Abstract
Objective
Adolescents from Puerto Rican backgrounds are found to have higher rates of obesity than adolescents from other ethnic groups in the US. The objective of this study is to examine whether sleeping the recommended number of hours and depression or anxiety disorder are independently related to risk for obesity in a sample of Island Puerto Rican adolescents, and whether the association between sleep and obesity is moderated by depression or anxiety disorder.
Methods
Data from the study were derived from the third wave of an island wide probability sample of Puerto Rican youth residing on the Island, 10–25 years of age (N = 825), with a response rate of 79.59%. The current study focuses on youth 10 to 19 years of age (n = 436).
Results
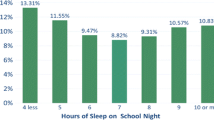
In this sample, youth who slept less than the recommended number of hours (defined as 7–9 h per night) had a significantly increased risk for obesity and were three times as likely to be obese. Youth who met criteria for a depressive/anxiety disorder were almost 2.5 times as likely to be obese. However, the presence of an anxiety/depressive disorders did not moderate the association between sleeping the recommended number of hours and risk for obesity.
Conclusion
Sleeping less than the recommended number of hours may be an important risk factor for obesity status in Island Puerto Rican youth. These findings suggest that attention to healthy sleep behaviors and a sleep environment that promotes high quality sleep may be important for Puerto Rican adolescents at risk for obesity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta-Perez, E., Canino, G., Ramirez, R., Prelip, M., Martin, M., & Ortega, A. N. (2012). Do Puerto Rican youth with asthma and obesity have higher odds for mental health disorders? Psychosomatics, 53, 162–171. doi:10.1016/j.psym.2011.07.011.
Alfano, C. A., Pina, A. A., Zerr, A. A., & Villalta, I. K. (2010). Pre-sleep arousal and sleep problems of anxiety-disordered youth. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 41, 156–167. doi:10.1007/s10578-009-0158-5.
American Psychiatric Association (1994). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Angold, A., Erkanli, A., Farmer, E. M., Fairbank, J. A., Burns, B. J., Keeler, G., & Costello, E. J. (2002). Psychiatric disorder, impairment, and service use in rural African American and white youth. Archives of General Psychiatry, 59, 893–901.
Binder, D. A. (1983). On the variances of asymptotically normal estimators from complex surveys. International Statistical Review, 51, 279–292.
Boergers, J., & Koinis-Mitchell, D. (2010). Sleep and culture in children with medical conditions. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 35, 915–926.
Bravo, M., Ribera, J., Rubio-Stipec, M., Canino, G., Shrout, P., Ramirez, R., ... Martinez-Taboas, A. (2001). Test-retest reliability of the spanish version of the Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children (DISC-IV). Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 5, 433–444.
Brook, J. S., Zhang, C., Saar, N. S., & Brook, D. W. (2009). Psychosocial predictors, higher body mass index, and aspects of neurocognitive dysfunction. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 108(1), 181–195.
Canino, G., Shrout, P. E., Rubio-Stipec, M., Bird, H. R., Bravo, M., Ramirez, R., Martinez-Taboas, A. (2004). The DSM-IV rates of child and adolescent disorders in Puerto Rico: Prevalence, correlates, service use, and the effects of impairment. Archives of General Psychiatry, 61, 85–93.
Cappuccio, F. P., Taggart, F. M., Kandala, N. B., Currie, A., Peile, E., Stranges, S., & Miller, M. A. (2008). Meta-analysis of short sleep duration and obesity in children and adults. Sleep, 31, 619–626.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2010a). Behavioral risk factor surveillance system survey questionnaire. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2010b). Growth Charts. Retrieved January 14, from http://www.cdc. gov/growthcharts/percentile_data_files.htm.
Chen, X., Beydoun, M. A., & Wang, Y. (2008). Is sleep duration associated with childhood obesity? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obesity (Silver Spring), 16, 265–274. doi:10.1038/oby.2007.63.
Dewald, J. F., Meijer, A. M., Oort, F. J., Kerkhof, G. A., & Bogels, S. M. (2010). The influence of sleep quality, sleep duration and sleepiness on school performance in children and adolescents: A meta-analytic review. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 14, 179–189. 10.1016/j.smrv.2009.10.004.
