Abstract
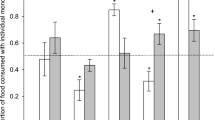
Plant secondary metabolites (PSMs) are a major constraint to the ingestion of food by folivorous and browsing herbivores. Understanding the way in which mammalian detoxification pathways are adapted to deal with PSMs is crucial to understanding how PSMs influence ingestive behavior of herbivores and hence their fitness and the impact that they have on vegetation. Pharmacological concepts can provide insights into the relationship between the absorption and metabolic fate of PSMs and ingestive behavior. Lipophilic PSMs will be absorbed into the bloodstream and must be removed fast enough to prevent their accumulation to toxic levels. Elimination depends on their metabolism, usually by cytochrome P450 enzymes, to more polar metabolites that can be excreted by the kidney. The concentration of PSM in blood (C) is a better measure of exposure to a toxin compared to the amount ingested because there can be great variability in the rate and degree of absorption from the gut. C rises and falls depending on the relative rates of absorption and elimination. These rates depend in part on metabolic and transport processes that are saturable and liable to inhibition and induction by PSMs, indicating that complex interactions are likely. Herbivores can use diet choice and the rate and amount of PSM consumption to prevent C from reaching a critical level that produces significant adverse effects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, M. J., Dawson, K. A., Mayberry, W. R., and Foss, J. G. 1985. Oxalobacter formigenes gen. nov., sp. nov.: Oxalate-degrading anaerobes that inhabit the gastrointestinal tract. Arch. Microbiol. 141:1–7.
Arnold, G. W. 1981. Grazing behavior, pp. 79–104, in F. W. Morley (ed.). Grazing Animals. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Ayrton, A. and Morgan, P. 2001. Role of transport proteins in drug absorption, distribution and excretion. Xenobiotica 31:469–497.
Bonnesen, C., Stephensen, P. U., Andersen, O., Sorensen, H., and Vang, O. 1999. Modulation of cytochrome P-450 and glutathione S-transferase isoform expression in vivo by intact and degraded indolyl glucosinolates. Nutr. Cancer 33:178–187.
Boyle, R., McLean, S., Foley, W. J., and Davies, N. W. 1999. Comparative metabolism of dietary terpene, p-cymene, in generalist and specialist folivorous marsupials. J. Chem. Ecol. 25:2109–2126.
Boyle, R., McLean, S., Foley, W. J., Moore, B. D., Davies, N. W., and Brandon, S. 2000. Fate of the dietary terpene, p-cymene, in the male koala. J. Chem. Ecol. 25:1095–1111.
Boyle, R., McLean, S., Foley, W., Davies, N. W., Peacock, E. J., and Moore, B. 2001. Metabolites of dietary 1,8-cineole in the male koala (Phascolarctos cinereus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 129:385–395.
Boyle, R. R., McLean, S., Brandon, S., Pass, G. J., and Davies, N. W. 2002. Application of solid-phase microextraction to the quantitative analysis of 1,8-cineole in blood and expired air in a Eucalyptus herbivore, the brushtail possum (Trichosurus vulpecula). J. Chromatogr. B. 780:397–406.
Boyle, R. R., McLean, S., Brandon, S., and Wiggins, N. 2005. Rapid absorption of dietary 1,8-cineole results in critical blood concentration of cineole and immediate cessation of eating in the common brushtail possum (Trichosurus vulpecula). J. Chem. Ecol. 31:2775–2790.
Bryant, J. P., Provenza, F. D., Pastor, J., Reichardt, P. B., Clausen, T. P., and Dutoit, J. T. 1991. Interactions between woody-plants and browsing mammals mediated by secondary metabolites. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 22:431–446.
Burritt, E. A. and Provenza, F. D. 2000. Role of toxins in intake of varied diets by sheep. J. Chem. Ecol. 26:1991–2005.
Carlson, J. R. and Breeze, R. G. 1984. Ruminal metabolism of plant toxins with emphasis on indolic compounds. J. Anim. Sci. 58:1040–1049.
Cork, S. J. and Sanson, G. D. 1991. Digestion and nutrition in the koala: A review, pp. 129–144, in A. K. Lee, K. A. Handasyde, and G. D. Sanson (eds.). Biology of the Koala. Surrey Beatty and Sons, Chipping Norton, NSW.
