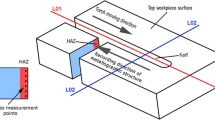
An investigation of thermal processes in the course of magnetorheological polishing has been carried out. Physical and mathematical description of heat transfer from a treated surface to a polishing tool is given with consideration of the specifics of the rheological and thermophysical properties of the tool acquired by it in a magnetic field in the zone of treatment. An analytical estimate of the thermal state of a magnetorheological abrasive tool and of a treated workpiece surface is given. The temperatures of the workpiece surface and of the magnetorheological abrasive tool in the zone of their contact interaction in an inhomogeneous magnetic field are determined experimentally. The increase in the temperature of the treatment zone by ΔT = 6.6°C at an absolute maximum temperature of T = 299.6 K is recorded experimentally, with the measured temperature gradient comprising 0.073 K/s.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. I. Karban′ and Yu. I. Borzakov, Treatment of Crystals in Microelectronics [in Russian], Radio i Svyaz′, Mosow (1988).
G. Guo and S. Malkin, Heat transfer in grinding, J. Mater. Process Manuf. Sci., 1, 16–27 (1992).
V. A. Sipailov, Thermal Processes in Grinding and Control of the Surface Quality [in Russian], Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1978).
K. V. Averkov, D. S. Rechenko, and A. M. Lasitsa, Thermal processes in high-velocity grinding, Omsk. Nauchn. Vestn., No. 3, Issue 103, 83–87 (2011).
V. V. Rogov and L. L. Burman, Workability of optical ceramics by a tool made of synthetic diamonds, Steklo Keram., No. 6, 24−26 (1979).
I. D. Marinescu, E. Uhlmann, and T. K. Doi (Eds.), Handbook of Lapping and Polishing, Taylor & Francis Group (2006).
P. I. Yashcheritsyn, A. N. Martynov, and A. D. Gridin, Finishing Treatment of Workpieces by a Compressed Abrasive Flux [in Russian], Nauka i Tekhnika, Minsk (1978).
D. G. Evseev, Formation of Surface Layer Properties in Abrasive Treatment [in Russian], Izd. Saratovsk. Univ., Saratov (1975).
P. I. Yashcheritsyn, Increasing the Operational Properties of Ground Surfaces [in Russian], Nauka i Tekhnika, Minsk (1966).
N. Ortega, H. Bravo, I. Pombo, J. A. Sanchez, and G. Vidal, Thermal analysis of creep feed grinding, Procedia Eng., 132, 1061–1068 (2015).
G. R. Shafto, T. D. Howes, and C. Andrew, Thermal aspects of creep feed grinding, Proc. 16th Int. Machine Tool and Research Conf., Manchester, England (1975), pp. 31–37.
J. Neauport, J. Destribats, C. Maunier, C. Ambard, P. Cormont, B. Pintault, and O. Rondeau, Loose abrasive slurries for optical glass lapping, Appl. Opt., 49, Issue 30, 5736−5745 (2010).
N. A. Petrov, State-of-the-art and prospects of development of the technology and equipment for superprecision treatment, Anal. Obzor, VNIITÉMP, Moscow (1991).
V. M. Vinokurov, Investigation of the Process of Glass Polishing [in Russian], Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1967).
D. Golini and S. D. Jacobs, Physics of loose abrasive microgrinding, Appl. Opt., 30, 2761–2777 (1991).
V. D. Kizilov, Yu. P. Trotsenko, and V. I. Karban′, Influence of the basic factors of chemical-mechanical polishing on the efficiency of silicon treatment, Diélektr. Poluprovodn., No. 12, 83–89 (1977).
P. N. Orlov, K. G. Marin, and I. A. Sverdlin, Investigation of the process of chemical-mechanical polishing of silicon substrates, Élektron. Tekh., Ser. Mater., No. 3, 80–83 (1979).
A. E. Garnak, V. M. D′yachkov, and T. N. Markova, Formation of second-phase depositions in the process of chemicalmechanical polishing of silicon plates, Élektron. Tekh., Ser. Mater., No. 5, 59–66 (1980).
L. L. Vrublevskii, I. I. Zaitsev, and E. B. Bychkov, Polishing of silicon–silicon dioxide–polycrystalline silicon structures, Élektron. Tekh., Ser. Poluprov. Prib., No. 3, 41–46 (1979).
N. T. Bublik, I. M. Kotelinskii, and A. N. Krikunov, Chemical-mechanical polishing of lithium niobate plates, Élektron. Tekh., Ser. Mater., No. 12, 17–18 (1981).
