Abstract
Background
KRN/I-Ag7 (KxB/N) is a mouse model of inflammatory arthritis, which resembles human rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis in these animals is caused by autoreactivity to a ubiquitously expressed autoantigen, glucose-6 phosphate isomerase. Tolerance is broken at both the T cell and B cell level. The sera from KRN/I-Ag7 mice can induce mouse arthritis in healthy mice. Complement components of the alternative complement pathway, including C3, have been shown to be required in induction of mouse arthritis by serum transfer.
Methods
We have bred KRN/I-Ag7 mice onto a C3-deficient background and followed cohorts for the spontaneous appearance of arthritis. We have also transferred KxB/N serum to B6.I-A g7 recipients.
Results
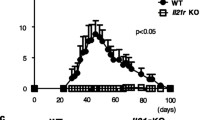
C3-deficient KRN/I-Ag7 mice spontaneously developed severe, destructive arthritis, comparable to that seen in C3-intact KRN/I-Ag7 mice. However, serum transfer experiments confirmed the strong requirement for C3 in the passive model.
Conclusion
The pathogenesis of spontaneous KRN/I-Ag7 arthritis can largely proceed by complement-independent pathways and must have pathology effector mechanisms in addition to those seen in the passive serum transfer model.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee DM, Weinblatt ME. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2001;358:903–11.
Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN. Rheumatoid arthritis. Cell. 1996;85:307–10.
Fox DA. The role of T cells in the immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: new perspectives. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:598–609.
Petkova SB, Konstantinov KN, Sproule TJ, Lyons BL, Awwami MA, Roopenian DC. Human antibodies induce arthritis in mice deficient in the low-affinity inhibitory IgG receptor Fc gamma RIIB. J Exp Med. 2006;203:275–80.
Youinou P, Jamin C, Saraux A. B-cell: a logical target for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007;25:318–28.
Smolen JS, Keystone EC, Emery P, Breedveld FC, Betteridge N, Burmester GR, et al. Consensus statement on the use of rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:143–50.
Monach PA, Benoist C, Mathis D. The role of antibodies in mouse models of rheumatoid arthritis, and relevance to human disease. Adv Immunol. 2004;82:217–48.
Kouskoff V, Korganow AS, Duchatelle V, Degott C, Benoist C, Mathis D. Organ-specific disease provoked by systemic autoimmunity. Cell. 1996;87:811–22.
Carrasco-Marin E, Shimizu J, Kanagawa O, Unanue ER. The class II MHC I-Ag7 molecules from non-obese diabetic mice are poor peptide binders. J Immunol. 1996;156:450–8.
Matsumoto I, Staub A, Benoist C, Mathis D. Arthritis provoked by linked T and B cell recognition of a glycolytic enzyme. Science (New York, NY). 1999;286:1732–5.
Basu D, Horvath S, Matsumoto I, Fremont DH, Allen PM. Molecular basis for recognition of an arthritic peptide and a foreign epitope on distinct MHC molecules by a single TCR. J Immunol. 2000;164:5788–96.
Korganow AS, Ji H, Mangialaio S, Duchatelle V, Pelanda R, Martin T, et al. From systemic T cell self-reactivity to organ-specific autoimmune disease via immunoglobulins. Immunity. 1999;10:451–61.
Ji H, Gauguier D, Ohmura K, Gonzalez A, Duchatelle V, Danoy P, et al. Genetic influences on the end-stage effector phase of arthritis. J Exp Med. 2001;194:321–30.
Solomon S, Rajasekaran N, Jeisy-Walder E, Snapper SB, Illges H. A crucial role for macrophages in the pathology of K/B x N serum-induced arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 2005;35:3064–73.
Circolo A, Garnier G, Fukuda W, Wang X, Hidvegi T, Szalai AJ, et al. Genetic disruption of the murine complement C3 promoter region generates deficient mice with extrahepatic expression of C3 mRNA. Immunopharmacology. 1999;42:135–49.
Monach PA, Verschoor A, Jacobs JP, Carroll MC, Wagers AJ, Benoist C, et al. Circulating C3 is necessary and sufficient for induction of autoantibody-mediated arthritis in a mouse model. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:2968–74.
