Abstract
Introduction
Selective IgA deficiency (IgAD; serum IgA concentration of <0.07 g/l) is the most common primary immunodeficiency in Caucasians with an estimated prevalence of 1/600. The frequency of the extended major histocompatibility complex haplotype HLA A1, B8, DR3, DQ2 (the “8.1” haplotype) is increased among patients with IgAD.
Materials and Methods
We carried out a direct measurement of the relative risk of homozygosity of the 8.1 haplotype for IgA deficiency in a population-based sample of 117 B8, DR3 homozygous individuals.
Results and Discussion
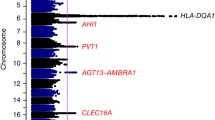
IgA deficiency was found to be present in 2 of 117 (1.7%) of these subjects, a figure that is concordant with estimates of relative risk from large case–control studies in the Swedish population. These data are consistent with a multiplicative model for the 8.1 haplotype contribution to IgA deficiency and contrasts with prior studies, suggesting a much higher risk for 8.1 homozygosity. Using a dense single nucleotide polymorphism marker analysis of the MHC region in HLA B8, DR3, DQ2 homozygous individuals, we did not observe consistent differences between cases (n = 26) and controls (n = 24). Overall, our results do not support the hypothesis that IgA deficiency is associated with a distinct subgroup of 8.1 related haplotypes, but rather indicate that risk is conferred by the common 8.1 haplotype acting in multiplicative manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hammarstrom L, Smith CI. Genetic approach to common variable immunodeficiency and IgA deficiency. In: Ochs H, Smith CI, Puck J, editors. Primary immunodeficiency diseases a molecular and genetic approach. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2007. p. 313–25.
Pan-Hammarstrom Q, Hammarstrom L. Antibody deficiency diseases. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38(2):327–33.
Burrows PD, Cooper MD. IgA deficiency. Adv Immunol. 1997;65:245–76.
Kanoh T, Mizumoto T, Yasuda N, Koya M, Ohno Y, Uchino H, et al. Selective IgA deficiency in Japanese blood donors: frequency and statistical analysis. Vox Sang. 1986;50(2):81–6.
Oen K, Petty RE, Schroeder ML. Immunoglobulin a deficiency: genetic studies. Tissue Antigens. 1982;19(3):174–82.
Vorechovsky I, Zetterquist H, Paganelli R, Koskinen S, Webster AD, Bjorkander J, et al. Family and linkage study of selective IgA deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995;77(2):185–92.
Vorechovsky I, Webster AD, Plebani A, Hammarstrom L. Genetic linkage of IgA deficiency to the major histocompatibility complex: evidence for allele segregation distortion, parent-of-origin penetrance differences, and the role of anti-IgA antibodies in disease predisposition. Am J Hum Genet. 1999;64(4):1096–109.
Cunningham-Rundles C, Fotino M, Rosina O, Peter JB. Selective IgA deficiency, IgG subclass deficiency, and the major histocompatibility complex. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991;61(2 Pt 2):S61–9.
Olerup O, Smith CI, Hammarstrom L. Different amino acids at position 57 of the HLA-DQ beta chain associated with susceptibility and resistance to IgA deficiency. Nature. 1990;347(6290):289–90.
MacHulla HK, Schonermarck U, Schaaf A, Muller LP, Kloss C, Kruger J, et al. HLA-A, B, Cw and DRB1, DRB3/4/5, DQB1, DPB1 frequencies in German immunoglobulin A-deficient individuals. Scand J Immunol. 2000;52(2):207–11.
Ashman RF, Schaffer FM, Kemp JD, Yokoyama WM, Zhu ZB, Cooper MD, et al. Genetic and immunologic analysis of a family containing five patients with common-variable immune deficiency or selective IgA deficiency. J Clin Immunol. 1992;12(6):406–14.
Gual L, Martinez A, Fernandez-Arquero M, Garcia-Rodriguez MC, Ferreira A, Fontan G, et al. Major histocompatibility complex haplotypes in Spanish immunoglobulin A deficiency patients: a comparative fine mapping microsatellite study. Tissue Antigens. 2004;64(6):671–7.
Schroeder HW Jr, Schroeder HW 3rd, Sheikh SM. The complex genetics of common variable immunodeficiency. J Investig Med. 2004;52(2):90–103.
de la Concha EG, Fernandez-Arquero M, Gual L, Vigil P, Martinez A, Urcelay E, et al. MHC susceptibility genes to IgA deficiency are located in different regions on different HLA haplotypes. J Immunol. 2002;169(8):4637–43.