Davis, A. R. and Lipson, A. H. 1986. Central-nervous-system tolerance to high blood-alcohol levels. Med. J. Aust. 144:9–12.
Deleu, D., Northway, M. G., and Hanssens, Y. 2002. Clinical pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of drugs used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 41:261–309.
Doherty, M. M. and Charman, W. N. 2002. The mucosa of the small intestine—how clinically relevant as an organ of drug metabolism? Clin. Pharmacokinet. 41:235–253.
Dresser, G. K. and Bailey, D. G. 2003. The effects of fruit juices on drug disposition: A new model for drug interactions. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 33:10–16.
Dresser, G. K., Schwarz, U. I., Wilkinson, G. R., and Kim, R. B. 2003. Coordinate induction of both cytochrome P4503A and MDRI by St John's wort in healthy subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 73:41–50.
Duncan, A. J., Frutos, P., and Young, S. A. 1997. Rates of oxalic acid degradation in the rumen of sheep and goats in response to different levels of oxalic acid administration. Anim. Sci. 65:451–455.
Duncan, A. J., Frutos, P., and Young, S. A. 2000. The effect of rumen adaptation to oxalic acid on selection of oxalic-acid-rich plants by goats. Br. J. Nutr. 83:59–65.
Falk, A., Lof, A., Hagberg, M., Hjelm, E. W., and Wang, Z. P. 1991. Human exposure to 3-carene by inhalation-toxicokinetics, effects on pulmonary-function and occurrence of irritative and CNS-symptoms. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 110:198–205.
Foley, W. J., Iason, G. R., and McArthur, C. 1999. Role of plant secondary metabolites in the nutritional ecology of mammalian herbivores: How far have we come in 25 years? pp. 130–209, in H.-J. G. Jung and G. C. Fahey (eds.). San Antonio, Texas, USA. American Society of Animal Science, Savoy, IL.
Freeland, W. J. and Janzen, D. H. 1974. Strategies in herbivory by mammals: The role of plant secondary compounds. Am. Nat. 108:268–289.
Fu, P. P., Xia, Q. S., Lin, G., and Chou, M. W. 2004. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids—genotoxicity, metabolism enzymes, metabolic activation, and mechanisms. Drug Metab. Rev. 36:1-55.
Gonzalez, F. J. and Nebert, D. W. 1990. Evolution of the P450 gene superfamily: Animal–plant “warfare”, molecular drive and human genetic differences in drug oxidation. Trends Genet. 6:182–186.
Greenblatt, D. J., von Moltke, L. L., Harmatz, J. S., Chen, G. S., Weemhoff, J. L., Jen, C., Kelley, C. J., LeDuc, B. W., and Zinny, M. A. 2003. Time course of recovery of cytochrome P450 3A function after single doses of grapefruit juice. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 74:121–129.
Hardman, J. G., Limbird, L. E., and Gilman, A. G. 2001. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Heady, H. F. 1964. Palatability of herbage and animal preference. J. Range Manag. 17:76–82.
Hellriegel, E. T., Bjornsson, T. D., and Hauck, W. W. 1996. Interpatient variability in bioavailability is related to the extent of absorption: Implications for bioavailability and bioequivalence studies. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 60:601–607.
Hester, A. J., Bergman, M., Iason, G. R., and Moen, J. 2006. Impact of large herbivores on plant community structure and dynamics, in K. Danell, R. Gergstrom, P. Duncan, and J. Pastor (eds.). Large Herbivore Ecology and Ecosystem Dynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, in press.
Hollenberg, P. F. 2002. Characteristics and common properties of inhibitors, inducers, and activators of CYP enzymes. Drug Metab. Rev. 34:17–35.
Hume, I. D. 1999. Marsupial Nutrition. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Iason, G. R. and Van Wieren, S. E. 1999. Digestive and ingestive adaptations of mammalian herbivores to low-quality forage, pp. 337–369, in H. H. Olff, V. K. Brown, and R. H. Drent (eds.). Herbivores: Between Plants and Predators, 38th Symposium of the British Ecological Society. Blackwell, Oxford.
