Abstract
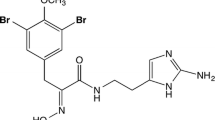
Sponges of the genus Aplysina accumulate brominated isoxazoline alkaloids in concentrations that sometimes exceed 10% of their dry weight. We previously reported a decrease in concentrations of these compounds and a concomitant increase in concentrations of the monocyclic nitrogenous compounds aeroplysinin-1 and dienone in Aplysina aerophoba following injury of the sponge tissue. Further investigations indicated a wound-induced enzymatic cleavage of the former compounds into the latter, and demonstrated that these reactions also occur in other Aplysina sponges. A recent study on Caribbean Aplysina species, however, introduced doubt regarding the presence of a wound-induced bioconversion in sponges of this genus. This discrepancy motivated us to reinvestigate carefully the fate of brominated alkaloids in A. aerophoba and in other Aplysina sponges following mechanical injury. As a result of this study we conclude that (1) tissue damage induces a bioconversion of isoxazoline alkaloids into aeroplysinin-1 and dienone in Aplysina sponges, (2) this reaction is likely catalyzed by enzymes, and (3) it may be ecologically relevant as the bioconversion products possibly protect the wounded sponge tissue from invasion of bacterial pathogens.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. R. Adler C. D. Harvell (1990) ArticleTitleInducible defenses, phenotypic variability and biotic environments Trends Ecol. Evol. 5 407–410 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0169-5347(90)90025-9
A. Aiello E. Fattorusso M. Menna M. Pansini (1995) ArticleTitleChemistry of Verongida sponges. 5. Brominated metabolites from the Caribbean sponge Pseudoceratina sp Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 23 377–381 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXot1Onu7g%3D
S. Albrizio P. Ciminiello E. Fattorusso S. Magno M. Pansini (1994) ArticleTitleChemistry of Verongida sponges. 1. Constituents of the Caribbean sponge Pseudoceratina crassa Tetrahedron 50 783–788 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0040-4020(01)80793-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXhsF2hsLk%3D
G. J. Bakus N. M. Targett B. Schulte (1986) ArticleTitleChemical ecology of marine organisms: An overview J. Chem. Ecol. 12 951–987 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01638991 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XksFGksb8%3D
M. A. Becerro X. Turon M. J. Uriz (1995) ArticleTitleNatural variation of toxicity in encrusting sponge Crambe crambe (Schmidt) in relation to size and environment J. Chem. Ecol. 21 1931–1946 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02033853 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xis1ymuw%3D%3D
M. A. Becerro X. Turon M. J. Uriz (1997) ArticleTitleMultiple functions for secondary metabolites in encrusting marine invertebrates J. Chem. Ecol. 23 1527–1547 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:JOEC.0000006420.04002.2e Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXksFCqsb8%3D
M. Betancourt-Lozano F. Gonzalez-Farias B. Gonzalez-Acosta A. Garcia-Gasca J. R. Bastida-Zavala (1998) ArticleTitleVariation of antimicrobial activity of the sponge Aplysina fistularis (Pallas, 1766) and its relation to associated fauna J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 223 1–18 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-0981(97)00153-6
P. Ciminiello V. Costantino E. Fattorusso S. Magno A. Mangoni M. Pansini (1994a) ArticleTitleChemistry of Verongida sponges. 2. Constituents of the Caribbean sponge Aplysina fistularis forma fulva J. Nat. Prod. 57 705–712 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXlsFeltbw%3D
P. Ciminiello E. Fattorusso S. Magno M. Pansini (1994b) ArticleTitleChemistry of Verongida sponges. 3. Constituents of a Caribbean Verongula sp J. Nat. Prod. 57 1564–1569 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXislKju70%3D
P. Ciminiello E. Fattorusso S. Magno M. Pansini (1995) ArticleTitleChemistry of Verongida sponges. 4. Comparison of the secondary metabolite composition of several specimens of Pseudoceratina crassa J. Nat. Prod. 58 689–696 Occurrence Handle10.1021/np50119a006 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXms1enu7g%3D
P. Ciminiello E. Fattorusso S. Magno M. Pansini (1996a) ArticleTitleChemistry of Verongida sponges. 6. Comparison of the secondary metabolic composition of Aplysina insularis and Aplysina fulva Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 24 105–107
P. Ciminiello C. Dell'aversano E. Fattorusso S. Magno L. Carrano M. Pansini (1996b) ArticleTitleChemistry of Verongida sponges. 7. Bromocompounds from the Caribbean sponge Aplysina archeri Tetrahedron 52 9863–9868 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0040-4020(96)00518-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XksVajtr4%3D
