Abstract
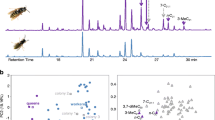
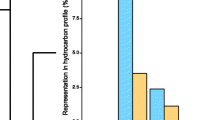
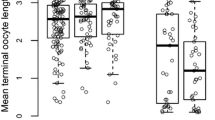
Ants use chemical signals to communicate for various purposes related to colony function. Social organization in the red imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta, is determined by the Sb supergene, with colonies of the monogyne (single-queen) form lacking the element and colonies of the polygyne (multiple-queen) form possessing it. Polygyne workers accept new reproductive queens in their nest, but only those carrying Sb; young winged queens lacking this genetic element are executed as they mature sexually in their natal nest or as they attempt to enter a foreign nest to initiate reproduction after mating and shedding their wings. It has been suggested that queen supergene genotype status is signaled to workers by unsaturated cuticular hydrocarbons, while queen reproductive status is signaled by piperidines (venom alkaloids). We used high-throughput behavioral assays to study worker acceptance of paper dummies dosed with fractions of extracts of polygyne queens, or blends of synthetic counterparts of queen cuticular compounds. We show that the queen supergene pheromone comprises a blend of monoene and diene unsaturated hydrocarbons. Our assays also reveal that unsaturated hydrocarbons elicit discrimination by polygyne workers only when associated with additional compounds that signal queen fertility. This synergistic effect was obtained with a polar fraction of queen extracts, but not by the piperidine alkaloids, suggesting that the chemical(s) indicating queen reproductive status are compounds more polar than cuticular hydrocarbons but are not the piperidine alkaloids. Our results advance understanding of the role of chemical signaling that is central to the regulation of social organization in an important invasive pest and model ant species.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data will be deposited to Dryad before publication. Data are also available upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Arsenault SV, King JT, Kay S, Lacy KD, Ross KG, Hunt BG (2020) Simple inheritance, complex regulation: Supergene-mediated fire ant queen polymorphism. Mol Ecol 29:3622–3636. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.15581
Ascunce MS, Yang CC, Oakey J, Calcaterra L, Wu WJ, Shih CJ, Goudet J, Ross KG, Shoemaker D (2011) Global invasion history of the fire ant Solenopsis invicta. Science 331:1066–1068. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1198734
Banks WA, Lofgren CS, Jouvenaz DP, Stringer CE, Bishop PM, Williams DF, Wojcik PD, Glancey BM (1981) Techniques for collecting, rearing, and handling imported fire ants. U.S. Dept Agric Tech AAT-S- 21:9
Blomquist GJ, Bagnères AG (2010) Insect hydrocarbons: biology, biochemistry, and chemical ecology. Cambridge University Press
Blomquist GJ, Ginzel MD (2021) Chemical ecology, biochemistry, and molecular biology of insect hydrocarbons. Ann Entomol Soc Am 66:45–60. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-031620-071754
Brand P, Robertson HM, Lin W, Pothula R, Klingeman WE, Jurat-Fuentes JL, Johnson BR (2018) The origin of the odorant receptor gene family in insects. Elife 7:e38340. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38340.001
Cohanim AB, Amsalem E, Saad R, Shoemaker D, Privman E (2018) Evolution of olfactory functions on the fire ant social chromosome. Genome Biol Evol 10:2947–2960. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evy204
Crozier RH, Pamilo P (1996) Evolution of social insect colonies. Oxford University Press
Crozier RH (2002) Pheromones and the single queen. Nat Genet 30:4–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0102-4
Dang VD, Cohanim AB, Fontana S, Privman E, Wang J (2019) Has gene expression neofunctionalization in the fire ant antennae contributed to queen discrimination behavior? Ecol Evol 9:12754–12766. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.5748
Eliyahu D, Ross KG, Haight KL, Keller L, Liebig J (2011) Venom alkaloid and cuticular hydrocarbon profiles are associated with social organization, queen fertility status, and queen genotype in the fire ant Solenopsis invicta. J Chem Ecol 37:1242–1254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-011-0037-y
Fletcher DJ, Blum MS (1981) Pheromonal control of dealation and oogenesis in virgin queen fire ants. Science 212:73–75. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.212.4490.73
