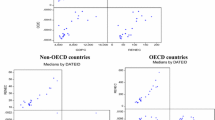
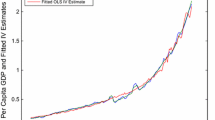
Abstract
We argue that a key empirical finding in environmental economics—the Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC)—and the core model of modern macroeconomics—the Solow model—are intimately related. Once we amend the Solow model to incorporate technological progress in abatement, the EKC is a necessary by product of convergence to a sustainable growth path. We explain why current methods for estimating an EKC are likely to fail; provide an alternative empirical method directly tied to our theory; and estimate our model on carbon emissions from 173 countries over the 1960–1998 period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acemoglu D. (2002) Directed technical change. The Review of Economic Studies 69(4): 781–809
Aghion P., Howitt P. (1998) Endogenous growth theory. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Andreoni J., Levinson A. (2001) The simple analytics of the Environmental Kuznets Curve. Journal of Public Economics 80: 269–286
Barbier E. B. (1997) Introduction to the Environmental Kuznets Curve special issue. Environment and Development Economics 2: 369–381
Barro R. J. (1991) Economic growth in a cross section of countries. Quarterly Journal of Economics 106: 407–443
Barro R. J., Sala-i-Martin X. (1991) Convergence across states and regions. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity 1: 107–182
Becker R., Henderson V. (2000) Effects of air quality regulations on polluting industries. Journal of Political Economy 108(2): 379–421
Bovenberg A. L., Smulders S. (1995) Environmental quality and pollution augmenting technological change in a two sector endogenous growth model. Journal of Public Economics 57: 369–391
Brock, W. A., & Taylor, M. S. (2003). The kindergarten rule of sustainable growth. NBER Working Paper No. 9597, Cambridge, MA.
Brock, W. A., & Taylor, M. S. (2004). The Green Solow model. Social Sciences Research Institute Working Paper No. 2004-16, Economics Department, University of Wisconsin.
Brock, W. A. & Taylor, M. S. (2005). Economic growth and the environment: A review of theory and empirics. In P. Aghion & S. Durlauf (Eds.), Handbook of economic growth (Vol. 1B). Amsterdam: Elsevier B.V.
Bruvoll A., Medin H. (2003) Factors behind the Environmental Kuznets Curve: A decomposition of the changes in air pollution. Environmental and Resource Economics 24: 27–48
Bulte E., List J. A., Strazicich M. C. (2007) Regulatory federalism and the distribution of air pollutant emissions. Journal of Regional Science 47(1): 155–178
Chay K. Y., Greenstone M. (2005) Does air quality matter? Evidence from the housing market. Journal of Political Economy 113(2): 376–424
Copeland B. R., Taylor M. S. (1994) North-South trade and the global environment. Quarterly Journal of Economics 109: 755–787
Copeland B. R., Taylor M. S. (2003) Trade and the environment: Theory and evidence. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ
Criado C. (2008) Temporal and spatial homogeneity in air pollutants panel EKC estimations. Environmental and Resource Economics 40: 265–283
Dewey, S. H. (2000). In D. L. Flores (Ed.), Don’t breathe the air: Air pollution and U.S. Environmental Politics: 1945–1970, No. 16, Environmental History Series. Texas A&M Publisher, College Station, TX.
Dijkgraaf E., Melenberg B., Vollebergh H. R. J. (2005) A test for parameter homogeneity in CO2 panel EKC estimations. Environmental and Resource Economics 32: 229–239
Durlauf S. N., Johnson P. A. (1995) Multiple regimes and cross-country growth behaviour. Journal of Applied Econometrics 10: 365–384
Durlauf S., Quah D. (1999) The new empirics of economic growth. In: Taylor J., Woodford M. (eds) Handbook of macroeconmics. North Holland, Amsterdam
Greenstone M. (2004) Did the Clean Air Act cause the remarkable decline in sulfur dioxide concentrations?. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management 47: 585–611
Grossman G. M., Krueger A. B. (1994) Environmental impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement. In: Garber P. (eds) The US-Mexico Free Trade Agreement. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Grossman G. M., Krueger A. B. (1995) Economic growth and the environment. Quarterly Journal of Economics 110: 353–377
Harbaugh W., Levinson A. M., Wilson D. M. (2002) Reexamining the empirical evidence for an Environmenal Kuznets Curve. Review of Economics and Statistics 84: 541–551
Holtz-Eakin D., Selden T. M. (1995) Stoking the fires? CO2 emissions and economic growth. Journal of Public Economics 57: 85–101
Islam N. (1995) Growth empirics, A panel data approach. Quarterly Journal of Economics 110(4): 1127–1170
Islam N. (2003) What we learnt from the convergence debate. Journal of Economic Surveys 17(3): 309–362
Lee J., List J.A. (2004) Examining trends of criteria air pollutants: Are the effects of government intervention transitory. Environmental and Resource Economics 29(1): 21–37
Lopez R. (1994) The environment as a factor of production: Economic growth and trade liberalization. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management 27: 163–184
Mankiw N. G., Romer D., Weil D. N. (1992) A contribution to the empirics of economic growth. Quarterly Journal of Economics 107: 407–437
Nordhaus W. D. (2008) A question of balance: Weighing the options on global warming policies. Yale University Press, New Haven
Pizer W. A., Popp D. (2008) Endogenizing technological change: Matching empirical evidence to modeling needs. Energy Economics 30: 2754–2770
Popp, D., Newell, R., & Jaffe, A. (2009). Energy, the environment, and technological change. National Bureau of Economic Analysis Working Paper No. 14832.
Selden T. M., Forrest A. S., Lockhart J. E. (1999) Analyzing reductions in U.S. air pollution emissions: 1970 to 1990. Land Economics 75: 1–21
Smulders S., de Nooij M. (2003) The impact of energy conservation on technology and economic growth. Resource and Energy Economics 25: 59–79
Solow R. M. (1956) A contribution to the theory of economic growth. Quarterly Journal of Economics 70: 65–94
Stern D. I. (2004) The rise and fall of the Environmental Kuznets Curve. World Development 32(8): 1419–1439
Stern D. I. (2005) Beyond the environmental Kuznets curve: Diffusion of emissions reducing technology. Journal of Environment and Development 14(1): 101–124
Stern D. I. (2007) The effect of NAFTA on energy and environmental efficiency in Mexico. Policy Studies Journal 35(2): 291–322
Stern D. I., Common M. S. (2001) Is there an Environmental Kuznets Curve for sulfur?. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management 41: 162–178
Stokey N. (1998) Are there limits to growth. International Economic Review 39(1): 1–31
Strazicich M. C., List J. (2003) Are CO2 emission levels converging among industrial coutries. Environmental and Development Economics 24: 263–271
Vogan C.R. (1996) Pollution abatement and control expenditures: 1972–1994. Survey of Current Business 76: 48–67
Xepapadeas A. (2005) Economic growth and the environment, Chapter 23. In: Vincent J., Maler K. G. (eds) Handbook of environmental economics. North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 1219–1271
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brock, W.A., Taylor, M.S. The Green Solow model. J Econ Growth 15, 127–153 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10887-010-9051-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10887-010-9051-0