Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate engraftment and adverse events with a conditioning and prophylactic regimen intended to achieve high rates of engraftment with minimal graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) in allogeneic transplantation for chronic granulomatous disease in a single center.
Methods
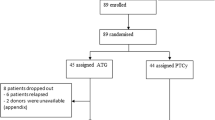
Forty patients, 37 male, with chronic granulomatous disease were transplanted. Transplant products were matched sibling peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs) in four and matched unrelated donor (MUD) bone marrow in three, and one patient received mismatched unrelated PBSCs. Thirty-two patients received MUD PBSCs. All patients received a conditioning regimen of busulfan/alemtuzumab (with low-dose total body irradiation for MUD recipients) with sirolimus graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis.
Results
Engraftment occured in 38/40 recipients (95%). Acute or chronic GVHD occurred in 18 (45%) and 5 (12.5%), respectively, with 6 episodes of grades III–IV and/or steroid refractory GVHD. Overall survival was 33/40 (82.5%) and event-free survival was 30/40 (80%). Successful engraftment was associated with myeloid and NK cell, but not CD3+ chimerism. Myeloid engraftment was greater than 70% in 30/32 recipients at mean follow-up of 3.4 years. Evidence of persistent immunodeficiency was not seen in successful transplants. Attempts to rescue failed or poorly functioning grafts were associated with unacceptable morbidity and mortality.
Conclusions
A reduced-intensity allogeneic transplant protocol based on alemtuzumab and busulfan with sirolimus GVHD prophylaxis produced high rates of successful engraftment and minimal regimen-related toxicity. Prolonged clinical follow-up has confirmed its efficacy in ameliorating CGD-related disease. Outcomes were not acceptable with donor cell infusion rescue of cause with poor graft function.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlin A, Fugelang J, de Boer M, Ringden O, Fasth A, Winiarski J. Chronic granulomatous disease-haematopoietic stem cell transplantation versus conventional treatment. Acta Paediatr. 2013;102(11):1087–94.
Gozdzik J, Pituch-Noworolska A, Skoczen S, Czogala W, Wedrychowicz A, Baran J, et al. Allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation as therapy for chronic granulomatous disease—single centre experience. J Clin Immunol. 2011;31(3):332–7.
Tewari P, Martin PL, Mendizabal A, Parikh SH, Page KM, Driscoll TA, et al. Myeloablative transplantation using either cord blood or bone marrow leads to immune recovery, high long-term donor chimerism and excellent survival in chronic granulomatous disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012;18(9):1368–77.
Soncini E, Slatter MA, Jones LB, Hughes S, Hodges S, Flood TJ, et al. Unrelated donor and HLA-identical sibling haematopoietic stem cell transplantation cure chronic granulomatous disease with good long-term outcome and growth. Br J Haematol. 2009;145(1):73–83.
Mehta B, Mahadeo K, Kapoor N, Abdel-Azim H. Low-dose total-body irradiation and alemtuzumab-based reduced-intensity conditioning regimen results in durable engraftment and correction of clinical disease among children with chronic granulomatous disease. Pediatr Transplant. 2015;19(4):408–12.
Martinez CA, Shah S, Shearer WT, Rosenblatt HM, Paul ME, Chinen J, et al. Excellent survival after sibling or unrelated donor stem cell transplantation for chronic granulomatous disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129(1):176–83.
Cole T, Pearce MS, Cant AJ, Cale CM, Goldblatt D, Gennery AR. Clinical outcome in children with chronic granulomatous disease managed conservatively or with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132(5):1150–5.
Seger RA, Gungor T, Belohradsky BH, Blanche S, Bordigoni P, Di Bartolomeo P, et al. Treatment of chronic granulomatous disease with myeloablative conditioning and an unmodified hemopoietic allograft: a survey of the European experience, 1985–2000. Blood. 2002;100(13):4344–50.
Gungor T, Teira P, Slatter M, Stussi G, Stepensky P, Moshous D, et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning and HLA-matched haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation in patients with chronic granulomatous disease: a prospective multicentre study. Lancet. 2014;383(9915):436–48.
Horwitz ME, Barrett AJ, Brown MR, Carter CS, Childs R, Gallin JI, et al. Treatment of chronic granulomatous disease with nonmyeloablative conditioning and a T-cell-depleted hematopoietic allograft. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(12):881–8.
Kuhns DB, Alvord WG, Heller T, Feld JJ, Pike KM, Marciano BE, et al. Residual NADPH oxidase and survival in chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(27):2600–10.