Fletcher DJ, Blum MS (1983) The inhibitory pheromone of queen fire ants: effects of disinhibition on dealation and oviposition by virgin queens. J Comp Physiol 153:467–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00612601
Fletcher DJ, Blum MS, Whitt TV, Temple N (1980) Monogyny and polygyny in the fire ant, Solenopsis invicta. Ann Entomol Soc Am 73:658–661. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/73.6.658
Fontana S, Chang NC, Chang T, Lee CC, Dang VD, Wang J (2020) The fire ant social supergene is characterized by extensive gene and transposable element copy number variation. Mol Ecol 29:105–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.15308
Gibbs A, Pomonis JG (1995) Physical properties of insect cuticular hydrocarbons: the effects of chain length, methyl-branching and unsaturation. Comp Biochem Phys B 112:243–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0491(95)00081-X
Gotzek D, Ross KG (2007) Genetic regulation of colony social organization in fire ants: an integrative overview. Quarterly Rev Biol 82:201–226. https://doi.org/10.1086/519965
Helmkampf M, Cash E, Gadau J (2015) Evolution of the insect desaturase gene family with an emphasis on social Hymenoptera. Mol Biol Evol 32:456–471. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu315
Hölldobler B, Wilson EO (1990) The ants. Harvard University Press
Hölldobler B (1995) The chemistry of social regulation: multicomponent signals in ant societies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:19–22. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.1.19
Holze H, Schrader L, Buellesbach J (2020) Advances in deciphering the genetic basis of insect cuticular hydrocarbon biosynthesis and variation. Heredity 126:219–234. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41437-020-00380-y
Huang YC, Wang J (2014) Did the fire ant supergene evolve selfishly or socially? BioEssays 36:200–208. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201300103
Jemal A, Hugh-Jones M (1993) A review of the red imported fire ant (Solenopsis invicta Buren) and its impacts on plant, animal, and human health. Prev Vet Med 17:19–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-5877(93)90051-T
Keller L, Nonacs P (1993) The role of queen pheromones in social insects: queen control or queen signal? Animal Behav 45:787–794. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbe.1993.1092
Keller L, Ross KG (1998) Selfish genes: A green beard in the red fire ant. Nature 394:573–575. https://doi.org/10.1038/29064
Kocher SD, Grozinger CM (2011) Cooperation, conflict, and the evolution of queen pheromones. J Chem Ecol 37:1263–1275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-011-0036-z
Krieger MJ, Ross KG (2002) Identification of a major gene regulating complex social behavior. Science 295:328–332. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1065247
Krieger MJ, Ross KG (2005) Molecular evolutionary analyses of the odorant-binding protein gene Gp-9 in fire ants and other Solenopsis species. Mol Biol Evol 22:2090–2103. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msi203
Martin S, Drijfhout F (2009) A review of ant cuticular hydrocarbons. J Chem Ecol 35:1151–1161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-009-9695-4
Mir B, Vinson SB, Piedrahita JA (2003) Artificial maturation of female alates for the purpose of the production of only male Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Southwest Entomol 28:19–26
Nipitwattanaphon M, Wang J, Dijkstra MB, Keller L (2013) A simple genetic basis for complex social behaviour mediates widespread gene expression differences. Mol Ecol 22:3797–3813. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.12346
Pelosi P, Iovinella I, Zhu J, Wang G, Dani FR (2018) Beyond chemoreception: diverse tasks of soluble olfactory proteins in insects. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 93:184–200. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12339
Pracana R, Levantis I, Martinez-Ruiz C, Stolle E, Priyam A, Wurm Y (2017) Fire ant social chromosomes: Differences in number, sequence and expression of odorant binding proteins. Evol Lett 1:199–210. https://doi.org/10.1002/evl3.22
R CORE TEAM (2017) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Ross KG (1988) Differential reproduction in multiple-queen colonies of the fire ant Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 23:341–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00303708
Ross KG (1997) Multilocus evolution in fire ants: effects of selection, gene flow, and recombination. Genetics 145:961–974. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/145.4.961
