Abstract
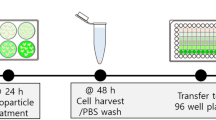
Amino functionalized, cross-linked, polystyrene microspheres were covalently loaded with streptavidin to which was coupled fluorescently labeled biotin and biotinylated-tagged DNA. These biotin–streptavidin microsphere conjugates were then successfully delivered into cells. The application of the streptavidin–biotin technology to these microspheres allows the effective delivery of any biotinylated material into intact mammalian cells, without the need for delicate procedures such as micro-injection.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Diaz-Mochon JJ, Bialy L, Watson J, Sanchez-Martin RM, Bradley M (2005) Synthesis and cellular uptake of cell delivering PNA-peptide conjugates. Chem Commun 26:3316–3318
Snyder EL, Dowdy SF (2004) Cell penetrating peptides in drug delivery. Pharm Res 21:389–393
Järver P, Langel U (2004) The use of cell-penetrating peptides as a tool for gene regulation. Drug Discov Today 9:395–402
Peretto I, Sanchez-Martin RM, Wang X, Ellard J, Mittoo S, Bradley M (2003) Cell penetrable peptoid carrier vehicles: synthesis and evaluation. Chem Commun 18:2312–2313
Yingyongnarongkul B, Howarth M, Elliott T, Bradley M (2004) Solid-phase synthesis of 89 polyamine-based cationic lipids for DNA delivery to mammalian cells. Chem Eur J 10:463–473
Simard P, Leroux JC, Allen C, Meyer O (2007) Liposomes for drug delivery. In: Domb AJ, Tabata Y, Ravi Kumar MNV, Farber S (eds) Nanoparticles for pharmaceutical applications. American Scientific, California, USA, pp 1–62
Gingras M, Raimundo JM, Chabre YM (2007) Cleavable dendrimers. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:1010–1017
Dufes C, Uchegbu IF, Schätzlein AG (2005) Dendrimers in gene delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57:2177–2202
Wong Shi Kam N et al (2004) Nanotube molecular transporters: internalization of carbon nanotube-protein conjugates into mammalian cells. J Am Chem Soc 126:6850–6851
Zhu H, McShane MJ (2005) Loading of hydrophobic materials into polymer particles: implications for fluorescent nanosensors and drug delivery. J Am Chem Soc 127:13448–13449
Buck SM, Xu H, Brasuel M, Philbert MA, Kopelman R (2004) Nanoscale probes encapsulated by biologically localized embedding (PEBBLEs) for ion sensing and imaging in live cells. Talanta 63:41–59
Steinkamp JA, Wilson JS, Saunders GC, Stewart CC (1982) Phagocytosis: flow cytometric quantitation with fluorescent microspheres. Science 215:64–66
Sanchez-Martin RM, Muzerelle M, Chitkul N, How SE, Mittoo S, Bradley M (2005) Bead-based cellular analysis, sorting and multiplexing. ChemBioChem 6:1341–1345
Sanchez-Martin RM, Cuttle M, Mittoo S, Bradley M (2006) Microsphere-based real-time calcium sensing. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:5472–5474
Bradley M, Alexander L, Duncan K, Chennaoui M, Jones AC, Sanchez-Martin RM (2008) pH sensing in living cells using fluorescent microspheres. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:313–317
Pardridge WM (2007) shRNA and siRNA delivery to brain. Adv Drug Deliver Rev 59:141–152
Susumu K, Uyeda HT, Medintz IL, Pons T, Delehanty JB, Mattoussi H (2007) Enhancing the stability and biological functionalities of quantum dots via compact multifunctional ligands. J Am Chem Soc 129(45):13987–13996
Niemeyer CM, Adler M, Wacker R (2007) Detecting antigens by quantitative immuno-PCR. Nature Protocols 2(8):1918–1930
Diamandis EP, Christopoulos TK (1991) The biotin-(strept)avidin system: principles and applications in biotechnology. Clin Chem 37:625–636
Green NM (1990) Avidin and streptavidin. Methods Enzymol 184:51–67
Wu CW, Lee JG, Lee WC (1998) Protein and enzyme immobilization on non-porous microspheres of polystyrene. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 27:225–230
Kada G, Falk H, Gruber HJ (1999) Accurate measurement of avidin and streptavidin in crude biofluids with a new, optimized biotin-fluorescein conjugate. Biochim Biophys Acta 1427:33–43
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the EPSRC. R.M.S.-M. thanks the Royal Society for a Dorothy Hodgkin Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bradley, M., Alexander, L. & Sanchez-Martin, R.M. Cellular Uptake of Fluorescent Labelled Biotin–Streptavidin Microspheres. J Fluoresc 18, 733–739 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-008-0334-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-008-0334-1