Abstract
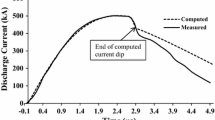
Drive parameter is one of the most important and influential factors in design and construction of plasma focus devices. This parameter controls the speed of current sheath both in the radial and the axial phases; as a result, the final temperature of the pinched plasma as well as the speed of moving-boiler (IEEE Trans Plasma Sci, 38:2096 in 2010). Therefore, to design a machine with high drive parameter, the IR-MPF-1 device (Iranian-Mather Type Plasma Focus1) was designed and constructed. In this work, Lee’s model and semi-empirical formulas were used to achieve the anode length. Using neutron counter (HVTC 1001 GM) in the IR-MPF-1 device (bank energy of 11.2 kJ and 3.2 torr pressure) with deuterium operational gas, the number of 5.7 × 108 neutron/shot was observed. High amount of neutron yield according to the relatively small size of the device represents the effective role of the drive parameter on the fusion products in plasma focus machines.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Soto, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion. 47, A361 (2005)
P. Silva et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 16 (2003)
M. Zakaullah et al., Plasma Sour. Sci. Technol. 11, 377–382 (2002)
E. Angeli et al., Appl. Radiat. Isot. 63, 545–551 (2005)
T. Zhang et al., IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 34, 5 (2006)
S. Lee, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 24, 3 (1996)
N.K. Neog, S.R. Mohanty, Phys. Lett. A. 361, 377–381 (2007)
C. Moreno, F. Casanova et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion. 45, 1989–1999 (2003)
C. Moreno, H. Bruzzone et al., IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 28(5), 1735–1741 (2000)
R.S. Rawat, T. Zhang et al., Plasma Sour. Sci. Technol. 13, 569–575 (2004)
H.R. Yousefi, F.M. Aghamir et al., Phys. Lett. A. 361, 360–363 (2007)
K. Hübner, H. Bruhnsand, K. Steinmetz, Phys. Lett. A. 69(4), 269–272 (1978)
S.L. YAP et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 44(11), 8125–8132 (2005)
H.R. Yousefi et al., Phys. Plasma. 13, 114506 (2006)
T.D. Mahabadi, M.A. Tafreshi, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion. 49, 1447–1455 (2007)
M. Abdollahzadeh, S.M. Sadat Kiai, J. Fusion Energ. 29, 218–222 (2010)
S. Goudarzi et al., Czech J. Phys. 55(1), 45–53 (2005)
V. Damideh et al., J Fusion Energ. Online First™, 9 April 2011
L. Soto, Plasma Phys.Control.Fusion. 47, 361 (2005)
A.A. Zaeem, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 38, 2096 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Damideh, V., Zaeem, A.A., Heidarnia, A. et al. Design and Fabrication of 11.2 kJ Mather-Type Plasma Focus IR-MPF-1 with High Drive Parameter. J Fusion Energ 31, 47–51 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-011-9427-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-011-9427-y