Abstract
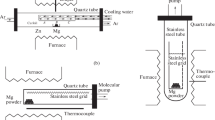
Metal oxide nanoparticles play an important role in many nanotechnical applications. Among these, magnesium oxide has attracted great attention in different applications. Here, hot wire chemical vapor deposition (HWCVD) method was employed for the deposition of magnesium oxide nanoparticles on pre-ultrasonically cleaned P type Si (111) substrates of 1 cm × 1 cm. High purity magnesium ribbon was heated up to high temperatures in the vicinity of tungsten filament in oxygen surrounding medium at a constant working pressure. The samples were deposited by the proposed method and their properties were studied by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and Energy Dispersive X-Ray spectroscopy (EDAX). The key parameters of our experiments including results of changes in filament temperature on the properties of Magnesium oxide nanoparticles are presented here. The mean size of the nano MgO Particles was between 80–120 nm.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Manin et al., Surf. coat. Technol 200, 1424–1429 (2005)
K.V. Rao, C.S. Sunandana, Synthesis, and reactivity In Inorg. Met. nano-met. chem 38, 173–178 (2008)
S.Y. Lee et al., J. Crystal. Growth 236, 635–639 (2002)
Y.W. Choi, J. Kim, Thin Solid Films 460, 295–299 (2004)
Y. Matsuda et al., Thin Solid Films 457, 64–68 (2004)
C. pan et al., SID 98 DIGEST. 865 (1998)
T. Hatanpaa et al., Chem. Mater 11, 1846 (1999)
T. Ishiguro et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Pt1 35, 3537 (1996)
T.X. Phuoc et al., Optics. laser s. Eng 46, 829–834 (2008)
F. Niu et al., Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc 606, 45 (2000)
L.D. Chang et al., Appl. Phys. Lett 60, 1753 (1992)
E. Knozinger et al., J. mol. catal. A 162, 83–95 (2000)
T. Matsumoto et al., Ceramics. Int 16, 325–331 (1990)
T. Maruyama et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 29, L810 (1990)
E. Fuji et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 33 (1994)
Y. Ding et al., Chem. Mater 13, 435 (2001)
J.G. Yoon et al., Appl. Phys. Lett 66, 2664 (1995)
J.G. Yoon et al., Appl. Phys. Lett 66, 2661 (1995)
In.-Chyuan. Ho et al., J. Sol-Gel Sci. Tech 9, 295–301 (1997)
Y.C. Hong et al., Chem. Phys. Lett. 422, 174–178 (2006)
B. J. Kooi et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 161914 (2006)
P.P. Fedorov et al., Inorg. Mater 43, 502–504 (2007)
J.Y. Park et al., J. Ind. Eng. Chem 12, 882–887 (2006)
A.G. Nasibulin et al., Cryst. Grow. design 10, 414–417 (2010)
Q. Yang et al., Nanotechnology 15, 1004–1008 (2004)
J. Thangala et al., Thin Solid Films 517, 3600–3605 (2009)
H.W. Kim, Chem. Phys. Lett. 442, 165–169 (2006)
J. Zhang et al., Appl. Phys. A 73, 773–775 (2001)
N. Takahashi, Solid. State. Sci 9, 722–724 (2007)
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge full support from the Karaj Branch of Islamic Azad University and also, Science and research branch of Islamic Azad University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borghei, S.M., Kamali, S., Shakib, M.H. et al. Filament Temperature Dependence of the Nano-size MgO Particles Prepared by the HWCVD Technique. J Fusion Energ 30, 433–436 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-011-9394-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-011-9394-3