P. Ciminiello E. Fattorusso M. Forino S. Magno M. Pansini (1997) ArticleTitleChemistry of Verongida sponges. 8. Bromocompounds from the Mediterranean sponges Aplysina aerophoba and Aplysina cavernicola Tetrahedron 53 6565–6572 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0040-4020(97)00311-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjtlymtL8%3D
P. Ciminiello C. Dell'aversano E. Fattorusso S. Magno M. Pansini (1999) ArticleTitleChemistry of Verongida sponges. 9. Secondary metabolite composition of the Caribbean sponge Aplysina cauliformis J. Nat. Prod. 62 590–593 Occurrence Handle10.1021/np9805138 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhvFSjtbc%3D Occurrence Handle10217716
P. Ciminiello C. Dell'aversano E. Fattorusso S. Magno M. Pansini (2000) ArticleTitleChemistry of Verongida sponges. 10. Secondary metabolite composition of the Caribbean sponge Verongula gigantea J. Nat. Prod. 63 263–266 Occurrence Handle10.1021/np990343e Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXksVSkug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10691724
E. E. Conn (1979) Cyanide and cyanogenic glycosides G. A. Rosenthal D. H. Janzen (Eds) Herbivores: Their Interaction with Secondary Plant Metabolites Academic Press New York 387–412
C. Debitus G. Guella I. Mancini J. Waikedre J. P. Guemas J. L. Nicolas F. Pietra (1998) ArticleTitleQuinolones from a bacterium and tyrosine metabolites from its host sponge, Suberea creba from the Coral Sea J. Mar. Biotechnol. 6 136–141 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlslChsbk%3D Occurrence Handle9701634
Ebel, R. (1998). Wundinduzierte Biotransformation bromierter Alkaloide in Schwämmen der Gattung Aplysina: Biochemische Charakterisierung und ökologische Bedeutung. PhD dissertation. University of Würzburg, Germany.
R. Ebel M. Brenzinger A. Kunze H. J. Gross P. Proksch (1997) ArticleTitleWound activation of protoxins in marine sponge Aplysina aerophoba J. Chem. Ecol. 23 1451–1462 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:JOEC.0000006475.10310.3a Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXktVyitb0%3D
R. Ebel A. Marin P. Proksch (1999) ArticleTitleOrgan-specific distribution of dietary alkaloids in the marine opisthobranch Tylodina perversa Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 27 769–777 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXltVCjt7o%3D
S. Engel P. R. Jensen W. Fenical (2002) ArticleTitleChemical ecology of marine microbial defense J. Chem. Ecol. 28 1971–1985 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1020793726898 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnvFOitbY%3D Occurrence Handle12474894
J. W. Fahey A. T. Zalcmann P. Talalay (2001) ArticleTitleThe chemical diversity and distribution of glucosinolates and isothiocyanates among plants Phytochemistry 56 5–51 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0031-9422(00)00316-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXitlakug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11198818
Fendert, T. (2000). Charakterisierung der enzymatischen Abwehrreaktion in Schwämmen der Gattung Aplysina und Isolierung von Bromotyrosinakaloiden aus Aplysina insularis. PhD dissertation. University of Würzburg, Germany.
R. M. Gleadow I. E. Woodrow (2002) ArticleTitleConstraints on effectiveness of cyanogenic glycosides in herbivore defense J. Chem. Ecol. 28 1301–1313 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1016298100201 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmsVGmsbs%3D Occurrence Handle12199497
W. A. Glen C. Y. Kramer (1958) ArticleTitleAnalysis of variance of a randomized block design with missing observations Appl. Stat. 7 173–185
G. Goldenstein T. Fendert P. Proksch E. Winterfeldt (2000) ArticleTitleEnantioselective preparation and enzymatic cleavage of spiroisoxazoline amides Tetrahedron 56 4173–4185 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0040-4020(00)00342-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXksVOnsbw%3D
G. Green (1977) ArticleTitleEcology of toxicity in marine sponges Mar. Biol. 40 207–215 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00390876
K. Hammerstrom M. N. Dethier D. O. Duggins (1998) ArticleTitleRapid phlorotannin induction and relaxation in five Washington kelps Mar. Ecol., Prog. Ser. 165 293–305 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXjtlGqtLk%3D
C. D. Harvell (1990) ArticleTitleThe ecology and evolution of inducible defenses Q. Rev. Biol. 65 323–340 Occurrence Handle10.1086/416841 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6D2cnms1Q%3D Occurrence Handle2236483
J. Havel (1986) Predator-induced defenses: A review W. C. Kerfoot A. Sih (Eds) Predation: Direct and Indirect Effects on Aquatic Communities University Press of New England Hanover, NH 263–278
M. E. Hay W. Fenical (1988) ArticleTitleMarine plant–herbivore interactions: The ecology of chemical defense Annu. Rev. Ecolog. Syst. 19 111–145