Feldman, J., Ortega, A., McQuaid, E., & Canino, G. (2006). Comorbidity between asthma attacks and internalizing disorders among Puerto Rican children at one-year follow-up. Psychosomatics, 47, 333–339.
Friedman, H. L. (1993). Adolescent social development: a global perspective. Implications for health promotion across cultures. Journal of Adolescent Health, 14, 588–594, 648–554.
Garza, J. R., Perez, E. A., Prelip, M., McCarthy, W. J., Feldman, J. M., Canino, G., & Ortega, A. N. (2011). Occurrence and correlates of overweight and obesity among island Puerto Rican youth. Ethnicity and Disease, 21(2), 163–169.
Goodwin, J. L., Kaemingk, K. L., Fregosi, R. F., Rosen, G. M., Morgan, W. J., Sherrill, D. L., & Quan, S. F. (2003). Clinical outcomes associated with sleep-disordered breathing in Caucasian and Hispanic children—The Tucson children’s assessment of sleep apnea study (TuCASA). Sleep, 26, 587–591.
Gore, S., Aseltine, R., & Colton, M. (1992). Social structure, life stress and depressive symptoms in high school-aged population. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 97–113.
Grills, A. E., & Ollendick, T. H. (2002). Issues in caregiver-child agreement: the case of structured diagnostic interviews. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 5, 57–83.
Jansen, P. W., Saridjan, N. S., Hofman, A., Jaddoe, V. W., Verhulst, F. C., & Tiemeier, H. (2011). Does disturbed sleeping precede symptoms of anxiety or depression in toddlers? The generation R study. Psychosomatic Medicine, 73, 242–249.
Jensen, P. S., Rubio-Stipec, M., Canino, G., Bird, H. R., Dulcan, M. K., Schwab-Stone, M. E., & Lahey, B. B. (1999). Caregiver and child contributions to diagnosis of mental disorder: Are both informants always necessary? Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 38, 1569–1579. doi:10.1097/00004583-199912000-00019.
Knutson, K. L., & Turek, F. W. (2006). The U-shaped association between sleep and health: The 2 peaks do not mean the same thing. Sleep, 29, 878–879.
Koinis-Mitchell, D., Craig, T., Esteban, C. A., & Klein, R. B. (2012). Sleep and allergic disease: A summary of the literature and future directions for research. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 130, 1275–1281. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.06.026.
Kozak, A. T., Daviglus, M. L., Chan, C., Kiefe, C. I., Jacobs, D. R., Jr., & Liu, K. (2011). Relationship of body mass index in young adulthood and health-related quality of life two decades later: The coronary artery risk development in young adults study. International Journal of Obesity (London), 35, 134–141. doi:10.1038/ijo.2010.120.
Kraemer, H. C., Measelle, J. R., Ablow, J. C., Essex, M. J., Boyce, W. T., & Kupfer, D. J. (2003). A new approach to integrating data from multiple informants in psychiatric assessment and research: mixing and matching contexts and perspectives. American Journal of Psychiatry, 160, 1566–1577.
Langellier, B. A., Martin, M. A., Canino, G., Garza, J. R., & Ortega, A. N. (2012). The health status of youth in Puerto Rico. Clinical Pediatrics, 51(6), 569–573. doi:10.1177/0009922812443123.
Lytle, L. A., Murray, D. M., Laska, M. N., Pasch, K. E., Anderson, S. E., & Farbakhsh, K. (2012). Examining the longitudinal relationship between change in sleep and obesity risk in adolescents. Health Education and Behavior, 40, 362–370. doi:10.1177/1090198112451446.
Maggs, J. L., Schulenberg, J., & Hurrelman, K. (1997). Developmental transitions during adolescence: Health promotion implications. In J. Schulenberg, J. L. Maggs & K. Hurrelman (Eds.), Health risks and developmental transitions during adolescence. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Miller, M. A., & Cappuccio, F. P. (2007). Inflammation, sleep, obesity and cardiovascular disease. Current Vascular Pharmacology, 5, 93–102.