Ammann AJ, Hong R. Selective IgA deficiency: presentation of 30 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1971;50(3):223–36.
Badcock LJ, Clarke S, Jones PW, Dawes PT, Mattey DL. Abnormal IgA levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62(1):83–4.
Rankin EC, Isenberg DA. IgA deficiency and SLE: prevalence in a clinic population and a review of the literature. Lupus. 1997;6(4):390–4.
Smith WI Jr, Rabin BS, Huellmantel A, Van Thiel DH, Drash A. Immunopathology of juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus. I. IgA deficiency and juvenile diabetes. Diabetes. 1978;27(11):1092–7.
Wilton AN, Cobain TJ, Dawkins RL. Family studies of IgA deficiency. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(4):333–42.
Kruskall M, Marcus-Bagley D, Awdeh Z, Eisenbarth G, Brink S, Katz A, et al. Many individuals with the MHC conserved extended [HLA -B8, SCO1, DR3] haplotype have immunoglobulin deficiency. Clin Res. 1993;41:277A.
Volanakis JE, Zhu ZB, Schaffer FM, Macon KJ, Palermos J, Barger BO, et al. Major histocompatibility complex class III genes and susceptibility to immunoglobulin a deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency. J Clin Invest. 1992;89(6):1914–22.
Olerup O, Aldener A, Fogdell A. HLA-DQB1 and -DQA1 typing by PCR amplification with sequence-specific primers (PCR-SSP) in 2 hours. Tissue Antigens. 1993;41(3):119–34.
de Bakker PI, McVean G, Sabeti PC, Miretti MM, Green T, Marchini J, et al. A high-resolution HLA and SNP haplotype map for disease association studies in the extended human MHC. Nat Genet. 2006;38(10):1166–72.
Avoustin PA, Tkaczuk J, Coppin HL, Cambon-Thomsen A, de Preval C. Extended HLA-DQw2 haplotypes: molecular analysis. Eur J Immunogenet. 1991;18(4):247–57.
Awdeh ZL, Raum D, Yunis EJ, Alper CA. Extended HLA/complement allele haplotypes: evidence for T/t-like complex in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983;80(1):259–63.
Mohammadi J, Pourpak Z, Jarefors S, Saghafi S, Zendehdel K, Pourfathollah AA, et al. Human leukocyte antigens (HLA) associated with selective IgA deficiency in Iran and Sweden. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008;7(4):209–14.
Bachmann R. Studies on the serum gamma-A-globulin level. 3. The frequency of A-gamma-A-globulinemia. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1965;17(4):316–20.
Olerup O. Retrospective analysis of HLA-DR typing by serology, TaqI RFLP analysis, and PCR amplification with sequence-specific primers. Transplant Proc. 1994;26(3):1750–1.
Schaffer M, Olerup O. HLA-AB typing by polymerase-chain reaction with sequence-specific primers: more accurate, less errors, and increased resolution compared to serological typing. Tissue Antigens. 2001;58(5):299–307.
Cucca F, Zhu ZB, Khanna A, Cossu F, Congia M, Badiali M, et al. Evaluation of IgA deficiency in Sardinians indicates a susceptibility gene is encoded within the HLA class III region. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998;111(1):76–80.
Farid NR, Barnard JM, Marshall WH. The association of HLA with autoimmune thyroid disease in Newfoundland. The influence of HLA homozygosity in Graves' disease. Tissue Antigens. 1976;8(3):181–9.
Zubillaga P, Vidales MC, Zubillaga I, Ormaechea V, Garcia-Urkia N, Vitoria JC. HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1 genetic markers and clinical presentation in celiac disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002;34(5):548–54.
Skarsvag S, Hansen KE, Holst A, Moen T. Distribution of HLA class II alleles among Scandinavian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): an increased risk of SLE among non[DRB1*03, DQA1*0501, DQB1*0201] class II homozygotes? Tissue Antigens. 1992;40(3):128–33.
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the Swedish Research Council and grant (U19AI067152) from the US National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Javad Mohammadi is supported by an educational grant from the Iranian government. We wish to thank Dr. Leonid Padyukov for careful review of the manuscript. We would also like to thank Drs. Leonid Padyukov and Lars Klareskog at the Rheumatology Unit, Department of Medicine at the Karolinska University hospital Solna, Sweden, for supplying some of the control samples used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadi, J., Ramanujam, R., Jarefors, S. et al. IgA Deficiency and the MHC: Assessment of Relative Risk and Microheterogeneity Within the HLA A1 B8, DR3 (8.1) Haplotype. J Clin Immunol 30, 138–143 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-009-9336-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-009-9336-2