Solomon S, Kolb C, Mohanty S, Jeisy-Walder E, Preyer R, Schollhorn V, et al. Transmission of antibody-induced arthritis is independent of complement component 4 (C4) and the complement receptors 1 and 2 (CD21/35). Eur J Immunol. 2002;32:644–51.
Ji H, Korganow AS, Mangialaio S, Hoglund P, Andre I, Luhder F, et al. Different modes of pathogenesis in T-cell-dependent autoimmunity: clues from two TCR transgenic systems. Immunol Rev. 1999;169:139–46.
Lee DM, Friend DS, Gurish MF, Benoist C, Mathis D, Brenner MB. Mast cells: a cellular link between autoantibodies and inflammatory arthritis. Science (New York, NY). 2002;297:1689–92.
Wipke BT, Allen PM. Essential role of neutrophils in the initiation and progression of a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 2001;167:1601–8.
Monach PA, Mathis D, Benoist C. The K/BxN arthritis model. In: Coligan JE et al., editors. Current protocols in immunology, Chapter 15: Unit 15 22. New York: Wiley; 2008.
Tsao PY, Jiao J, Ji MQ, Cohen PL, Eisenberg RA. T cell-independent spontaneous loss of tolerance by anti-double-stranded DNA B cells in C57BL/6 mice. J Immunol. 2008;181:7770–7.
Ji H, Ohmura K, Mahmood U, Lee DM, Hofhuis FM, Boackle SA, et al. Arthritis critically dependent on innate immune system players. Immunity. 2002;16:157–68.
Maccioni M, Zeder-Lutz G, Huang H, Ebel C, Gerber P, Hergueux J, et al. Arthritogenic monoclonal antibodies from K/BxN mice. J Exp Med. 2002;195:1071–7.
Kneilling M, Hultner L, Pichler BJ, Mailhammer R, Morawietz L, Solomon S, et al. Targeted mast cell silencing protects against joint destruction and angiogenesis in experimental arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1806–16.
Monach PA, Nigrovic PA, Chen M, Hock H, Lee DM, Benoist C, et al. Neutrophils in a mouse model of autoantibody-mediated arthritis: critical producers of Fc receptor gamma, the receptor for C5a, and lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:753–64.
Victoratos P, Kollias G. Induction of autoantibody-mediated spontaneous arthritis critically depends on follicular dendritic cells. Immunity. 2009;30:130–42.
Raposo BR, Rodrigues-Santos P, Carvalheiro H, Agua-Doce AM, Carvalho L, Pereira da Silva JA, et al. Monoclonal anti-CD8 therapy induces disease amelioration in the K/BxN mouse model of spontaneous chronic polyarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2953–62.
Einav S, Pozdnyakova OO, Ma M, Carroll MC. Complement C4 is protective for lupus disease independent of C3. J Immunol. 2002;168:1036–41.
Sekine H, Reilly CM, Molano ID, Garnier G, Circolo A, Ruiz P, et al. Complement component C3 is not required for full expression of immune complex glomerulonephritis in MRL/lpr mice. J Immunol. 2001;166:6444–51.
Elliott MK, Jarmi T, Ruiz P, Xu Y, Holers VM, Gilkeson GS. Effects of complement factor D deficiency on the renal disease of MRL/lpr mice. Kidney Int. 2004;65:129–38.
Watanabe H, Garnier G, Circolo A, Wetsel RA, Ruiz P, Holers VM, et al. Modulation of renal disease in MRL/lpr mice genetically deficient in the alternative complement pathway factor B. J Immunol. 2000;164:786–94.
Swaak AJ, Van Rooyen A, Planten O, Han H, Hattink O, Hack E. An analysis of the levels of complement components in the synovial fluid in rheumatic diseases. Clin Rheumatol. 1987;6:350–7.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Diane Mathis for the generous sharing of mice, constructs, and protocols. This study was supported by the Arthritis Foundation, the American Autoimmune Related Disease Association, Bracco Research USA, the NIH (R01-AR-34156; R01-AI063626) and the Small Animal Imaging Facility, Department of Radiology, University of Pennsylvania.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsao, P.Y., Arora, V., Ji, M.Q. et al. KRN/I-Ag7 Mouse Arthritis Is Independent of Complement C3. J Clin Immunol 31, 857–863 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-011-9562-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-011-9562-2