Abstract
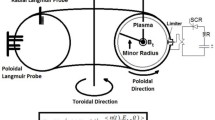
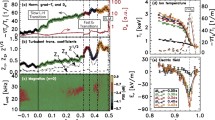
In this work, the turbulent transport in the edge plasma and Scrape-Off Layer (SOL) region of IR-T1 tokamak at the presence of biased limiter has been investigated and analyzed. The time and radial evolution of floating potential, electric field and turbulent transport have been measured by using two arrays of the Langmuir probes in both the radial and poloidal directions. The analyses have been done by the Fast Fourier Transport method and spectral features of them are obtained with the help of the standard Auto-Correlation technique and modified covariance power spectral density estimate. The probability distribution function and actual transfer function magnitude of the radial and poloidal turbulent transport (Γr and Γp) have been investigated and compared in the edge plasma and SOL region. Also the histogram of turbulent transport has been analyzed and compared in the edge and SOL at presence of positive limiter biasing. The results show that in the edge plasma poloidal turbulent transport (Γp) is about of 60 % more than SOL region whereas radial turbulent transport (Γr) is about of 40 % less. During the application of positive biasing, it was found that Γr in the IR-T1 reduces by about 80 % in the edge plasma and 45–50 % in the SOL. Increase of Γp is about of 50 % after applied positive biasing in the edge while it increases 70 % nearly, in the SOL. Consequently, the improvement in confinement can be obtained for positive limiter biasing.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.N. Rogers et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 4396 (1998)
C. Schröder et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5711 (2001)
B.A. Carreras et al., Phys. Plasmas 3, 2664 (1996)
V. Naulin, New J. Phys. 4, 28.1–28.18 (2002)
V. Naulin, J. Nucl. Mater. 363–365, 24 (2007)
J.A. Boedo et al., Phys. Plasmas 8, 4826 (2001)
G.Y. Antar et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 065001 (2001)
B. Viatcheslav et al., J. Plasma Fusion Res. 5, 418–423 (2002)
A. Salar Elahi et al., IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 40, 892–897 (2012)
E.Y. Wang et al., Nucl. Fusion 35, 467 (1995)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Iran National Science Foundation (INSF-87040631).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meshkani, S., Ghoranneviss, M., Lafouti, M. et al. Turbulent Transport in the Tokamak Edge Plasma and SOL Region. J Fusion Energ 32, 496–502 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-013-9600-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-013-9600-6