Abstract
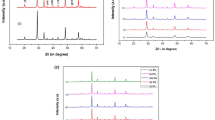
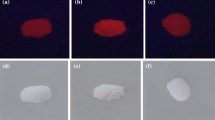
This paper reports the structural and optical properties of rare earth doped and codoped yttrium oxide nanophosphors. Dysprosium (Dy3+) and Terbium (Tb3+) doped and codoped yttrium oxide (Y2O3) phosphors were prepared by combustion synthesis method and subsequently annealed to high temperature to eliminate the hydroxyl group (−OH) and to get more crystallinity. The formation of compounds was confirmed by the X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR). The diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS) of doped and codoped Y2O3 powder phosphors were measured and it is observed that the absorption edge of the doped samples is shifted towards blue region with respect to undoped sample. The bandgap of the prepared samples were evaluated with the help of Kubelka-Munk function using Diffuse Reflectance Spectra (DRS) and an increase in bandgap was observed with the decrease in crystallite size. A strong characteristics emission from Tb3+ and Dy3+ ions was identified and the influence of doping concentration and annealing temperature on photoluminescence properties was systematically studied. Transfer of energy was observed in dysprosium–terbium codoped Y2O3 nanophosphor at room temperature from Dy3+ ions toTb3+ ions.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cho SH, Kwon SH, Yoo JS, Oh CW, Lee JD, Hong KJ, Kwon SJ (2000) Cathodoluminescent characteristics of a spherical Y2O3: Eu phosphor screen for field emission display application. J Electrochem Soc 147:3143–3147
Martinez-Rubio MI, Ireland TG, Fern GR, Silver J, Snowden MJ (2001) A New Application for Microgels: Novel Method for the Synthesis of Spherical Particles of the Y2O3: Eu Phosphor Using a Copolymer Microgel of NIPAM and Acrylic Acid. Langmuir 17:7145–7149. doi:10.1021/la0105883
Chien Wen-Chen Y, Yang-Yen YC-C (2010) A novel synthetic route to Y2O3:Tb3+ phosphors by bicontinuous cubic phase process. Mater Des 31:1737–1741. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2009.01.046
Singh LR, Ningthoujam RS, Sudarsan V, Srivastav I, Singh SD, Dey GK, Kulshreshtha SK (2008) Luminescence Study of Eu3+ doped Y2O3 Nanoparticles: Particle Size, Concentration and core-Shell Formation Effects. Nanotechnology 19:055201–8. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/19/05/055201
Xin-Yuan S, Gua M, Shi-Ming H, Xiao-Lin L, Bo L, Chen N (2009) Enhancement of Tb3+ emission by non-radiative energy transfer from Dy3+ in silicate glass. Physica B 404:111–114. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2008.10.039
Maruyama N, Honma T, Komatsu T (2009) Enhanced quantum yield of yellow photoluminescence of Dy3+ ions in nonlinear optical Ba2TiSi2O8 nanocrystals formed in glass. Journal of Solid State Chemistry 182(2):246–252. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2008.10.028
Kharabe VR, Dhoble SJ, Moharil SV (2008) Synthesis of Dy3+ and Ce3+ activated Sr6BP5O20 and Ca6BP5O20 borophosphate phosphors. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:205413. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/41/20/205413
Jayasimhadri M, Moorthy LR, Kojima K, Yamamoto K, Wada N, Wada N (2006) Optical properties of Dy3+ ions in alkali Tellurophosphate glasses for laser materials. J Phys D Appl Phys 39:635–641. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/39/4/007
Qingyu M, Chen Baojiu XW, Yanmin Y, Xiaoxia Z, Di Weihua L, Shaozhe WX, Jiashi S, Cheng Lihong Y, Tao PY (2007) Size-dependent excitation spectra and energy transfer in Tb3+-doped Y2O3 nanocrystalline. J Appl Phys 102:093505–6. doi:10.1063/1.2803502
Nash Kelly L, Dennis Robert C, Gruber John B, Sardar Dhiraj K (2009) Intensity analysis and energy-level modeling of Nd3+ in Nd3+:Y2O3 nanocrystals in polymeric hosts. J Appl Phys 105:033102–6. doi:10.1063/1.3074313
Morales AE, Mora ES, Pal U (2007) Use of diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for optical characterization of un-supported nanostructures. Revista Mexicana de F´isica S 53(5):18–22
Vu N, Anh TK, Yi G, Strek W (2007) Photoluminescence and cathodoluminescence properties of Y2O3: Eu nanophosphors prepared by combustion synthesis. J Lumin 122–123:776–779. doi:10.1016/j.lumin.2006.01.286
Chatterjee S K (2010) X-Ray Diffraction Its Theory and Applications. PHI Learning Private Ltd. 2nd Edn.: 92–98.
Yen-Pei F (2007) Preparation and characterization of Y2O3:Eu phosphors by combustion process. J Mater Sci 42:5165–5169. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-1289-8
Vij A, Kumar R, Chawla AK, Lochab SP, Chandra R, Singh N (2010) Swift heavy ion induced synthesis and enhanced photoluminescence of SrS: Ce nanoparticles. Opt Mater 33:58–62. doi:10.1016/j.optmat.2010.07.024
Wang C, Zhao J, Yong LI, Zhang W, Yin M (2009) Influence of dispersant on Y2O3: Eu3+ powders synthesized by combustion method. Journal of Rare Earths 27(6):879–885. doi:10.1016/S1002-0721(08)60354-3
Rao G R, Sahu H R (2001) XRD and UV–vis diffuse reflectance analysis of CeO2– ZrO2 solid solutions synthesized by combustion method. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Chem. Sci.), 113: 651.
Gao D, Li Y, Lai X, Wei Y, Bi J, Li Y, Liu M (2011) Fabrication and Luminescence properties of Dy3+ doped CaMoO4 powders. Material Chemistry and Physics 126:391–397. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.10.053
Liu Zhilong Y, Lianxiang WQ, Yanchun T, Hua Y (2011) Effect of Eu, Tb codoping on the luminescent properties of Y2O3 nanorods. J Lumin 131:12–16. doi:10.1016/j.jlumin.2010.08.012
Pitale SS, Sharma SK, Dubey RN, Qureshi MS, Malik MM (2009) Luminescence behavior of SrS:Pr3+ micron-sized phosphor fabricated through chemical co-precipitation route and post-annealing processes. Opt Mater 31:923–930. doi:10.1016/j.optmat.2008.10.048
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to University Grants Commission, New Delhi, Government of India for funding this work (Project F. No. 37-200/2009 (SR)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Research Highlights
• This Paper discusses the effect of doping concentration and annealing temperature on the structural and photoluminescence properties of yttrium oxide phosphor.
• Structural parameters and Band gap are calculated.
• Enhancement of Tb3+ emission by energy transfer from Dy3+ is observed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Som, S., Sharma, S.K. & Shripathi, T. Influences of Doping and Annealing on the Structural and Photoluminescence Properties of Y2O3 Nanophosphors. J Fluoresc 23, 439–450 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-013-1160-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-013-1160-7