Abstract
Purpose
Previous clinical studies have indicated that natural IgM antibodies have the ability to induce apoptosis of tumor cells but IgE and IgA may also mediate tumor cell killing (in addition to IgG). The aim of the study was to analyse induction of IgM, IgA and IgE antibodies in patients vaccinated with the tumor associated antigen CEA.
Methods
Twenty-four resected CRC patients without macroscopic disease were immunized seven times with CEA ± GM-CSF. Four different dose schedules were used over a 12-month period. IgM, IgA and IgE antibody responses against recombinant CEA were determined by ELISA. Patients were monitored immunologically for 36 months and clinically for 147 months.
Results
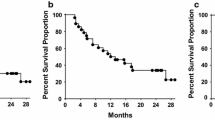
GM-CSF significantly augmented the anti-CEA response for all three antibody classes. Low dose of CEA tended to induce a higher IgM, IgA or IgE anti-CEA antibody response than higher. Anti-CEA IgA antibodies could lyse CEA positive tumor cells in antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) as well as in complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). A significant correlation between survival and high IgA anti-CEA titers was noted (p = 0.02) irrespective of GM-CSF treatment.
Conclusions
The observation that IgA anti-CEA antibodies were cytotoxic and associated with improved survival might indicate that also these antibodies may exert a clinical anti-tumor effect.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
Colorectal carcinoma
- rCEA:
-
Recombinant carcinoembryonic antigen
- GM-CSF:
-
Granulocyte/monocyte colony stimulating factor
References
Baseler MW, Maxim PE, Veltri RW. Circulating IgA immune complexes in head and neck cancer, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, lung cancer, and colon cancer. Cancer. 1987;59:1727–31.
Brandlein S, Lorenz J, Ruoff N, Hensel F, Beyer I, Muller J, Neukam K, Illert B, Eck M, Muller-Hermelink HK, et al. Human monoclonal IgM antibodies with apoptotic activity isolated from cancer patients. Hum Antibodies. 2002;11:107–19.
Brandlein S, Pohle T, Ruoff N, Wozniak E, Muller-Hermelink HK, Vollmers HP. Natural IgM antibodies and immunosurveillance mechanisms against epithelial cancer cells in humans. Cancer Res. 2003;63:7995–8005.
Gould HJ, Mackay GA, Karagiannis SN, O’Toole CM, Marsh PJ, Daniel BE, Coney LR, Zurawski Jr VR, Joseph M, Capron M, et al. Comparison of IgE and IgG antibody-dependent cytotoxicity in vitro and in a SCID mouse xenograft model of ovarian carcinoma. Eur J Immunol. 1999;29:3527–37.
Julien S, Picco G, Sewell R, Vercoutter-Edouart AS, Tarp M, Miles D, Clausen H, Taylor-Papadimitriou J, Burchell JM. Sialyl-Tn vaccine induces antibody-mediated tumour protection in a relevant murine model. Br J Cancer. 2009;100:1746–54.
Karagiannis SN, Bracher MG, Hunt J, McCloskey N, Beavil RL, Beavil AJ, Fear DJ, Thompson RG, East N, Burke F, et al. IgE-antibody-dependent immunotherapy of solid tumors: cytotoxic and phagocytic mechanisms of eradication of ovarian cancer cells. J Immunol. 2007;179:2832–43.
Albanopoulos K, Armakolas A, Konstadoulakis MM, Leandros E, Tsiompanou E, Katsaragakis S, Alexiou D, Androulakis G. Prognostic significance of circulating antibodies against carcinoembryonic antigen (anti-CEA) in patients with colon cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:1056–61.
Livingston PO, Wong GY, Adluri S, Tao Y, Padavan M, Parente R, Hanlon C, Calves MJ, Helling F, Ritter G, et al. Improved survival in stage III melanoma patients with GM2 antibodies: a randomized trial of adjuvant vaccination with GM2 ganglioside. J Clin Oncol. 1994;12:1036–44.
Beutner U, Lorenz U, Illert B, Rott L, Timmermann W, Vollmers HP, Muller-Hermelink HK, Thiede A, Ulrichs K. Neoadjuvant therapy of gastric cancer with the human monoclonal IgM antibody SC-1: impact on the immune system. Oncol Rep. 2008;19:761–9.
Riemer AB, Untersmayr E, Knittelfelder R, Duschl A, Pehamberger H, Zielinski CC, Scheiner O, Jensen-Jarolim E. Active induction of tumor-specific IgE antibodies by oral mimotope vaccination. Cancer Res. 2007;67:3406–11.
Dechant M, Valerius T. IgA antibodies for cancer therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2001;39:69–77.
Ullenhag GJ, Frodin JE, Jeddi-Tehrani M, Strigard K, Eriksson E, Samanci A, Choudhury A, Nilsson B, Rossmann ED, Mosolits S, et al. Durable carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-specific humoral and cellular immune responses in colorectal carcinoma patients vaccinated with recombinant CEA and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:3273–81.
