Abstract
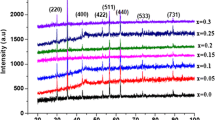
NiFe2−x Bi x O4 (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3) nanoparticles with various grain sizes were synthesized via annealing treatment followed by ball milling of its bulk component materials. Commercially available bismuth, nickel and iron oxide powders were first mixed and then annealed at 1200 °C in an oxygen environment furnace for 4 h. The samples were then milled for 2 h by high-energy ball milling. X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern indicated that in this stage the samples are single phase. The microstructure investigation was carried out by a scanning electron microscope with maximum magnification of 30,000. The average grain size for different samples was estimated by XRD technique and transmission electron microscopy. Magnetic behavior of the samples at room temperature was studied using an alternating gradient force magnetometry. The Néel temperature of the powders was measured by a Faraday balance. Based on magnetic studies, increase in bismuth content leads to a decrease in the saturation magnetization, coercive field and Néel temperature. This can be attributed to the substitution of Bi3+ ion in the ferrite system as a nonmagnetic cation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. S. Benjamin (1970). Metal. Trans. 1, 2943.
P. S. Gilman and J. S. Benjamin (1983). Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci. 13, 279.
H. Bea, M. Gajek, M. Bibes, and A. Barthelemy (2008). J. Phys. Cond. Matter. 20, 434221.
A. H. Morrish The Physical Principles of Magnetism (IEEE Press, New York, 2001).
M. N. Ashiq, M. F. Ehsan, M. J. Iqbal, and I. H. Gul (2011). J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 5119.
K. Maaz, S. Karim, A. Mashiatullah, J. Liu, M. D. Hou, Y. M. Sun, J. L. Duan, H. J. Yao, D. Mob, and Y. F. Chen (2009). Phys. B. 404, 3947.
M. J. Nasr Isfahani, M. Jafari Fesharaki, and V. Šepelák (2013). Ceram. Int. 39, 1163.
M. J. Nasr Isfahani, P. Nasr Isfahani, K. L. Da Silva, A. Feldhoff, and V. Šepelák (2011). Ceram. Int. 37, 1905.
B. D. Cullity Elements of X-ray Diffraction (Addison-Wesley Publishing, Reading, 1956).
M. Muroi, P. G. McCormick, and R. Street (2000). J. Solid State Chem. 152, 503.
N. Mo, Y.-Y. Song, and C. E. Patton (2005). J. Appl. Phys. 97, 093901.
M. J. Nasr Isfahani, M. Myndyk, V. Šepelák, and J. Amighian (2009). J. Alloy Compd. 470, 434.
J. Smit Magnetic Properties of Materials (McGraw Hill Book Co., New York, 1971).
S. Chikazumi Physics of Ferromagnetism, 2nd ed (Oxford University Press, New York, 1997).
B. D. Cullity Introduction to magnetic materials (Addison-Wesley Publishing, Reading, 2001).
A. Goldman Modern Ferrite Technology (Springer, New York, 2006).
D. Craik Magnetism Principles and Application (Wiley, Chichester, 1995).
G. Nabiyouni, M. Jafari Fesharaki, and M. Mozafari (2010). J. Amighian Chin. Phys. Lett. 27, 126401.
M. Muroi, R. Street, P. G. McCormic, and J. Amighian (2001). Phys. Rev. 63, 184414.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the “Shahid Chamran University, Ahvaz, Iran”; for TEM image, “Kashan University, Kashan, Iran”; for AGFM measurements, “Falavarjan Free University, Esfahan, Iran”; for Néel temperature and “Arak University, Arak, Iran” for XRD patterns preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jafari Fesharaki, M., Nabiyouni, G., Shahdoost, B. et al. Magnetic Investigation of Various NiFe2−x Bi x O4 Ferrite Nanostructures Synthesized by Ball Milling Technique. J Clust Sci 27, 1005–1015 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-015-0907-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-015-0907-5