J. Watanabe, J. Susuki, and A. Kobayashi, High precision polishing of semiconductor materials using hydrodynamic principle, CIRP Ann., 30, Nо. 1, 91–95 (1981).
T. Himaguti, M. Kimura, E. Etami, and N. Endo, Noncontact polishing of semiconducting plates with hydrostatic control of the gap, Prib. Nauchn. Issled., No. 11, 143–144 (1984).
J. V. Gormley, M. J. Manfra, and A. R. Calawa, Hydroplane polishing of semiconductor crystals, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 52, Nо. 8, 1256–1259 (1981).
H. Kumar, S. Singh, and P. Kumar, Magnetic abrasive finishing. A review, Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol., 2, Issue 3, 1–9 (2013).
Y. Tani, Development of high-efficient fine finishing process using magnetic fluid, Ann. CIRP, 33, Nо. 1, 217–220 (1984).
T. Kurobe, O. Imanaka, and K. Shimeno, Magnetic field-assisted lapping, Bull. Jpn. Soc. Prec. Eng., 20, Nо. 1, 49–51 (1986).
Y. Saito, H. Niikura, T. Oshio, and T. Yanaoka, Float polishing using magnetic fluid with abrasive grains, in: Proc. 6th Conf. on Production Engineering, Osaka, 1987, pp. 335–340.
K. Kenji and T. Yasuhiro, A study of magneto-abrasive fine polishing, J. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng., 55, Nо. 4, 691–696 (1989).
R. E. Rosensweig, Fluidmagnetic buoyancy, AIAA J., 4, No. 10, 1751–1758 (1966).
R. E. Rosensweig, Buoyancy and stable levitation of a magnetic body immersed in a magnetizable fluid, Nature, 210, Nо. 5036, 613–614 (1966).
R. E. Rosensweig, Ferrohydrodynamics, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge (1985).
V. I. Kordonskii, S. R. Gorodkin, B. É. Kashevskii, and I. V. Prokhorov, Energy dissipation and heat exchange in magnetorheological suspensions in a rotating magnetic field, J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys., 52, No. 1, 44–47 (1987).
V. V. Rogov, Finishing Diamond-Abrasive Treatment of Nonmetallic Workpieces [in Russian], Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1985).
M. L. Levin, Thermophysics and Rheology in Polishing by a Structurally Reversible Magnetosensitive Tool, Candidate′s Dissertation (in Engineering), Minsk (1994).
W. L. Wilkinson, Non-Newtonian fluids, in: Fluid Mechanics, Mixing and Heat Transfer, Pergamon Press, London (1960), Vol. 1.
R. B. Bird, W. E. Stewart, and E. N. Lightfoot, Transport Phenomena, revised 2nd edn., John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken (2007).
I. P. Ginzburg, Applied Hydrodynamics [in Russian], LGU, Leningrad (1958).
S. S. Kutateladze, Principles of Heat Transfer Theory [in Russian], Atomizdat, Moscow (1979).
S. Kohli, C. Guo, and S. Malkin, Energy partition to the workpiece for grinding with aluminum oxide and CBN abrasive wheels, Trans. ASME, 117, 160–168 (1995).
V. L. Dragun, D. F. Ustinovich, A. P. Kozlova, and S. A. Filatov, Characteristic Features of Thermal Processes in Magnetic Abrasive Treatment of Rotating Bodies, Preprint of the Heat and Mass Transfer Institute of the Academy of Sciences of BSSR, No. 2, Minsk (1990).
V. L. Dragun, D. F. Ustinovich, and S. A. Filatov, Investigation of regimes in magnetic abrasive treatment of rotating bodies with the use of a system of computational IR thermography, Izv. Akad. Nauk BSSR, No. 4, 34–37 (1990).
V. L. Dragun, N. Ya. Skvorchevskii, D. F. Ustinovich, A. P. Kozlova, and S. A. Filatov, Characteristic features of the thermal regimes in magnetic abrasive treatment of rotating bodies, Izv. Akad. Nauk BSSR, No. 1, 53–61 (1991).
V. D. Durnev and V. P. Olenichev, temperature stresses in the surface layer of a cylindrical sample under magnetic abrasive effect, Fiz. Khim. Obrab. Mater., No. 4, 94–99 (1989).
C. Gaurl and D. K. Singh, The analysis of temperature during magnetic abrasive finishing of plane surface, Int. J. Sci. Res. Dev., 3, Issue 4, 1835–1841 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 91, No. 3, pp. 848–856, May–June, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levin, M.L., Khudolei, A.L. Heat Transfer in the Course of Magnetorheological Polishing. J Eng Phys Thermophy 91, 797–805 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-018-1802-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-018-1802-3