Iason, G. R. and Villalba, J. J. 2006. Behavioral strategies of mammal herbivores against plant secondary metabolites: The avoidance–tolerance continuum. J. Chem. Ecol., this issue.
Ioannides, C. 1999. Effect of diet and nutrition on the expression of cytochromes 450. Xenobiotica 29:109–154.
Kinirons, M. T. and O'Mahony, M. S. 2004. Drug metabolism and ageing. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 57:540–544.
Lawler, I. R., Foley, W. J., Pass, G. J., and Eschler, B. M. 1998. Administration of a 5HT(3) receptor antagonist increases the intake of diets containing Eucalyptus secondary metabolites by marsupials. J. Comp. Physiol. B 168:611–618.
Le Houezec, J. 1998. Nicotine: Abused substance and therapeutic agent. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 23:95–108.
Lee, W. and Kim, R. B. 2004. Transporters and renal drug elimination. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 44:137–166.
Lewis, D. F., Watson, E., and Lake, B. G. 1998. Evolution of the cytochrome P450 superfamily: Sequence alignments and pharmacogenetics. Mutat. Res. 410:245–270.
Lin, J. H. and Lu, A. Y. H. 2001. Interindividual variability in inhibition and induction of cytochrome P450 enzymes. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 41:535–567.
Lin, J. H. and Yamazaki, M. 2003. Role of P-glycoprotein in pharmacokinetics—clinical implications. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 42:59–98.
Lotsch, J., Skarke, C., Liefhold, J., and Geisslinger, G. 2004. Genetic predictors of the clinical response to opioid analgesics: Clinical utility and future perspectives. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 43:983–1013.
Machala, M., Soucek, P., Neca, J., Ulrich, R., Lamka, J., Szotakova, B., and Skalova, L. 2003. Inter-species comparisons of hepatic cytochrome P450 enzyme levels in male ruminants. Arch. Toxicol. 77:555–560.
Manach, C., Scalbert, A., Morand, C., Remesy, C., and Jimenez, L. 2004. Polyphenols: Food sources and bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 79:727–747.
McLean, S., Brandon, S., Davies, N. W., Foley, W. J., and Muller, H. K. 2004. Jensenone: Biological reactivity of a marsupial antifeedant from Eucalyptus. J. Chem. Ecol. 30:19–36.
McNaughton, S. J. 1983. Compensatory plant growth as a response to herbivory. Oikos 40:329–336.
Meibohm, B. and Derendorf, H. 1997. Basic concepts of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) modelling. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 35:401–413.
Moore, B. D. and Foley, W. J. 2005. Tree use by koalas in a chemically complex landscape. Nature 435:488–490.
Moore, B. D., Wallis, I. R., Pala-Paul, J., Brophy, J. J., Willis, R. H., and Foley, W. J. 2004. Antiherbivore chemistry of Eucalyptus—cues and deterrents for marsupial folivores. J. Chem. Ecol. 30:1743–1769.
Moore, L. B., Goodwin, B., Jones, S. A., Wisely, G. B., Serabjit-Singh, C. J., Willson, T. M., Collins, J. L., and Kliewer, S. A. 2000. St. John's wort induces hepatic drug metabolism through activation of the pregnane X receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97:7500–7502.
Moriwaki, H., Tsujimoto, Y., Shimizu, M., Noda, T., Warashina, M., and Tanaka, M. 2005. Influence of sodium benzoate on the metabolism of o-xylene in the rat. Xenobiotica 35:487–497.
Nelson, D. R. 2003. Comparison of P450s from human and fugu: 420 million years of vertebrate P450 evolution. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 409:18–24.
Nutt, D. 1999. Alcohol and the brain—pharmacological insights for psychiatrists. Br. J. Psychiatry 175:114–119.
O'Brien, C. P. 2001. Drug addiction and drug abuse, pp. 621–642, in J. G. Hardman, L. E. Limbird, and A. G. Gilman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Olthof, M. R., Hollman, P. C. H., Buijsman, M., van Amelsvoort, J. M. M., and Katan, M. B. 2003. Chlorogenic acid, quercetin-3-rutinoside and black tea phenols are extensively metabolized in humans. J. Nutr. 133:1806–1814.