A. Hickel M. Hasslacher H. Griengl (1996) ArticleTitleHydroxynitrile lyases: Functions and properties Physiol. Plant. 98 891–898 Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1399-3054.1996.980430.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXhs1arsQ%3D%3D
V. Jung G. Pohnert (2001) ArticleTitleRapid wound-activated transformation of the green algal defensive metabolite caulerpenyne Tetrahedron 57 7169–7172 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXlslCms78%3D
V. Jung T. Thibaut A. Meinesz T. G. Pohner (2002) ArticleTitleComparison of the wound-activated transformation of caulerpenyne by invasive and noninvasive Caulerpa species of the Mediterranean J. Chem. Ecol. 28 2091–2105 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1020710230532 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnvFOiurg%3D Occurrence Handle12474902
S. R. Kelly P. R. Jensen T. P. Henkel W. Fenical J. R. Pawlik (2003) ArticleTitleEffects of Caribbean sponge extracts on bacterial attachment Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 31 175–182
S. M. Lewis J. N. Norris R. B. Searles (1987) ArticleTitleThe regulation of morphological plasticity in tropical reef algae by herbivory Ecology 68 636–641
C. C. Li (1964) Introduction to Experimental Statistics McGraw-Hill New York
M. Lurling (2003) ArticleTitleThe effect of substances from different zooplankton species and fish on the induction of defensive morphology in the green alga Scenedesmus obliquus J. Plankton Res. 25 979–989
Marinlit Version October 2003. A marine literature database produced and maintained by the Department of Chemistry, University of Canterbury, New Zealand.
J. B. McClintock D. Swenson H. Trapido-Rosenthal L. Banghart (1997) ArticleTitleIchthyodeterrent properties of lipophilic extracts from Bermudian sponges J. Chem. Ecol. 23 1607–1620 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:JOEC.0000006425.86488.8d Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXksFCqsbg%3D
W. E. G. Müller M. Klemt N. L. Thakur H. C. Schröder A. Aiello M. D'esposito M. Menna E. Fattorusso (2004) ArticleTitleMolecular/chemical ecology in sponges: Evidence for an adaptive antibacterial response in Suberites domuncula Mar. Biol. 144 19–29 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00227-003-1184-7
M. Page L. West P. Northcote C. Battershill M. Kelly (2005) ArticleTitleSpatial and temporal variability of cytotoxic metabolites in populations of the New Zealand sponge Mycale hentscheli J. Chem. Ecol. 31 1161–1174 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10886-005-4254-0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXks1eksr0%3D Occurrence Handle16124239
V. J. Paul M. P. Puglisi (2004) ArticleTitleChemical mediation of interactions among marine organisms Nat. Prod. Rep. 21 189–209 Occurrence Handle10.1039/b302334f Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXisFWgtbo%3D Occurrence Handle15039843
V. J. Paul K. L. Alstyne ParticleVan (1992) ArticleTitleActivation of chemical defenses in the tropical green algae Halimeda spp J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 160 191–203 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-0981(92)90237-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXhs1CqsLY%3D
M. Puyana W. Fenical J. R. Pawlik (2003) ArticleTitleAre there activated chemical defenses in sponges of the genus Aplysina from the Caribbean? Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 246 127–135 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXivVCjsLk%3D
E. Richelle-Maurer M. J. Kluijver Particlede S. Feio S. Gaudencio H. Gaspar R. Gomez R. Tavares G. Vyver ParticleVan de R. W. M. Soest Particlevan (2003) ArticleTitleLocalization and ecological significance of oroidin and sceptrin in the Caribbean sponge Agelas conifera Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 31 1073–1091 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXls1eku78%3D
A. L. Roda I. T. Baldwin (2003) ArticleTitleMolecular technology reveals how the induced direct defenses of plants work Basic Appl. Ecol. 4 15–26 Occurrence Handle10.1078/1439-1791-00130 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXit1Ghtro%3D
H. C. Steel R. Cockeran R. Anderson (2002) ArticleTitlePlatelet-activating factor and lyso-PAF possess direct antimicrobial properties in vitro APMIS 110 158–164 Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1600-0463.2002.100206.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjvFGlsrY%3D Occurrence Handle12064871
R. S. Steneck W. H. Adey (1976) ArticleTitleRole of environment in control of morphology in Lithophyllum congestum, a Caribbean algal ridge builder Bot. Mar. 19 197–215
G. S. Stoewsand (1995) ArticleTitleBioactive organosulfur phytochemicals in Brassica oleracea vegetables—a review Food Chem. Toxicol. 33 537–543 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXmsFyls7k%3D Occurrence Handle7797181
