Abstract
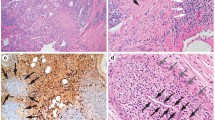
Isolated IgG4 tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) is a rare disorder characterized by raised serum IgG4 levels and histological findings of dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates rich in IgG4 positive plasma cells. We report a case of isolated IgG4 TIN that presented with acute kidney injury in an 84 year old man with a polyclonal increase in his total IgG and a raised IgE of 381 kUA/L but without evidence of systemic autoimmunity. We draw a parallel with IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis and show raised levels of circulating regulatory T cells. Importantly the plasma levels of the T regulatory cell cytokine, IL10, the TH1 cytokines IL12 and IFNγ, the proinflammatory TNF α and immune regulatory IL27 were all highly raised. Furthermore, the level of IL21 that promotes IgG4 production was also very significantly elevated. These results suggest efforts of the immune system to reduce inflammation and suppress an exaggerated Th2 response. A raised serum IgG in the setting of acute kidney injury and in the absence of autoimmunity and chronic infection should encourage an assessment of the IgG subclasses. Prompt steroid treatment of those with a raised IgG4 may reduce ongoing renal damage.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, Yi EE, Sato Y, Yoshino T, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012;25(9):1181–92.
Stone J, Yoh Z, Deshpande V. IgG4-Related disease—NEJM. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:539–51.
Raissian Y, Nasr SH, Larsen CP, Colvin RB, Smyrk TC, Takahashi N, et al. Diagnosis of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22(7):1343–52.
Van der Zee JS, Van Swieten P, Aalberse RC. Inhibition of complement activation by IgG4 antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986;64(2):415–22.
Saeki T, Nishi S, Imai N, Ito T, Yamazaki H, Kawano M, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of patients with IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2010;78(10):1016–23.
Kamisawa T, Okamoto A. IgG4-related sclerosing disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(25):3948–55.
Fukumura Y, Takase M, Mitani K, Suda K, Imamhasan A, Nobukawa B, et al. Amount of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in autoimmune pancreatitis and pilonidal sinus. Pancreas. 2012;41(6):910–5.
Kusuda T, Uchida K, Miyoshi H, Koyabu M, Satoi S, Takaoka M, et al. Involvement of inducible costimulator- and interleukin 10-positive regulatory T cells in the development of IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2011;40(7):1120–30.
Satoguina JS, Adjobimey T, Arndts K, Hoch J, Oldenburg J, Layland LE, et al. Tr1 and naturally occurring regulatory T cells induce IgG4 in B cells through GITR/GITR-L interaction, IL-10 and TGF-beta. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38(11):3101–13.
Mizushima I, Yamada K, Fujii H, Inoue D, Umehara H, Yamagishi M, et al. Clinical and histological changes associated with corticosteroid therapy in IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22(6):859–70.
Maehara T, Moriyama M, Nakashima H, Miyake K, Hayashida J-N, Tanaka A, et al. Interleukin-21 contributes to germinal centre formation and immunoglobulin G4 production in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis, so-called Mikulicz’s disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(12):2011–9.
Stumhofer JS, Hunter CA. Advances in understanding the anti-inflammatory properties of IL-27. Immunol Lett. 2008;117(2):123–30.
Acknowledgments
Nil
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, L.Y.W., Yap, H., Sampson, S. et al. IgG4- Related Disease as a Rare Cause of Tubulointerstitial Nephritis. J Clin Immunol 34, 548–550 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-014-0049-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-014-0049-9