Abstract
Purpose
Dysregulation of toll-like receptors (TLR) signaling can result in chronic inflammatory and over-exuberant repair responses. The aim of this study was to investigate the expression and clinical relevance of TLR in colorectal polyps.
Methods
The expression levels of six TLR were analyzed in 70 patients with different histological types of colorectal polyps, 38 of which developed colorectal carcinoma (CC). These analyses were performed by real-time polymerase chain reaction, western blot, and immunohistochemistry.
Results
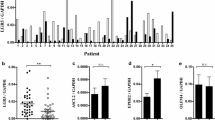
TLR9 expression was higher in hyperplastic or adenomatous polyps compared to other polyp types. Hyperplastic polyps also showed increased TLR7 levels compared to the other polyp types. TLR7 expression was lower in both hyperplastic and tubulovillous adenoma polyps from patients who developed CC. TLR9 expression was decreased in hyperplastic and villous polyps from patients who developed CC.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest a possible protective role of TLR expression against malignant transformation in the colorectal mucosa. TLR may represent a pathological marker of CC risk in colorectal polyps. The role of these factors in the pathology of colorectal polyps deserves further investigation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300.
Bujanda L, Cosme A, Gil I, Arenas-Mirave JI. Malignant colorectal polyps. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:3103–11.
Winawer S, Fletcher R, Rex D, Bond J, Burt R, Ferrucci J, et al. Colorectal cancer screening and surveillance: clinical guidelines and rationale—update based on new evidence. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:544–60.
Levin TR, Zhao W, Conell C, Seeff LC, Manninen DL, Shapiro JA, et al. Complications of colonoscopy in an integrated health care delivery system. Ann Intern Med. 2006;145:880–6.
Markowitz AJ, Winawer SJ. Screening and surveillance for colorectal carcinoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1997;11:579–608.
Kawai T, Akira S. TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:816–25.
Xiao H, Gulen MF, Qin J, Yao J, Bulek K, Kish D, et al. The Toll-interleukin-1 receptor member SIGIRR regulates colonic epithelial homeostasis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis. Immunity. 2007;26:461–75.
Abreu MT. Toll-like receptor signalling in the intestinal epithelium: how bacterial recognition shapes intestinal function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:131–44.
Lowe EL, Crother TR, Rabizadeh S, Hu B, Wang H, Chen S, et al. Toll-like receptor 2 signaling protects mice from tumor development in a mouse model of colitis-induced cancer. PLoS One. 2010;5:e13027.
Tsan MF. Toll-like receptors, inflammation and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006;16:32–7.
Shi SR, Liu C, Balgley BM, Lee C, Taylor CR. Protein extraction from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections: quality evaluation by mass spectrometry. J Histochem Cytochem. 2006;54:739–43.
Zucchini N, Bessou G, Traub S, Robbins SH, Uematsu S, Akira S, et al. Cutting edge: overlapping functions of TLR7 and TLR9 for innate defense against a herpesvirus infection. J Immunol. 2008;180:5799–803.
Coelho TR, Almeida L, Lazo PA. JC virus in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer, an etiological agent or another component in a multistep process? Virol J. 2010;7:42.
Rollison DE, Helzlsouer KJ, Lee JH, Fulp W, Clipp S, Hoffman-Bolton JA, et al. Prospective study of JC virus seroreactivity and the development of colorectal cancers and adenomas. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18:1515–23.
Shibolet O, Podolsky DK. TLRs in the gut. IV. Negative regulation of Toll-like receptors and intestinal homeostasis: addition by subtraction. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007;292:G1469–73.
Wang D, Lou J, Ouyang C, Chen W, Liu Y, Liu X, et al. Ras-related protein Rab10 facilitates TLR4 signaling by promoting replenishment of TLR4 onto the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:13806–11.
Niedzielska I, Niedzielski Z, Tkacz M, Orawczyk T, Ziaja K, Starzewski J, et al. Toll-like receptors and the tendency of normal mucous membrane to transform to polyp or colorectal cancer. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009;60 Suppl 1:65–71.
Chen XZ, Mao XH, Zhu KJ, Jin N, Ye J, Cen JP, et al. Toll like receptor agonists augment HPV 11 E7-specific T cell responses by modulating monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Arch Dermatol Res. 2010;302:57–65.
Sun S, Rao NL, Venable J, Thurmond R, Karlsson L. TLR7/9 antagonists as therapeutics for immune-mediated inflammatory disorders. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2007;6:223–35.
Pawar RD, Ramanjaneyulu A, Kulkarni OP, Lech M, Segerer S, Anders HJ. Inhibition of Toll-like receptor-7 (TLR-7) or TLR-7 plus TLR-9 attenuates glomerulonephritis and lung injury in experimental lupus. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:1721–31.
Zhang Y, Lee AS, Shameli A, Geng X, Finegood D, Santamaria P, et al. TLR9 blockade inhibits activation of diabetogenic CD8+ T cells and delays autoimmune diabetes. J Immunol. 2010;184:5645–53.
Liljegren A, Lindblom A, Rotstein S, Nilsson B, Rubio C, Jaramillo E. Prevalence and incidence of hyperplastic polyps and adenomas in familial colorectal cancer: correlation between the two types of colon polyps. Gut. 2003;52:1140–7.
Lim HK, Lee KH, Kim SY, Kim KJ, Kim B, Lee H, et al. Does the amount of tagged stool and fluid significantly affect the radiation exposure in low-dose CT colonography performed with an automatic exposure control? Eur Radiol. 2011;21:345–52.
Omata F, Deshpande G, Tokuda Y, Takahashi O, Ohde S, Carr-Locke DL, et al. Meta-analysis: somatostatin or its long-acting analogue, octreotide, for prophylaxis against post-ERCP pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:885–95.
Vizoso FJ, Gonzalez LO, Corte MD, Rodriguez JC, Vazquez J, Lamelas ML, et al. Study of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2007;96:903–11.
Escaff S, Fernandez JM, Gonzalez LO, Suarez A, Gonzalez-Reyes S, Gonzalez JM, et al. Study of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 2010;102:922–9.
Altadill A, Rodriguez M, Gonzalez LO, Junquera S, Corte MD, Gonzalez-Dieguez ML, et al. Liver expression of matrix metalloproteases and their inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis. 2009;41:740–8.
Gonzalez-Reyes S, Fernandez JM, Gonzalez LO, Aguirre A, Suarez A, Gonzalez JM, et al. Study of TLR3, TLR4, and TLR9 in prostate carcinomas and their association with biochemical recurrence. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011;60:217–26.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Fondo de Inversión Sanitaria del Instituto Carlos III (FIS-PI070306 and EXPTE: PI070306) and FICEMU.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eiró, N., González, L., González, L.O. et al. Study of the Expression of Toll-Like Receptors in Different Histological Types of Colorectal Polyps and Their Relationship with Colorectal Cancer. J Clin Immunol 32, 848–854 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9666-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9666-3