R. Tanaka H. Ishizaki S. Kawano H. Okuda K. Miyahara N. Noda (1997) ArticleTitleFruiting-inducing activity and antifungal properties of lipid components in members of Annelida Chem. Pharm. Bull. 45 1702–1704 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXntVKqtrs%3D Occurrence Handle9353899
R. B. Taylor E. Sotka M. E. Hay (2002) ArticleTitleTissue-specific induction of herbivore resistance: Seaweed response to amphipod grazing Oecologia 132 68–76 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00442-002-0944-2
R. Teeyapant P. Proksch (1993) ArticleTitleBiotransformation of brominated compounds in the marine sponge Verongia aerophoba. Evidence for an induced chemical defense? Naturwissenschaften 80 369–370 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01138794 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXmt1ais7Y%3D
R. Teeyapant H. J. Woerdenbag P. Kreis J. Hacker V. Wray L. Witte P. Proksch (1993) ArticleTitleAntibiotic and cytotoxic activity of brominated compounds from the marine sponge Verongia aerophoba Z. Naturforsch. 48c 939–945
R. W. Thacker M. A. Becerro W. A. Lumbang V. J. Paul (1998) ArticleTitleAllelopathic interactions between sponges on a tropical reef Ecology 79 1740–1750
J. E. Thompson K. D. Barrow D. J. Faulkner (1983) ArticleTitleLocalization of two brominated metabolites, aerothionin and homoaerothionin, in spherulous cells of the marine sponge Aplysina fistularis Acta Zool. Stockh. 64 199–210
C. Thoms M. Horn M. Wagner U. Hentschel P. Proksch (2003a) ArticleTitleMonitoring microbial diversity and natural product profiles of the sponge Aplysina cavernicola following transplantation Mar. Biol. 142 685–692 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXisFCqurY%3D
C. Thoms R. Ebel U. Hentschel P. Proksch (2003b) ArticleTitleSequestration of dietary alkaloids by the spongivorous marine mollusc Tylodina perversa Z. Naturforsch. 58c 426–432
C. Thoms M. Wolff K. Padmakumar R. Ebel P. Proksch (2004) ArticleTitleChemical defense of Mediterranean sponges Aplysina cavernicola and Aplysina aerophoba Z. Naturforsch. 59c 113–122
X. Turon M. A. Becerro M. J. Uriz (2000) ArticleTitleDistribution of brominated compounds within the sponge Aplysina aerophoba: Coupling of X-ray microanalysis with cryofixation techniques Cell Tissue Res. 301 311–322 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004410000233 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmtFKitbo%3D Occurrence Handle10955726
K. L. Alstyne ParticleVan L. T. Houser (2003) ArticleTitleDimethylsulfide release during macroinvertebrate grazing and its role as an activated chemical defense Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 250 175–181
K. L. Alstyne ParticleVan G. V. Wolfe T. L. Freidenburg A. Neill C. Hicken (2001) ArticleTitleActivated defense systems in marine macroalgae: Evidence for an ecological role for DMSP cleavage Mar. Ecol., Prog. Ser. 213 53–65
H. Wajant F. Effenberger (1996) ArticleTitleHydroxynitrile lyases of higher plants Biol. Chem. 377 611–617 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XnsVems7w%3D Occurrence Handle8922588
B. Weiss R. Ebel M. Elbrächter M. Kirchner P. Proksch (1996) ArticleTitleDefense metabolites from the marine sponge Verongia aerophoba Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 24 1–12 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XhslCnu7g%3D
G. V. Wolfe M. Steinke (1996) ArticleTitleGrazing-activated production of dimethyl sulfide (DMS) by two clones of Emiliania huxleyi Limnol. Oceanogr. 41 1151–1160 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmtVCjsg%3D%3D
G. V. Wolfe M. Steinke G. O. Kirst (1997) ArticleTitleGrazing-activated chemical defence in a unicellular marine alga Nature 387 894–897 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXkt1Grtrc%3D
J. H. Zar (1999) Biostatistical Analysis Prentice-Hall Upper Saddle River, NJ
Acknowledgment
We acknowledge Prof. Werner E.G. Müller, Prof. Renato Batel, and the staff of the Ruder Boscovic Center for Marine Research for assistance during organization of sample collections and laboratory work at Rovinj, Croatia. We also thank Sabine Borstel for help in isolating the sponge metabolites and Arno Kunze for samples from Caribbean Aplysina sponges. Carsten Thoms acknowledges support with a Fedodor Lynen Fellowship from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, Bonn. This work was supported by the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (project: Center of Excellence BIOTECmarin). Finally, we thank two anonymous referees who helped to improve this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thoms, C., Ebel, R. & Proksch, P. Activated Chemical Defense in Aplysina Sponges Revisited. J Chem Ecol 32, 97–123 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-006-9355-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-006-9355-x