Mindell, J. A., Owens, J. A., & Carskadon, M. A. (1999). Developmental features of sleep. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 8, 695–725.
National Sleep Foundation. (2010). Sleep in America Poll. Retrieved from http://www.sleepfoundation.org, March 13, 2012.
Nguyen-Rodriguez, S. T., McClain, A. D., & Spruijt-Metz, D. (2010). Anxiety mediates the relationship between sleep onset latency and emotional eating in minority children. Eating Behaviors, 11, 297–300.
O’Connor, G. T., Lind, B. K., Lee, E. T., Nieto, F. J., Redline, S., Samet, J. M., ...& Foster, G, L. (2003). Variation in symptoms of sleep-disordered breathing with race and ethnicity: The sleep heart health study. Sleep, 26, 74–79.
Patel, N. P., Grandner, M. A., Xie, D., Branas, C. C., & Gooneratne, N. (2010). “Sleep disparity” in the population: poor sleep quality is strongly associated with poverty and ethnicity. Boston Medical Center Public Health, 10, 475. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-10-475.
Patel, S. R., & Hu, F. B. (2008). Short sleep duration and weight gain: a systematic review. Obesity (Silver Spring), 16, 643–653. doi:10.1038/oby.2007.118.
Patel, S. R., Malhotra, A., Gottlieb, D. J., White, D. P., & Hu, F. B. (2006). Correlates of long sleep duration. Sleep, 29, 881–889.
Prats-Puig, A., Grau-Cabrera, P., Riera-Perez, E., Cortes-Marina, R., Fortea, E., Soriano-Rodriguez, P., Lopez-Bermejo, A. (2012). Variations in the obesity genes FTO, TMEM18 and NRXN3 influence the vulnerability of children to weight gain induced by short sleep duration. International Journal of Obesity (London), 37, 182–187. doi:10.1038/ijo.2012.27.
Prochaska, J.J., Sallis, J.F., & Long B. (2001). A physical activity screening measure for use with adolescents in primary care. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 155 (5), 554–559.
Roberts, R. E., Roberts, C. R., & Chen, I. G. (2000). Ethnocultural differences in sleep complaints among adolescents. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 188, 222–229.
Shaffer, D., Fisher, P., Dulcan, M. K., Davies, M., Piacentini, J., Schwab-Stone, M. E., ... & Regier, D. A. (1996). The NIMH diagnostic interview schedule for children (DISC 2.3): Description, acceptability, prevalences, and performance in the MECA study. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 35, 865–877. doi:10.1097/00004583-199607000-00012.
Taylor, D. J., Lichstein, K. L., Durrence, H. H., Reidel, B. W., & Bush, A. J. (2005). Epidemiology of insomnia, depression, and anxiety. Sleep, 28, 1457–1464.
U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), (2005). Dietary guidelines for Americans USDA;42.
Venegas, H. L., Perez, C. M., Suarez, E. L., & Guzman, M. (2003). Prevalence of obesity and its association with blood pressure, serum lipids and selected lifestyles in a Puerto Rican population of adolescents 12–16 years of age. Puerto Rico Health Sciences Journal, 22, 137–143.
Vgontzas, A. N., Bixler, E. O., & Chrousos, G. P. (2003). Metabolic disturbances in obesity versus sleep apnoea: The importance of visceral obesity and insulin resistance. Journal of Internal Medicine, 254, 32–44.
Funding
Supported in part by award number R25RR017589 from the National Center for Research Resources, National Institutes of Health, and National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) grant R01 MH069849 (A. Ortega, PI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Daphne Koinis-Mitchell, Nicolás Rosario-Matos, Rafael R. Ramírez, Pedro García, Glorisa J. Canino and Alexander N. Ortega declare they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Informed Consent
All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koinis-Mitchell, D., Rosario-Matos, N., Ramírez, R.R. et al. Sleep, Depressive/Anxiety Disorders, and Obesity in Puerto Rican Youth. J Clin Psychol Med Settings 24, 59–73 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10880-017-9483-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10880-017-9483-1