Abstract
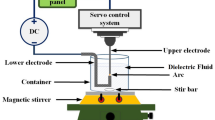
This Study synthesized the nanosilver colloid (NSC) via arc discharge. The electric force ionizes the deionized water (DW) inter electrode gap, and the plenty of electrons and ions are attracted by opposite electricity. The electrons and ions strike surface of the electrodes, and sputter the nanosilver particles (NSP). The NSP stably suspend in the DW without surface-active agent. It is a novel and rapid preparation in the standard temperature and pressure. Although the industrial electric discharge machine (EDM) could synthesize NSC, it’s too costly and big size. The self-designing micro-EDM that can real-time monitor the processing is substitute the industrial-EDM. By the spectrophotometry, the zetasizer and the scanning electron microscope validate the properties of the NSC that synthesized by the micro-EDM. The results show that the NSC is the same as the features of nanomaterials. The energy of the discharge can be controlled, that can determine the process time. The concentration of the NSP can effectively reduce the difference between the products of the NSC. As the arcing rate (AR) and the absorption peaks are highly correlated, the concentration of the NSP can be predicted during processing. It’s a speedy and preliminary determine of the concentration.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jonathan A. Scholl, Aitzol García-Etxarri, Ai Leen Koh, and Jennifer A. Dionne (2013). Nano Lett. 13, 564.
Kuo-Hsiung Tseng, Chih-Yu Liao, Jen-Chuen Huang, Der-Chi Tien, and Tsing-Tshih Tsung (2008). Mater. Lett. 62, 3341.
D. C. Tien, C. Y. Liao, J. C. Huang, K. H. Tseng, J. K. Lung, and T. T. Tsung (2008). Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 18, 750.
Chih-Yu Liao, Kuo-Hsiung Tseng, and Hong-Shiou Lin (2013). Metallu. Mater. Trans. B 44, 91.
Kuo-Hsiung Tseng, Juei-Long Chiu, Heng-Lin Lee, Chih-Yu Liao, Hong-Shiou Lin, and Yi-Syuan Kao (2015). Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1.
F. Fang, J. Kennedy, J. Futter, T. Hopf, A. Markwitz, E. Manikandan, and G. Henshaw (2011). Nanotechlogy 22, 33.
R. K. Sahu, S. H. Somashekhar, and P. V. Manivannan (2013). Proc. Eng. 64, 946.
Enbo Yang and Masaaki Nagatsu (2014). Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 53, 1.
Marin Gostimirovic, Pavel Kovac, Milenko Sekulic, and Branko Skoric (2012). J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 26, 173.
Tushara Prakash, Grant V. M. Williams, John Kennedy, Peter P. Murmu, Jérôme Leveneur, Shen V. Chong, and Sergey Rubanovd (2014). J. Alloy. Compd. 608, 153.
A. Cuche, B. Stein, A. Canaguier-Durand, E. Devaux, C. Genet, and T. W. Ebbesen (2012). Nano Lett. 12, 4329.
Ian C. Bourg and Garrison Sposito (2011). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 360, 701.
Jun Liu, Yangyang Gao, Dapeng Cao, Liqun Zhang, and Zhanhu Guo (2011). Langmuir 27, 7926.
Jie Lana, Yong Yang, and Xiaochun Li (2004). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 386, 284.
Kadir Aslana, Joseph R. Lakowiczb, and Chris D. Geddesa (2004). Anal. Biochem. 330, 145.
Yu A Akimov, W. S. Koh, and K. Ostrikov (2009). Opt. Express 17, 10195.
F. Fang, J. Kennedy, E. Manikandan, J. Futter, and A. Markwitz (2012). Chem. Phys. Lett. 521, 86.
Majid Darroudi, Mansor Bin Ahmad, Reza Zamiri, A. K. Zak, Abdul Halim Abdullah, and Nor Azowa Ibrahim (2011). Int. J. Nanomed. 6, 677.
Kuo-Hsiung Tseng, Juei-Long Chiu, Heng-Lin Lee, Yi-Syuan Kao, and Der-Chi Tien (2016). Mater. Manuf. Process. 31, 186.
Jiunn-Woei Liaw, Shiao-Wen Tsaib, Hung-Hsun Lina, Tzu-Chen Yend, and Bae-Renn Cheng (2012). J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 113, 2234.
Zhaowei Liua, Guogang Renb, Tao Zhangc, and Zhuo Yang (2009). Toxicology 264, 179.
M. M. Mukaka (2012). Malawi Med. J. 24, 69.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 103-2221-E-027-070-) for financial supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tseng, K.H., Kao, YS. & Chang, CY. Development and Implementation of a Micro-electric Discharge Machine: Real-Time Monitoring System of Fabrication of Nanosilver Colloid. J Clust Sci 27, 763–773 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-016-0985-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-016-0985-z