Ullenhag GJ, Frodin JE, Strigard K, Mellstedt H, Magnusson CG. Induction of IgG subclass responses in colorectal carcinoma patients vaccinated with recombinant carcinoembryonic antigen. Cancer Res. 2002;62:1364–9.
Kass E, Panicali DL, Mazzara G, Schlom J, Greiner JW. Granulocyte/macrophage-colony stimulating factor produced by recombinant avian poxviruses enriches the regional lymph nodes with antigen-presenting cells and acts as an immunoadjuvant. Cancer Res. 2001;61:206–14.
Abe J, Wakimoto H, Yoshida Y, Aoyagi M, Hirakawa K, Hamada H. Antitumor effect induced by granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor gene-modified tumor vaccination: comparison of adenovirus- and retrovirus-mediated genetic transduction. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1995;121:587–92.
Samanci A, Yi Q, Fagerberg J, Strigard K, Smith G, Ruden U, Wahren B, Mellstedt H. Pharmacological administration of granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor is of significant importance for the induction of a strong humoral and cellular response in patients immunized with recombinant carcinoembryonic antigen. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1998;47:131–42.
Oikawa S, Nakazato H, Kosaki G. Primary structure of human carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) deduced from cDNA sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987;142:511–8.
Schrewe H, Thompson J, Bona M, Hefta LJ, Maruya A, Hassauer M, Shively JE, von Kleist S, Zimmermann W. Cloning of the complete gene for carcinoembryonic antigen: analysis of its promoter indicates a region conveying cell type-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:2738–48.
Bjorklund JE, Stibler H, Kristiansson B, Johansson SG, Magnusson CG. Immunoglobulin levels in patients with carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndrome type I. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1997;114:116–9.
Magnusson CG, Nelson DF, Magnusson MA. Disproportional distribution of isotype and non-isotype-specific IgG subclass anti-IgE autoantibodies in human cord serum. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1996;110:31–40.
Bruggemann M, Williams GT, Bindon CI, Clark MR, Walker MR, Jefferis R, Waldmann H, Neuberger MS. Comparison of the effector functions of human immunoglobulins using a matched set of chimeric antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987;166:1351–61.
Daneshmanesh AH, Mikaelsson E, Jeddi-Tehrani M, Bayat AA, Ghods R, Ostadkarampour M, Akhondi M, Lagercrantz S, Larsson C, Osterborg A, et al. Ror1, a cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase is expressed in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and may serve as a putative target for therapy. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:1190–5.
Teeling JL, French RR, Cragg MS, van den Brakel J, Pluyter M, Huang H, Chan C, Parren PW, Hack CE, Dechant M, et al. Characterization of new human CD20 monoclonal antibodies with potent cytolytic activity against non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Blood. 2004;104:1793–800.
Liljefors M, Nilsson B, Mellstedt H, Frodin JE. Influence of varying doses of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on pharmacokinetics and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2008;57:379–88.
Frodin JE, Faxas ME, Hagstrom B, Lefvert AK, Masucci G, Nilsson B, Steinitz M, Unger P, Mellstedt H. Induction of anti-idiotypic (ab2) and anti-anti-idiotypic (ab3) antibodies in patients treated with the mouse monoclonal antibody 17–1A (ab1). Relation to the clinical outcome–an important antitumoral effector function? Hybridoma. 1991;10:421–31.
Enterline PE. Pitfalls in epidemiological research. An examination of the asbestos literature. J Occup Med. 1976;18:150–6.
Kalblfeisch J, Prentice R-L. Time dependant covariates and further remarks on likelihood construction. The statistical analysis of failure time data, John Wiley and sons, New York 1st ed. 1980;122–142.
Mota G, Manciulea M, Cosma E, Popescu I, Hirt M, Jensen-Jarolim E, Calugaru A, Galatiuc C, Regalia T, Tamandl D, et al. Human NK cells express Fc receptors for IgA which mediate signal transduction and target cell killing. Eur J Immunol. 2003;33:2197–205.
Huls G, Heijnen IA, Cuomo E, van der Linden J, Boel E, van de Winkel JG, Logtenberg T. Antitumor immune effector mechanisms recruited by phage display-derived fully human IgG1 and IgA1 monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 1999;59:5778–84.
Dechant M, Vidarsson G, Stockmeyer B, Repp R, Glennie MJ, Gramatzki M, van De Winkel JG, Valerius T. Chimeric IgA antibodies against HLA class II effectively trigger lymphoma cell killing. Blood. 2002;100:4574–80.
Roos A, Bouwman LH, van Gijlswijk-Janssen DJ, Faber-Krol MC, Stahl GL, Daha MR. Human IgA activates the complement system via the mannan-binding lectin pathway. J Immunol. 2001;167:2861–8.
Hiemstra PS, Gorter A, Stuurman ME, Van Es LA, Daha MR. Activation of the alternative pathway of complement by human serum IgA. Eur J Immunol. 1987;17:321–6.