Ross KG, Keller L (1998) Genetic control of social organization in an ant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14232–14237. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.24.14232
Ross KG, Keller L (2002) Experimental conversion of colony social organization by manipulation of worker genotype composition in fire ants (Solenopsis invicta). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 51:287–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00265-001-0431-5
Ross KG, Shoemaker D (2018) Unexpected patterns of segregation distortion at a selfish supergene in the fire ant Solenopsis invicta. BMC Genet 19:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-018-0685-9
RSTUDIO TEM, Inc., Boston, MA (2016) RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio. http://www.rstudio.com/
Trible W, Ross KG (2016) Chemical communication of queen supergene status in an ant. J Evol Biol 29:502–513. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeb.12799
Tschinkel WR (2013) The fire ants. Belknap Press
Valles SM, Porter SD (2003) Identification of polygyne and monogyne fire ant colonies (Solenopsis invicta) by multiplex PCR of Gp-9 alleles. Insectes Soc 50:199–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00040-003-0662-8
Vander Meer RK, Alonso LE (1998) Pheromone directed behavior in ants. In: Vander Meer RK, Breed MD, Winston M, Espelie KE (eds) Pheromone communication in social insects: ants, wasps, bees, and termites. CRC Press, pp 159–192
Vander Meer RK, Glancey BM, Lofgren CS, Glover A, Tumlinson JH, Rocca J (1980) The poison sac of red imported fire ant queens: source of a pheromone attractant. Ann Entomol Soc Am 73:609–612. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/73.5.609
Van Oystaeyen A, Oliveira RC, Holman L et al (2014) Conserved class of queen pheromones stops social insect workers from reproducing. Science 343:287–290. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1244899
Vargo EL (1992) Mutual pheromonal inhibition among queens in polygyne colonies of the fire ant Solenopsis invicta. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 31:205–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168648
Vargo EL (1999) Reproductive development and ontogeny of queen pheromone production in the fire ant Solenopsis invicta. Physiol Entomol 24:370–376. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3032.1999.00153.x
Vargo EL, Laurel M (1994) Studies on the mode of action of a queen primer pheromone of the fire ant Solenopsis invicta. J Insect Physiol 40:601–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1910(94)90147-3
Vargo EL, Hulsey CD (2000) Multiple glandular origins of queen pheromones in the fire ant Solenopsis invicta. J Insect Physiol 46:1151–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-1910(99)00226-7
Wang J, Wurm Y, Nipitwattanaphon M, Riba-Grognuz O, Huang YC, Shoemaker D, Keller L (2013) A Y-like social chromosome causes alternative colony organization in fire ants. Nature 493:664–668. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11832
Wurm Y, Wang J, Riba-Grognuz O et al (2011) The genome of the fire ant Solenopsis invicta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:5679–5684. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1009690108
Wylie R, Yang CCS, Tsuji K (2020) Invader at the gate: The status of red imported fire ant in Australia and Asia. Ecol Res 35:6–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1703.12076
Yan H, Jafari S, Pask G, Zhou X, Reinberg D, Desplan C (2020) Evolution, developmental expression and function of odorant receptors in insects. J Exp Biol 223. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.208215
Acknowledgements
HZ and KGR were supported by US NSF grants to KR (1354479) and to Brendan G. Hunt and KR (1755130), and by US Federal Hatch project funds to KR. LK and KGR were supported by a grant from the Swiss National Science Foundation (310030B_176406). JGM gratefully acknowledges support from US Federal Hatch project CA-R*ENT-5181-H.
Funding
See acknowledgement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 41438 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, H., Millar, J.G., Chen, L. et al. Characterization of Queen Supergene Pheromone in the Red Imported Fire Ant Using Worker Discrimination Assays. J Chem Ecol 48, 109–120 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-021-01336-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-021-01336-0