Parkinson, A. 2001. Biotransformation of xenobiotics, pp. 133–224, in C. D. Klaasen (ed.). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology: The Basic Science of Poisons. 6th ed. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Pass, G. J. and Foley, W. J. 2000. Plant secondary metabolites as mammalian feeding deterrents: Separating the effects of the taste of salicin from its post-ingestive consequences in the common brushtail possum (Trichosurus vulpecula). J. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 170.
Pass, G. J. and McLean, S. 2002. Inhibition of the microsomal metabolism of 1,8-cineole in the common brushtail possum (Trichosurus vulpecula) by terpenes and other chemicals. Xenobiotica 32:1109–1126.
Pass, G. J., McLean, S., and Stupans, I. 1999. Induction of xenobiotic metabolising enzymes in the common brushtail possum, Trichosurus vulpecula, by Eucalyptus terpenes. J. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 124:239–246.
Pass, G. J., McLean, S., Stupans, I., and Davies, N. 2001. Microsomal metabolism of the terpene 1,8-cineole in the common brushtail possum (Trichosurus vulpecula), koala (Phascolarctos cinereus), rat and human. Xenobiotica 31:205–221.
Pass, G. J., McLean, S., Stupans, I., and Davies, N. W. 2002. Microsomal metabolism and enzyme kinetics of the terpene p-cymene in the common brushtail possum (Trichosurus vulpecula), koala (Phascolarctos cinereus) and rat. Xenobiotica 32:383–397.
Pfister, J. A., Provenza, F. D., Manners, G. D., Gardner, D. R., and Ralphs, M. H. 1997. Tall larkspur ingestion: Can cattle regulate intake below toxic levels? J. Chem. Ecol. 23:759–777.
Provenza, F. D. 1995. Postingestive feedback as an elementary determinant of food preference and intake in ruminants. J. Range Manag. 48:2–17.
Provenza, F. D., Villalba, J. J., and Bryant, B. P. 2003. Foraging by herbivores: Linking the biochemical diversity of plants to herbivore culture and landscape diversity, pp.387–421, in J. A. Bissonette and I. Staoch (eds.). Landscape Ecology and Resource Management. Linking Theory with Practice. Island Press, Washington.
Rechner, A. R., Smith, M. A., Kuhnle, G., Gibson, G. R., Debnam, E. S., Srai, S. K. S., Moore, K. P., and Rice-Evans, C. A. 2004. Colonic metabolism of dietary polyphenols: Influence of structure on microbial fermentation products. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 36:212–225.
Rhoades, D. F. 1979. Evolution of plant chemical defence against herbivores, pp. 3–54, in G. A. Rosenthal and D. H. Janzen (eds.). Herbivores. Their Interaction with Secondary Plant Metabolites. Academic Press, New York.
Rodighiero, V. 1999. Effects of liver disease on pharmacokinetics. An update. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 37:399–431.
Rosenthal, G. A. and Berenbaum, M. R. 1991. Herbivores. Their interactions with Secondary Plant Metabolites. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Illinois.
Ross, E. M. and Kenakin, T. P. 2001. Pharmacodynamics: Mechanisms of drug action and the relationship between drug concentration and effect, pp. 31–42, in J. G. Hardman, L. E. Limbird, and A. G. Gilman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Rowland, M. and Tozer, T. N. 1995. Clinical Pharmacokinetics—Concepts and Applications. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, p. 601.
Saito, R., Takano, Y., and Kamiya, H. O. 2003. Roles of substance P and NK(1) receptor in the brainstem in the development of emesis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 91:87–94.
Shargel, L. and Yu, A. 1999. Applied Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Shimada, T., Mimura, M., Inoue, K., Nakamura, S., Oda, H., Ohmori, S., and Yamazaki, H. 1997. Cytochrome P450-dependent drug oxidation activities in liver microsomes of various animal species including rats, guinea pigs, dogs, monkeys, and humans. Arch. Toxicol. 71:401–408.
Smith, R. H. 1980. Kale poisoning: The brassica anaemia factor. Vet. Rec. 107:12–15.