Vassal G, Michel G, Esperou H, Gentet JC, Valteau-Couanet D, Doz F, et al. Prospective validation of a novel IV busulfan fixed dosing for paediatric patients to improve therapeutic AUC targeting without drug monitoring. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008;61(1):113–23.
Malar R, Sjoo F, Rentsch K, Hassan M, Gungor T. Therapeutic drug monitoring is essential for intravenous busulfan therapy in pediatric hematopoietic stem cell recipients. Pediatr Transplant. 2011;15(6):580–8.
Morillo-Gutierrez B, Beier R, Rao K, Burroughs L, Schulz A, Ewins AM, et al. Treosulfan-based conditioning for allogeneic HSCT in children with chronic granulomatous disease: a multicenter experience. Blood. 2016;128(3):440–8.
Bhatia S, Davies SM, Scott Baker K, Pulsipher MA, Hansen JA. NCI, NHLBI first international consensus conference on late effects after pediatric hematopoietic cell transplantation: etiology and pathogenesis of late effects after HCT performed in childhood—methodologic challenges. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011;17(10):1428–35.
Ottinger HD, Rebmann V, Pfeiffer KA, Beelen DW, Kremens B, Runde V, et al. Positive serum crossmatch as predictor for graft failure in HLA-mismatched allogeneic blood stem cell transplantation. Transplantation. 2002;73(8):1280–5.
Remberger M, Mattsson J, Olsson R, Ringden O. Second allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a treatment for graft failure. Clin Transpl. 2011;25(1):E68–76.
Oshrine B, Morsheimer M, Heimall J, Bunin N. Reduced-intensity conditioning for hematopoietic cell transplantation of chronic granulomatous disease. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015;62(2):359–61.
Chakraverty R, Orti G, Roughton M, Shen J, Fielding A, Kottaridis P, et al. Impact of in vivo alemtuzumab dose before reduced intensity conditioning and HLA-identical sibling stem cell transplantation: pharmacokinetics, GVHD, and immune reconstitution. Blood. 2010;116(16):3080–8.
Marsh RA, Kim MO, Liu C, Bellman D, Hart L, Grimley M, et al. An intermediate alemtuzumab schedule reduces the incidence of mixed chimerism following reduced-intensity conditioning hematopoietic cell transplantation for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19(11):1625–31.
Ketterl TG, Flesher M, Shanley R, Miller W. Early CD3+/CD15+ peripheral blood leukocyte chimerism patterns correlate with long-term engraftment in non-malignant hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49(4):572–5.
Breuer S, Preuner S, Fritsch G, Daxberger H, Koenig M, Poetschger U, et al. Early recipient chimerism testing in the T- and NK-cell lineages for risk assessment of graft rejection in pediatric patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Leukemia. 2012;26(3):509–19.
Zecher D, Li Q, Oberbarnscheidt MH, Demetris AJ, Shlomchik WD, Rothstein DM, et al. NK cells delay allograft rejection in lymphopenic hosts by downregulating the homeostatic proliferation of CD8+ T cells. J Immunol. 2010;184(12):6649–57.
Laffont S, Seillet C, Ortaldo J, Coudert JD, Guery JC. Natural killer cells recruited into lymph nodes inhibit alloreactive T-cell activation through perforin-mediated killing of donor allogeneic dendritic cells. Blood. 2008;112(3):661–71.
Noval Rivas M, Hazzan M, Weatherly K, Gaudray F, Salmon I, Braun MY. NK cell regulation of CD4 T cell-mediated graft-versus-host disease. J Immunol. 2010;184(12):6790–8.
Powell JD, Fitzhugh C, Kang EM, Hsieh M, Schwartz RH, Tisdale JF. Low-dose radiation plus rapamycin promotes long-term bone marrow chimerism. Transplantation. 2005;80(11):1541–5.
Hsieh MM, Kang EM, Fitzhugh CD, Link MB, Bolan CD, Kurlander R, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for sickle cell disease. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(24):2309–17.
Acknowledgements
This project has been funded in whole or in part with federal funds from the following components of the National Institutes of Health (NIH): National Cancer Institute, NIH, under Contract No. HHSN261200800001E; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease under Intramural Project No. 1-ZAI-AI000989. The content of this publication does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the Department of Health and Human Services, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U.S. Government. This research was supported [in part] by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, National Cancer Institute, Center for Cancer Research; and [in part] by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study under IRB approved NIH Protocol No. 07-I-0075.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parta, M., Kelly, C., Kwatemaa, N. et al. Allogeneic Reduced-Intensity Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Chronic Granulomatous Disease: a Single-Center Prospective Trial. J Clin Immunol 37, 548–558 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-017-0422-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-017-0422-6