinical assessment in neuropsychiatry. Archives of General Psychiatry, 47, 589–593.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by funds from The State of São Paulo Research Funding Agency (02/02653-87 and 02/0009-3) and the Ontario Problem Gambling Research Centre. We thank the Gambling Outpatient Unit group in São Paulo for help with data collection. We also thank the Laboratory of Medical Investigation LIM-23 (Institute of Psychiatry, University of São Paulo) and the Neurogenetics Laboratory staff (Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, University of Toronto) for genotyping assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was performed at the Institute of Psychiatry, University of São Paulo, São Paulo, SP, Brazil
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabbatini da Silva Lobo, D., Vallada, H.P., Knight, J. et al. Dopamine Genes and Pathological Gambling in Discordant Sib-Pairs. J Gambl Stud 23, 421–433 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10899-007-9060-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10899-007-9060-x