Sorensen, J. S., Heward, E., and Dearing, M. D. 2005. Plant secondary metabolites alter the feeding patterns of a mammalian herbivore (Neotoma lepida). Oecologia 146:415–422.
Terrill, T. H., Waghorn, G. C., Woolley, D. J., McNabb, W. C., and Barry, T. N. 1994. Assay and digestion of C-14-labeled condensed tannins in the gastrointestinal-tract of sheep. Br. J. Nutr. 72:467–477.
Tibballs, J. 1995. Clinical effects and management of eucalyptus oil ingestion in infants and young children. Med. J. Aust. 163:177–180.
Von Rudloff, E. 1975. Volatile leaf oil analysis in chemosystematic studies of North American conifers. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2:131–167.
Walter-Sack, I. and Klotz, U. 1996. Influence of diet and nutritional status on drug metabolism. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 31:47–64.
Weaver, R. J. 2001. Assessment of drug–drug interactions: Concepts and approaches. Xenobiotica 31:499–538.
Weinshilboum, R. 2003. Genomic medicine—inheritance and drug response. N. Engl. J. Med. 348:529–537.
Werck-Reichhart, D. and Feyerreisen, R. 2000. Cytochromes P450: A success story. Genome Biol. 1:3002.9–3003.1.
Wiggins, N. L., McArthur, C., McLean, S., and Boyle, R. 2003. Effects of two plant secondary metabolites, cineole and gallic acid, on nightly feeding patterns of the common brushtail possum. J. Chem. Ecol. 29:1447–1464.
Wiggins, N. L., Marsh, K. J., Wallis, I. R., Foley, W. J., and McArthur, C. 2005. Sideroxylonal in Eucalyptus foliage influences foraging behavior of an arboreal folivore. Oecologia http://www.springerlink.com/link.asp?id=32tj3775u2341578.
Wiggins, N. L., McArthur, C., Davies, N. W., and McLean, S. 2006. Behavioral responses of a generalist mammalian folivore to the physiological constraints of a chemically defended diets. J. Chem. Ecol., in this issue.
Wilkinson, G. R. 2001. Pharmacokinetics: The dynamics of drug absorption, distribution, and elimination, pp. 3–29, in J. G. Hardman, L. E. Limbird, and A. G. Gilman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Williams, S. H. and Kay, R. F. 2001. A comparative test of adaptive explanations for hypsodonty in ungulates and rodents. J. Mammal. Evol. 8:207–229.
Woodhouse, K. 1992. Drugs and the liver. Part III. Ageing of the liver and the metabolism of drugs. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 13:311–320.
Yamaguchi, T., Caldwell, J., and Farmer, P. B. 1994. Metabolic fate of [H-3]-l-menthol in the rat. Drug Metab. Dispos. 22:616–624.
Zahorik, D. M., Houpt, K. A., and Swartzmanandert, J. 1990. Taste-aversion learning in 3 species of ruminants. Appl. Animal Behav. Sci. 26:27–39.
Zhou, S. F., Gao, Y. H., Jiang, W. Q., Huang, M., Xu, A. L., and Paxton, J. W. 2003. Interactions of herbs with cytochrome P450. Drug Metab. Rev. 35:35–98.
Zhou, S. F., Koh, H. L., Gao, Y. H., Gong, Z. Y., and Lee, E. J. D. 2004a. Herbal bioactivation: The good, the bad and the ugly. Life Sci. 74:935–968.
Zhou, S. F., Lim, L. Y., and Chowbay, B. 2004b. Herbal modulation of P-glycoprotein. Drug Metab. Rev. 36:57–104.
Acknowledgments
Our thanks to Takuya Shimada and Bill Foley for convening the symposium and stimulating the writing of this review, and to Glenn Iason for useful commments on a draft manuscript. We are also grateful to our coworkers, in particular, Rebecca Boyle and Sue Brandon. This work has in part been supported by the Australian Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McLean, S., Duncan, A.J. Pharmacological Perspectives on the Detoxification of Plant Secondary Metabolites: Implications for Ingestive Behavior of Herbivores. J Chem Ecol 32, 1213–1228 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-006-9081-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-006-9081-4