Vollmers HP, Zimmermann U, Krenn V, Timmermann W, Illert B, Hensel F, Hermann R, Thiede A, Wilhelm M, Ruckle-Lanz H, et al. Adjuvant therapy for gastric adenocarcinoma with the apoptosis-inducing human monoclonal antibody SC-1: first clinical and histopathological results. Oncol Rep. 1998;5:549–52.
Karagiannis SN, Bracher MG, Beavil RL, Beavil AJ, Hunt J, McCloskey N, Thompson RG, East N, Burke F, Sutton BJ, et al. Role of IgE receptors in IgE antibody-dependent cytotoxicity and phagocytosis of ovarian tumor cells by human monocytic cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2008;57:247–63.
Kershaw MH, Darcy PK, Trapani JA, MacGregor D, Smyth MJ. Tumor-specific IgE-mediated inhibition of human colorectal carcinoma xenograft growth. Oncol Res. 1998;10:133–42.
Reali E, Greiner JW, Corti A, Gould HJ, Bottazzoli F, Paganelli G, Schlom J, Siccardi AG. IgEs targeted on tumor cells: therapeutic activity and potential in the design of tumor vaccines. Cancer Res. 2001;61:5517–22.
Luiten RM, Fleuren GJ, Warnaar SO, Litvinov SV. Target-specific activation of mast cells by immunoglobulin E reactive with a renal cell carcinoma-associated antigen. Lab Invest. 1996;74:467–75.
Nakatsura T, Senju S, Ito M, Nishimura Y, Itoh K. Cellular and humoral immune responses to a human pancreatic cancer antigen, coactosin-like protein, originally defined by the SEREX method. Eur J Immunol. 2002;32:826–36.
Carr A, Rodriguez E, Arango Mdel C, Camacho R, Osorio M, Gabri M, Carrillo G, Valdes Z, Bebelagua Y, Perez R, et al. Immunotherapy of advanced breast cancer with a heterophilic ganglioside (NeuGcGM3) cancer vaccine. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:1015–21.
Ragupathi G, Livingston PO, Hood C, Gathuru J, Krown SE, Chapman PB, Wolchok JD, Williams LJ, Oldfield RC, Hwu WJ. Consistent antibody response against ganglioside GD2 induced in patients with melanoma by a GD2 lactone-keyhole limpet hemocyanin conjugate vaccine plus immunological adjuvant QS-21. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:5214–20.
Gilewski TA, Ragupathi G, Dickler M, Powell S, Bhuta S, Panageas K, Koganty RR, Chin-Eng J, Hudis C, Norton L, et al. Immunization of high-risk breast cancer patients with clustered sTn-KLH conjugate plus the immunologic adjuvant QS-21. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:2977–85.
Rieser C, Ramoner R, Holtl L, Rogatsch H, Papesh C, Stenzl A, Bartsch G, Thurnher M. Mature dendritic cells induce T-helper type-1-dominant immune responses in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Urol Int. 1999;63:151–9.
Miyagi Y, Imai N, Sasatomi T, Yamada A, Mine T, Katagiri K, Nakagawa M, Muto A, Okouchi S, Isomoto H, et al. Induction of cellular immune responses to tumor cells and peptides in colorectal cancer patients by vaccination with SART3 peptides. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:3950–62.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Maggy Magnusson for expert technical assistance and Bo Nilsson for excellent statistical support. Recombinant CEA was a kind gift from Protein Sciences Corp. Meriden, CT, USA. This study was supported by grants from the Swedish Cancer Society, the Cancer Society in Stockholm, the King Gustaf V Jubilee Fund, the Cancer and Allergy Foundation, Torsten and Ragnar Söderberg Foundation, Tornspiran, Hesselman, the Goldi and Ludvig Berglund Foundation, the Research Fund of the Department of Oncology, Uppsala University Hospital, Swedish Medical Society and the Karolinska Institute Foundations.
Disclosures
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Figure 1S. IgM (A), IgA (B) and IgE (C) anti-CEA antibody responses (median) in CRC patients (n = 24) vaccinated with rCEA in relation to the rCEA dose. Six patients were included in each dose cohort. Arrows indicate immunization times. No statistically significant differences were observed at any time point (Mann–Whitney U-test). Figure 2S. Overall survival of rCEA vaccinated CRC patients in relation to IgA and IgG anti-CEA antibody levels. Solid line indicates patients with IgA as well as IgG anti-CEA antibody levels (through value) above the median (n = 9) and dotted line the remaining patients (n = 15). The difference is statistically significance (p = 0.05) (univariate Wilcoxon Gehan exact life table test). (PDF 133 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Staff, C., Magnusson, C.G.M., Hojjat-Farsangi, M. et al. Induction of IgM, IgA and IgE Antibodies in Colorectal Cancer Patients Vaccinated with a Recombinant CEA Protein. J Clin Immunol 32, 855–865 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9662-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9662-7